Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to CAP Theorem
Consistency, Availability and Partition tolerance is three main aspects of the modern distributed data system. The CAP theorem was coined by Eric Brewer in 2000 to address the standard way to maintain the network-based database systems. In the era or petabyte-scale data, it became immensely important to develop and maintain distributed data systems to main the load. In this article, we will see the key points of the CAP theorem, how it is different from ACID and why it is important for the current technological landscape.
Key Points of CAP Theorem
The three aspects of the CAP theorem are consistency, Availability, and Partition tolerance. Let’s first discuss all of these separately then we will join the pieces.
1. Consistency
According to this theorem, all connected nodes of the distributed system see the same value at the same time and partial transactions will not be saved. Suppose there are multiple steps inside a transaction and due to some malfunction some middle operation got corrupted, now if part of the connected nodes read the corrupted value, the data will be inconsistent and misleading. So according to the CAP principle, we will not allow such a transaction. A transaction cannot be executed partially. It will always be ‘All or none’. If something goes wrong in between the execution of a transaction, the whole transaction needs to be rolled back.
2. Availability
According to this, the connected or distributed systems should remain operational all the time. There should be a response for every client request in the system irrespective of a particular node is being available or not. Though in a practical scenario it is purely based on the traffic requirements. The key point of this is every functioning node must return a response for all read and write requests in a reasonable amount of time.
3. Partition Tolerance
According to the partition tolerance policy, if a subpart of the network is compromised, the entire distributed system should not go down. A system that is partition tolerance should recover fast from partial outrage. In practical scenarios partition tolerance cannot be an optional criterion, it should be maintained thoroughly. So adhering CAP theorem became always a choice between high consistency and high availability.
Why CAP Theorem is Important?
After the internet boom in 2005, the size of data is growing exponentially day by day. At the early stages to maintain the ever-changing scale of data and plan the capacity properly the only option was to increase the capacity vertically which means adding more machines or increasing the machine capabilities. But it is not always feasible and cost-effective. Instead of this, the new concept is to add the capacity horizontally which means leveraging distributed computing. To standardize the network, we need to maintain the principles of the CAP theorem.
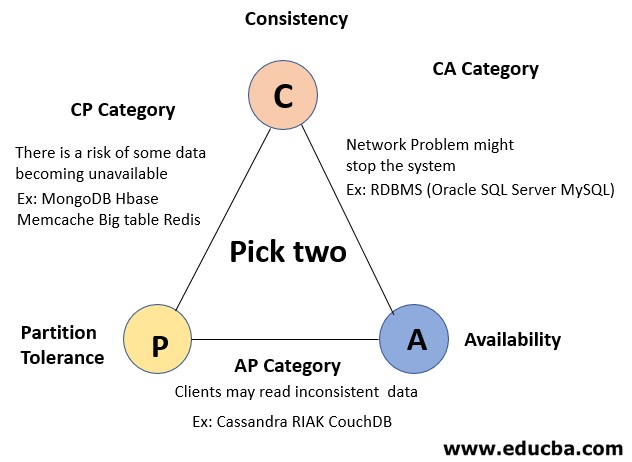
We cannot maintain all three principles of the CAP theorem simultaneously. Theoretically, we can maintain only CA, CP, or AP.
- Consistency and Availability: These are systems with high consistency and very lesser downtime but the option of partition tolerance is not enforced. For example, network issues can down the entire distributed RDBMS system.
- Consistency and Partition Tolerance: These systems adhere to high consistency and partition tolerance but there is a risk of some data being unavailable. Ex. MongoDB.
- Availability and Partition Tolerance: These systems adhere to high availability and partition tolerance but there is a risk of reading inconsistent data. Ex. Cassandra.
How CAP Theorem is Different from ACID Properties?
Before we see about the differences, let’s first see about the ACID properties in brief:
1. Atomicity
All changes to data are performed as a single operation. That is, all or none, either all of the operations are performed or one of them is performed. For example, in an application we are transferring funds from one account to another, the atomicity property ensures that, if a debit is made successfully from one account, then the associated credit is also done to the other account.
2. Consistency
For each transaction, the system should move from one consistent state to another consistent state.
3. Isolation
All transactions should be executed in isolation from other transactions. During concurrent transaction execution, intermediate transaction results from parallel executed transactions should be mutually exclusive. Failure of one module should not affect another transaction.
4. Durability
After every successful transaction, the changes made in the database should persist. Even if the system comprises or failed somehow, still the successfully committed or aborted operations should persist. Now we can see that, these terms technically refer to different things. The way in which they are related is that a distributed database system that guarantees the ACID transactions must choose consistency over availability according to the CAP Theorem (i.e it is a CP system).
On the other hand, if a distributed database chooses availability over consistency in accordance with the CAP Theorem (suppose it is an AP system), it cannot tightly follow the properties of the ACID principles.
Conclusion
In this article we have seen the principles of CAP theorem and why this is still important in the current context. We also saw how the CAP theorem differs or is related to another database design principle (ACID). In most practical use cases the principle of partition tolerance needs to be followed always and it becomes a choice between high availability and high consistency.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the CAP Theorem. Here we discuss the introduction, key points on CAP theorem, how CAP theorem is different from ACID properties? You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


