Updated June 7, 2023
Introduction to Brute Force Algorithm
“Data is the new oil” is the new mantra ruling the global economy. We live in the digital world, and every business revolves around data, which translates into profits and helps industries stay ahead of their competition. With rapid digitization, and an exponential increase in the app-based business model, cyber-crimes is a constant threat. One such common activity that hackers perform is Brute Force.
Brute Force is a trial-and-error approach where attackers use programs to try various combinations to break into any websites or systems. They use automated software to repetitively generate the User id and password combinations until it generates the right combination.
Brute-Force Search
Brute force search is the most common search algorithm as it does not require any domain knowledge; all required is a state description, legal operators, the initial state, and the description of a goal state. It does not improve performance and entirely relies on computing power to try out possible combinations.
The brute force algorithm searches all the positions in the text between 0 and n-m, whether the occurrence of the pattern starts there or not. After each attempt, it shifts the pattern by exactly 1 position to the right. The time complexity of this algorithm is O(m*n). If we search for n characters in a string of m characters, it will take n*m tries.
Let’s see a classic example of a traveling salesman to understand the algorithm easily.
Suppose a salesman needs to travel to 10 different cities in a country, and he wants to determine the shortest possible routes out of all the possible combinations. Here brute force algorithm simply calculates the distance between all the cities and selects the shortest one.
Another example is to attempt to break the 5-digit password; then brute Force may take up to 105 attempts to crack the code.
Brute Force Sort
In the brute force sort technique, the data list is scanned multiple times to find the smallest element in the list. After each iteration over the list, it replaces the smallest element at the top of the stack and starts the next iteration from the second smallest data in the list.
The above statement can be written in pseudo-code as follows.
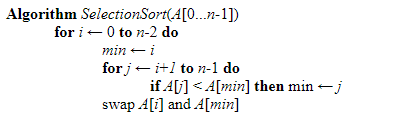
Here the problem is of size’ n,’ and the essential operation is the ‘if’ test where the data items are being compared in each iteration. There will be no difference between the worst and best cases as the no of swaps is always n-1.
Brute Force String Matching
If all the characters in the pattern are unique, then Brute force string matching can be applied with the complexity of Big O(n), where n is the string’s length. Brute force String matching compares the pattern with the substring of a text character by character until it gets a mismatched character. When a mismatch is found, the substring’s remaining character is dropped, and the algorithm moves to the next substring.
The below pseudo-codes explain the string-matching logic. Here, the algorithm searches for a P pattern [0…m-1] in the text T[0….n-1].
The worst case would be when a shift to another substring is not made until the MTh comparison.
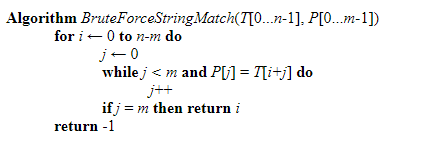
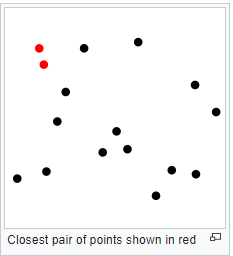
Closest Pair
Problem statement: To find out the two closest points in a set of n points in the two-dimensional cartesian plane. There is n number of scenarios where this problem arises. A real-life example would be in an air traffic control system where you have to monitor the planes flying near each other and find out the safest minimum distance these planes should maintain.
Source Link: Wikipedia
The brute force algorithm computes the distance between every distinct set of points and returns the point’s indexes for which the space is the smallest.
Brute Force solves this problem with the time complexity of [O(n2)], where n is the number of points.
Below, the pseudo-code uses the brute force algorithm to find the closest point.
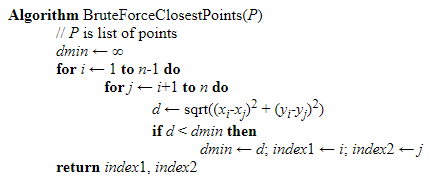
Convex Hull
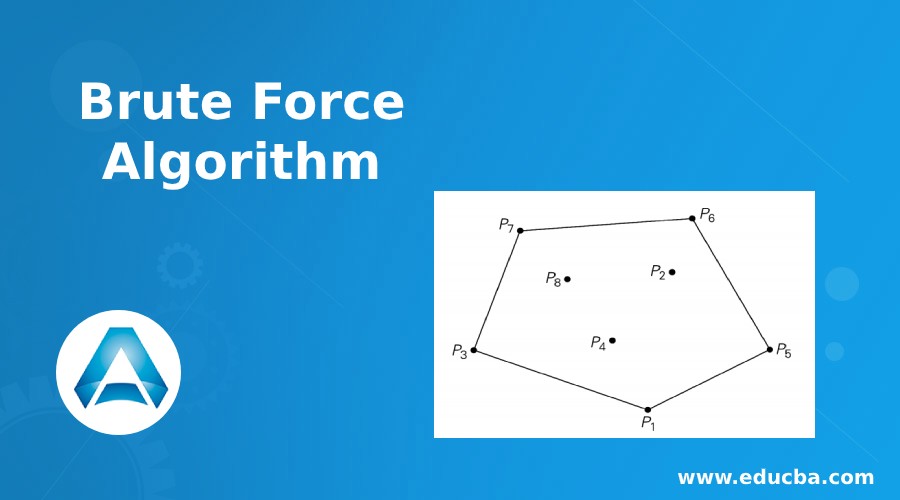
Problem Statement: A convex hull is the smallest polygon that contains all the points. The convex hull of a set s of the point is the smallest convex polygon containing s.
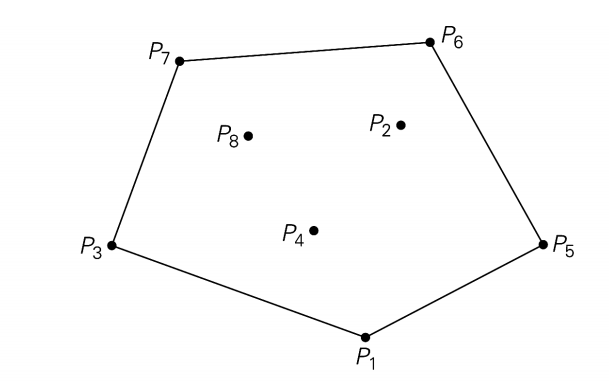
The convex hull for this set of points is the convex polygon with vertices at P1, P5, P6, P7, P3.
A line segment P1 and Pn of a set of n points is a part of the convex hull if and only if all the other points of the set lie inside the polygon boundary formed by the line segment.
Let’s relate it to the rubber band,
Point (x1, y1), (x2,y2) make the line ax+by = c
When a = y2-y1, b = x2-x1 and c = x1*y2 – x2*y1 and divides the plane by ax+by-c < 0 and ax+by-c > 0
So we need to check ax+by-c for the other points.
Brute Force solves this problem with the time complexity of O(n3)
Exhaustive Search
For discrete problems in which there is no known efficient solution, it becomes necessary to test each and every possible solution sequentially.
Exhaustive search is an activity to find all the possible solutions to a problem systematically.
Let’s try to solve the Travelling salesman problem (TSP) using a Brute exhaustive search algorithm.
Problem Statement: There are n cities that salesmen need to travel to, and he wants to find out the shortest route covering all the cities.
We are considering Hamilton Circuit to solve this problem. If a circuit exists, any point can start vertices and end vertices. Once the start vertices are selected, then we only need the order for the remaining vertices, i.e., n-1
Then there would be (n-1)! Possible combinations and the total cost for calculating the path would be O(n). thus the total time complexity would be O(n!).
Conclusion
Now that we have reached the end of this tutorial, I hope you guys have a fair idea of what Brute Force is. We have also seen the various Brute force algorithm you can apply to your application.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Brute Force Algorithm. Here we discussed the Basic concepts of the Brute Force Algorithm. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


