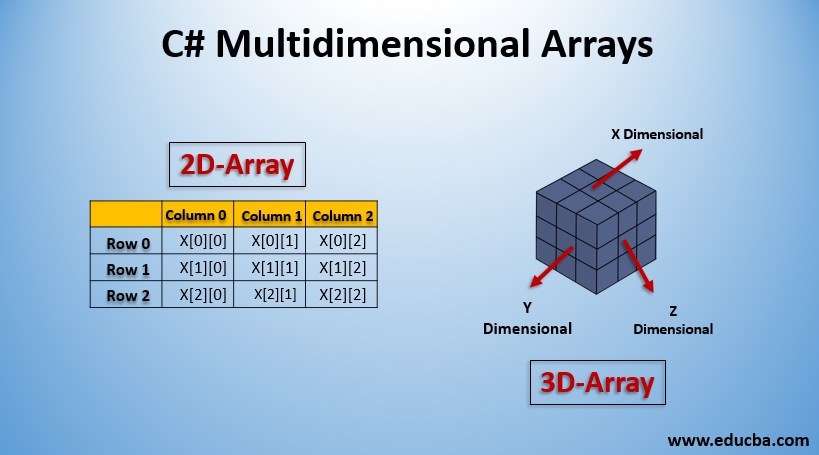
Introduction to Multidimensional Arrays in C#
In C#, the rectangular arrays or multidimensional arrays refer to the organization of the elements in a matrix format. A multidimensional array can only be of two or three dimensions. Dimensions of an array refer to the organization format of the data in the variable. Thus we can define a multidimensional array as an organization of elements in series or sequence as rows or columns.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax of Multidimensional Arrays:
Declaration of the 2D array.
int[,] x=new int[1,2];Declaration of the 3D array.
int[,,] x=new int[1,2,3];The syntax above specifies the format to declare two-dimensional and 3-dimensional arrays (x). the first array contains two elements, 1 and 2, whereas the three-dimensional array contains the element 1,2,3.
Initialization of the Multidimensional Arrays
A multidimensional array can be initialized in three different ways
1. Complete Declaration
int[,] x = new int[6,6];The above specification initializes a two-dimensional array completely, including the use of array type, array size, and the new operator.
2. Initialising without Using the New Operator
int[,] x = { { 3,2,1 }, { 6,5,4 }, { 9,8,7 } };3. Initializing the Array without Declaring the Size
int[,] x = new int[,]{ { 3,2,1 }, { 6,5,4 }, { 9,8,7 } };Examples of C# multidimensional array
Below are the examples of Multidimensional Arrays in C#:
Example #1
Program to illustrate declaring and initialization of a multidimensional array. The example below illustrates the creation of a multidimensional array in C#.
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
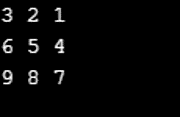
int[,] x = { { 3, 2, 1 }, { 6, 5, 4 }, { 9, 8, 7 } };
for (int a = 0; a < 3; a++)
{
for (int b = 0; b < 3; b++)
{
Console.Write(x[a, b] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}Output:
Example #2
Program to illustrate the initialization, declaration of a two-dimensional array, and access the elements.
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* declaring and initialising a two dimensional array*/
int[,] b = new int[6, 2] { { 1, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 6 }, { 8,7 }, { 9 , 10 }, { 2, 3 } };
int i, j;
/* accessing each of the elements value for the array */
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}] = {2}", i, j, b[i, j]);
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}Output:
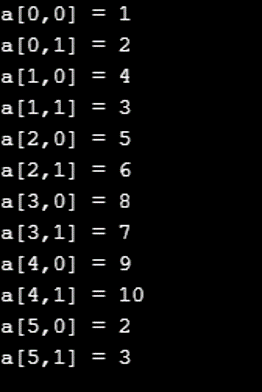
The program above demonstrates the use of indices as a positional marker for accessing the elements of the array in a multidimensional array.
Example #3
Program for the addition of two multidimensional arrays.
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int[,] array1 = new int[3, 3];
int[,] array2 = new int[3, 3];
int[,] resultArray = new int[3, 3];
int i, j;
Console.WriteLine("specify the members of the first array: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
array1[i, j] = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
}
Console.WriteLine("elements of the array1: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", array1[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
Console.WriteLine("specify the members of the array2: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
array2[i, j] = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
}
Console.WriteLine("elements of the array2: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", array2[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
resultArray[i, j] = array1[i, j] + array2[i, j];
}
}
Console.WriteLine("resultArray of the array1 and array2 looks as below : ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", resultArray[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
}
}Output:
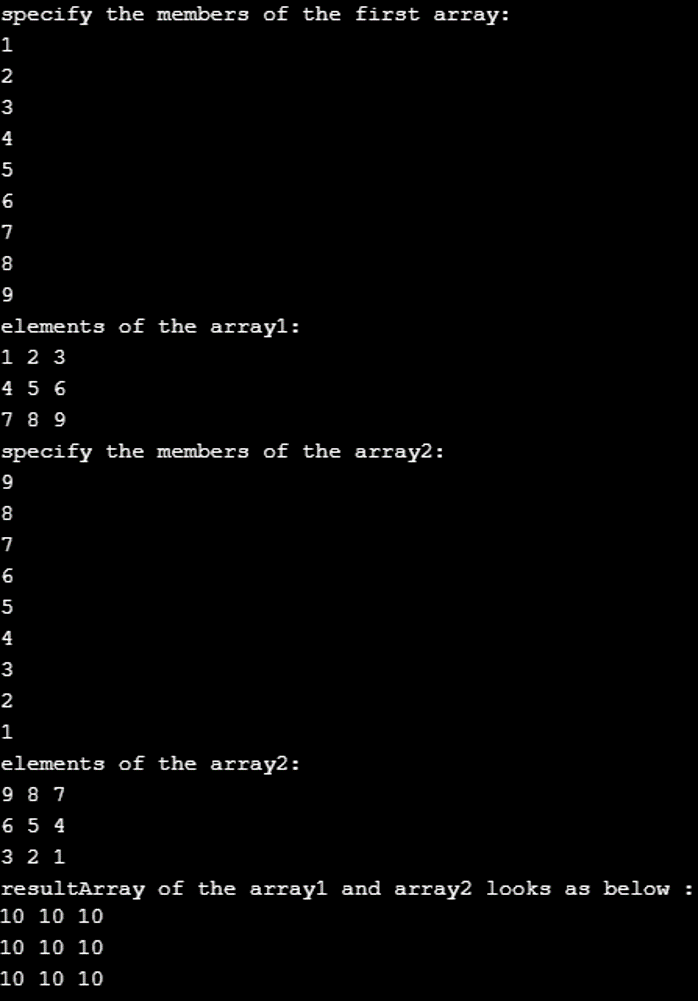
Using the program above, we have completed the addition operation on the array, with each element in the first array added to the second array’s counter element. For example, the first element in array1 is 1; similarly, the first element in array2 is 9. The resultant of addition should contain an array with the first element as 10.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Below are the advantages and disadvantages of Multidimensional Arrays:
Advantages
- Multidimensional arrays can be used to organize subgroups of data within an array; multidimensional arrays can also be used to store data memory addresses in a pointer array.
- In the program, multidimensional arrays have a static size and initialization at the beginning. Any extension in size shall require the relevant size to be specified during initialization.
- Multidimensional arrays enable performing matrix operations and maintaining large data values under the same variable allocation.
- Multidimensional arrays are used to implement stacks, heaps and Queues, and hash tables.
Disadvantages
- The elements are located in contiguous memory locations for an array; hence any insertion and deletion of an element shall be more complex than similar operations on single elements.
- Also, the elements cannot be inserted into the middle of an array.
- Static allocation can cause wastage and failure to release unused memory if it allocates more memory than necessary. This can have a negative impact.
- Multidimensional arrays can be slower when compared to their single-dimensional array counterparts, which is a major disadvantage. To overcome this, we can replace jagged arrays with multidimensional arrays.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C# Multidimensional Arrays. Here we discuss a brief overview of Multidimensional Arrays in C#, its Examples, and its Code Implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


