Updated March 18, 2023
Introduction to C++ Algorithm
The finite set of steps arranged sequentially which acts as a guide to solve any problem. This c++ algorithm word is particularly used in computer science to define the procedure for solving complex problems. The architecture of the solution can be different for different algorithms. The most efficient algorithm is the one that provides the solution in less time and consumes less memory in comparison to other algorithmic solutions. In the C++ header <algorithm> contains the functions designed to operate on the number ranges. These functions operate on the number but do not make any manipulations to the data. It just works while iterating or pointing to the numbers without touching its data.
Some member functions under <algorithm> header are:
- algorithm::adjacent_find(): Points the first occurrence of two identical consecutive numbers.
- algorithm::all_of(): Returns true if the numbers lie under the range of first and last elements.
- algorithm::binary_search(): Checks if the “value to be searched” is present in the sorted sequence or not.
- algorithm::copy(): This function helps in copying a range of elements from one location to the new location.
- algorithm::count_if(): This function returns the number of occurrences of particular elements if the condition mentioned in “if condition” is satisfied.
- algorithm::equal(): This function tests whether two sets of elements are equal or not. There are a lot of similar functions predefined in C++ which can be sued by coders in the advantage of their business.
Explanation of C++ Algorithm
C++ provides versions of these algorithms in the namespace std::ranges. Algorithms are the vast topic that covers topics from searching, sorting to min/max heaps. These can be categorized as:
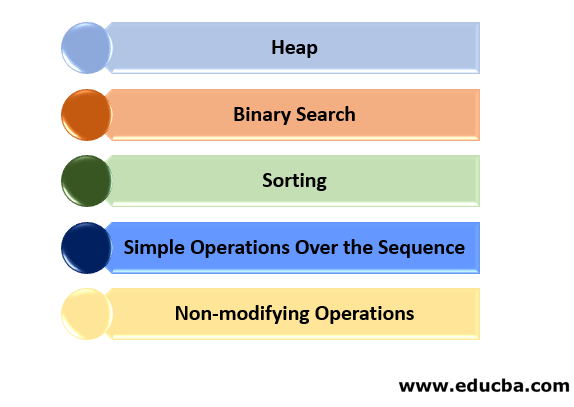
1. Heap: In such types, we construct a heap to find out the max or min value of the sequence. This used the data structure of trees to achieve its output.
2. Binary Search: This C++ algorithm divides the whole sequence into two parts iteratively until it finds the actual value we are searching from the targeted sequence. It is a highly effective algorithm as it reduces time by half. The preliminary condition to use this C++ algorithm is that the sequence provided to it should be sorted in any order.
3. Sorting: There are different types of sorting that can be used to generate the sorted sequence. They are insertion sort, bubble sort, selection sort, heap sort, quick sort, merge sort. Some of these algorithms work on the principle of “divide and rule” like merge and quick sort. These are quick and efficient in comparison to others although uses more memory in their operations.
4. Simple Operations Over the Sequence: Algorithms can be used to perform simple operations like replace, remove, reverse the numbers in a sequence. There are many ways to reach this output using different algorithms all aiming to achieve the same output.
5. Non-modifying Operations: Some operations like search, find, count the number of elements in the sequence. These operations do not modify the data values of the element but function around these elements.
Example of Algorithms with Steps
Here are some examples of the C++ algorithm with steps explained below:
Example #1
Write a C++ algorithm to write a program to add two numbers.
Algorithm
Steps are given below:
- Start
- Accept num1, num 2
- Sum= num1+ num2
- Display sum
- Stop
Example #2
Write a C++ algorithm to determine if a student is pass or fail based on the grades. Grades are the average of total marks obtained in all the subjects.
Algorithm
Steps are given below:
- Start
- Input Marks1, Marks2, Marks3, Marks4
- Grade= (Marks1+Marks2+Marks3+Marks4)/4
- If (Grade<50) then
- Print “Fail”
- Else
- Print “Pass”
- End if
- Stop
Example #3
Bubble sort- This is the C++ algorithm to sort the number sequence in ascending or descending order. It compares the nearest two numbers and puts the small one before a larger number if sorting in ascending order. This process continues until we reach a sequence where we find all the numbers sorted in sequence.
The time complexity of this algorithm is O(n) as the controls have to go through all the number of elements that are there in the sequence and then check if 2 adjacent numbers are sorted. If not then it sorts and moves to the other two adjacent pairs in the series.
Implementation of the above C++ algorithm
Here is the example of the C++ algorithm with code implementation given below:
Code:
#include <iostream>
void swap(int *p1, int *p2)
{
int temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
// This is an optimised code for the bubble sort
void bSort(int arrnumbers[], int n)
{
int i, j;
bool check;
for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
{
check = false;
for (j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++)
{
if (arrnumbers[j] > arrnumbers[j+1])
{
swap(&arrnumbers[j], &arrnumbers[j+1]);
check = true;
}
}
// We are breaking from the loop in case two elements were not swapped by inner loop.
if (check == false)
break;
}
}
//This function is to print the array sequence as final output after sorting
void print(int arrnumbers[], int sizeofarray)
{
int i;
for (i=0; i < sizeofarray; i++)
printf("%d ", arrnumbers[i]);
}
// This the main program from where the execution will start
int main()
{
int arrnumbers[] = {5, 6, 1, 0, 2, 9};
int n = sizeof(arrnumbers)/sizeof(arrnumbers[0]);
bSort(arrnumbers, n);
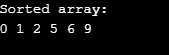
printf("Sorted array: \n");
print(arrnumbers, n);
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
C++ algorithm is a detailed step by step generic solution guide which is designed keeping in focus to provide the most efficient and less time-consuming solution to any problem provided. There are many tools to check the efficiency of algorithms like big Oh notation, Omega or Gama notations which is useful to find the efficacy of algorithms. Every algorithm has its own privilege and advantages and we choose the right fit solution as per the problem statement. This plays a crucial role when we design a solution for the problem as it becomes the base of the final product’s performance.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the C++ Algorithm. Here we discuss the introduction and detailed explanation of the C++ algorithm along with the various examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


