Updated June 22, 2023
Introduction to C# Literals
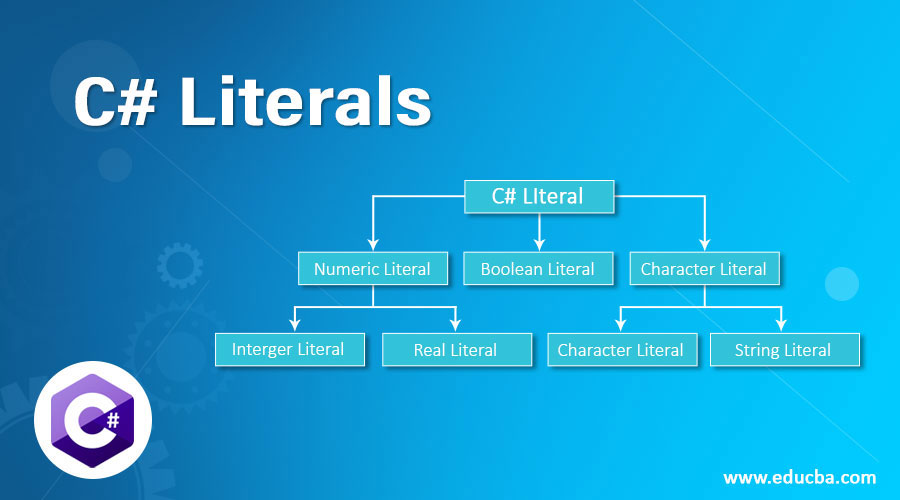
Literals in C# are the fixed value used by a predefined variable that cannot be modified during the execution of the code. These are the convenient form of constant values like other variables, but their values cannot be changed. The value used by a variable can be integer, decimal, floating type, or string. There are different types of literals in C# with different forms. There are various types of literals in C#.
- Integer Literals
- String Literals
- Character Literals
- Floating-point Literals
- Boolean Literals
Top 5 Types of Literals in C#
Following are the different types of literals in C#.
1. Integer Literals
The literal of integer type can be octal, decimal, or hexadecimal. The prefix is used to specify whether it is decimal, octal, or hexadecimal. U and u are also used as a suffix with integer-type literals for unsigned numbers, and l and L are used for long numbers. Every literal is of integer type by default.
- Decimal Literals: 0-9 digits are allowed in the decimal type of literals. No prefix is required for the decimal type of literals.
int x = 100; // decimal type
- Octal Literals: 0-7 digits are allowed in the octal type of literals. 0 is used as a prefix to specify the form of octal-type literals.
int x = 072; // octal type
- Hexa-decimal literals: In the hexadecimal type of literals, digits from 0- 9 and characters from A-f are allowed. Uppercase and lowercase both types of characters are allowed in this case. 0X or 0x is used as a prefix to specify the form of the hexadecimal type of literals.
int x = 0x123f; // hexadecimal type
2. String Literals
The string type literals are enclosed in (“”)/ double quotes and also can be started with @””. Long lines can be broken into multiple lines with string literals and separated using blank spaces.
string s= "Hi"; // string literals3. Character Literals
You enclose the character type literals in (“)/single quotes. There are three ways to specify character literals.
- Single Quote: Characters’ literals can be specified as single char using a single quote.
- Unicode Representation: Character literals can be specified using Unicode Representation’ \uxxxx,’ where xxxx are the hexadecimal numbers.
- Escape Sequence: We know some escape characters as char literals.
char c = '\n';Following are some escape sequence literals explained with their meanings.
| Escape Sequence | Meaning |
| \\ | Character |
| \’ | Character |
| \’’ | Character |
| \? | Character |
| \a | Alert |
| \b | Backspace |
| \n | Newline |
| \f | Form feed |
| \v | Vertical tab |
| \xhh | Hexadecimal number |
4. Floating Point Literals
In the floating type of literal, there is an integer part, a fractional part, a decimal part, and an exponent part. The floating type literal is of double type. You can use F or f as a suffix to specify the value because you cannot assign it directly to the float variable.
5. Boolean Literals
In the Boolean type of literals, true and false will be the only two values.
Examples of C# Literals
Below are the examples that show how we can implement all the above literals in C#
Example #1 – Integer Literal
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Literals
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 212; // decimal literal
int y = 0145; // octal literal
int z = 0x4b; // hexadecimal literal
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine(y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Explanation: In the above example, there are various forms of integer-type literals. You use no prefix for the decimal form, use 0 to specify the octal form, and use 0x to specify the hexadecimal number. Using prefixes, we can define the form of integer type literal. In this code, first, there is a literal of decimal type with no prefix, a second type is an octal form with 0 as a prefix, and last, we have a hexadecimal type with 0x as a prefix.
Example #2 – Floating Point Literal
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Literals
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
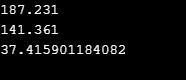
double x = 187.231;
double y = 0141.361;
double z = 374159E-4F;
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine(y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Explanation: The above example implements floating-point literals. It can be a decimal number, fractional, or any exponent. So we can represent it either in decimal or in exponential form. The floating type literal is of double type. You can use F or f as a suffix to specify the value because you cannot assign it directly to the float variable.
Example #3 – Character Literals
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Literals
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
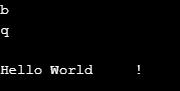
char c = 'b';
char ch = '\u0071';
Console.WriteLine(c);
Console.WriteLine(ch);
Console.WriteLine("\nHello World\t!");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Explanation: The above example implements character-type literals. The above code shows all three forms of character type. We can specify the character using a single quote, Unicode representation, and escape sequence. We have multiple types of escape characters with their meanings. In this code, the first single quote character is specified where the second one has Unicode representation, and then, at last, we have escape form type of character literals.
Example #4 – String Literal
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Literals
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
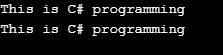
String s1 = "This is C# programming";
String s2 = @"This is C# programming";
Console.WriteLine(s1);
Console.WriteLine(s2);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Explanation: The above example implements string literals. There are two ways to specify string literals, as shown in the code. To implement the string, use double quotes first, then follow with the @ symbol.
Example #5 – Boolean Type Literal
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Literals
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool x = true;
bool y = false;
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine(y);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Explanation: In the example provided, the implementation of Boolean type literals, which consist of two true or false values, can be seen.
Conclusion
So literals are the fixed values. In C#, there are different types of literals with specific form types. It can be of integer, Boolean, string, or a character literal.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C# Literals. Here we discuss the basic concept and top 5 types of C# Literals along with different examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –