What Is a Brand Strategy?
Brand strategy is a long-term plan that defines how a brand will be perceived, connect with its audience, and stand out in the market. It aligns a company’s purpose, values, voice, and visuals to build trust, loyalty, and recognition.
Apple’s brand strategy focuses on simplicity, innovation, and user-centric design. It does not just sell products, it promotes a lifestyle of creativity and forward-thinking, making emotional connections with its customers.
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- Importance
- Types
- Core Elements
- Brand Strategy Vs. Market Strategy
- How to develop?
- Success Metric
- Mistakes to Avoid
Key Takeaways
- A brand strategy is more than visual identity; it defines a company’s purpose, values, and emotional connection with its audience.
- A strong brand strategy drives business growth by building recognition, trust, and long-term customer loyalty.
- Companies must select the appropriate brand strategy: personal, product, corporate, or global, based on their objectives and target market.
- Core elements, such as brand purpose, positioning, messaging, voice, and visual identity, must align to create a cohesive brand experience.
- Developing a brand strategy is an ongoing process that requires thorough research, a deep understanding of the audience, and consistent execution across all channels.
- Measuring success through brand awareness, loyalty, engagement, and market share ensures the strategy remains effective and relevant.
Why Is Brand Strategy Important?
A brand strategy forms the foundation of a thriving business by influencing how it’s perceived, establishing credibility, and supporting sustained growth. Below are the main reasons why a well-defined brand strategy is essential.
1. Drives Business Growth
A well-crafted brand strategy enhances recognition, fosters customer loyalty, and drives long-term revenue growth by establishing a strong market presence.
2. Ensures Consistency
It aligns messaging, visuals, and values across all platforms, both internally and externally, ensuring a unified brand experience that fosters trust and credibility.
3. Builds Emotional Connection
A clear strategy enables brands to connect authentically with their audience, fostering emotional loyalty and enhancing customer lifetime value.
4. Differentiates from Competitors
In saturated markets, a strategic brand identity helps you stand out, clarify your value proposition, and guide customers toward choosing you over others.
Types of Brand Strategy
Different companies employ various brand strategies tailored to their industry, size, customer base, and business objectives. Below are the most common types, each with a clear real-world example:
1. Personal Brand Strategy
This strategy revolves around promoting an individual rather than a business entity. It focuses on building trust through personal values, expertise, and authentic communication, a strategy often employed by influencers, thought leaders, and entrepreneurs.
2. Corporate Brand Strategy
A corporate brand strategy focuses on establishing a unified image for the entire company, rather than promoting each product or service individually. It unifies messaging across all offerings and aligns company culture with its public image.
3. Product Brand Strategy
This approach gives individual products their own identities, positioning, and branding, allowing a company to target various customer segments independently.
4. Service Brand Strategy
Here, the emphasis is on delivering exceptional service quality and consistent experiences. Trust, responsiveness, and emotional satisfaction become key brand differentiators.
5. Co-Branding Strategy
This strategy involves two or more brands collaborating to launch a joint offering, combining audiences, brand equity, and market power.
Example: Nike and Apple collaborated to create wearable fitness technology that merged athletic and digital innovation.
6. Global Brand Strategy
Companies using this strategy maintain a consistent global identity while making minor adaptations to suit regional markets.
7. Retail Brand Strategy
This strategy focuses on the store itself as the brand, creating a unique shopping experience and emotional connection that drives foot traffic and loyalty.
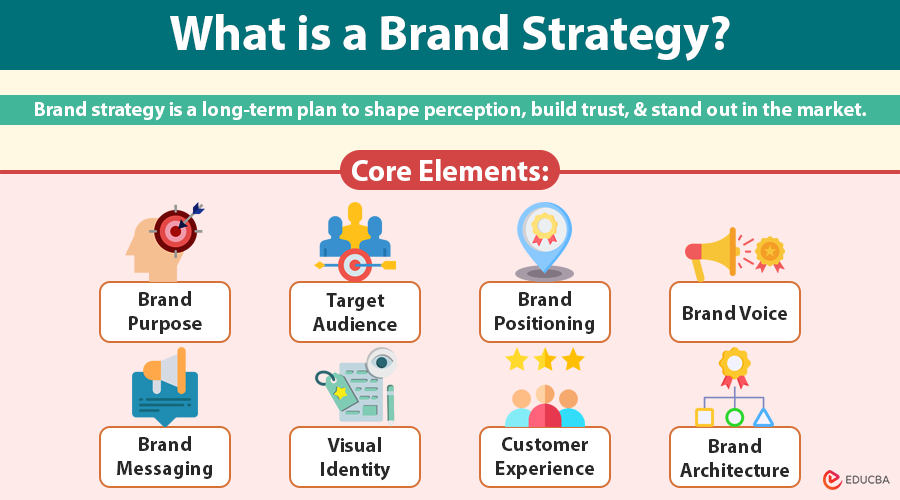
Core Elements of an Effective Brand Strategy
An effective brand strategy integrates several key components that work together to shape how people perceive, interact with, and trust your brand. Here’s a breakdown of the essential elements every strong brand strategy must include:
1. Brand Purpose
Your brand purpose defines the meaningful reason behind your business’s existence beyond profit. It acts as a guiding force for decision-making and inspires both your internal team and your customers. When clearly defined, it fosters strong loyalty, particularly among customers who value and care about the company’s impact on the world.
2. Target Audience
Knowing who you are speaking to is foundational. Identify your ideal customers by researching their demographics, behaviors, goals, and pain points. A focused audience enables the creation of tailored messaging and products that resonate more deeply with the target audience.
3. Brand Positioning
Brand positioning outlines how your brand is perceived in comparison to competitors. It highlights your unique strengths and gives customers a clear reason to choose you over other options.
4. Brand Personality and Voice
Your brand should have a personality, just like a person, fun, bold, trustworthy, elegant, and so on. This personality is expressed through the tone of voice in all forms of communication. A consistent voice builds familiarity and emotional connection.
5. Brand Messaging
This includes your core brand statements, such as your mission, vision, tagline, and key messages. Messaging should be clear, persuasive, and consistent across all platforms to reinforce your brand identity.
6. Visual Identity
Visual identity represents the outward expression of your brand. It encompasses elements like the logo, color scheme, fonts, imagery, and overall design style. These components should consistently convey your brand’s personality across both online and offline platforms.
7. Customer Experience
Your brand is not defined solely by your messaging; it is shaped by how customers feel during every interaction with you. Providing a smooth, positive experience across all touchpoints, whether it is your website, customer service, or delivery, builds trust, loyalty, and long-term advocacy.
8. Brand Architecture
Brand architecture defines how your various offerings relate to one another. It helps customers navigate your portfolio and understand what each product or sub-brand stands for.
Types:
- Branded House: Google (Search, Maps, Drive)
- House of Brands: Unilever (Dove, Axe, Lipton)
- Hybrid: Coca-Cola Company (Coca-Cola, Sprite, Minute Maid)
Brand Strategy vs. Marketing Strategy
| Aspect | Brand Strategy | Marketing Strategy |
| Focus | Long‑term identity, perception, and emotional connection | Short‑ to mid‑term goals like lead generation and sales |
| Purpose | Builds brand trust, value, and positioning | Promotes products/services to achieve measurable results |
| Core Elements | Purpose, values, positioning, voice, visual identity | Campaigns, pricing, promotions, distribution |
| Example | Defining Nike as a brand of empowerment and athletic drive | Launching a seasonal sale for Nike running shoes |
Steps to Develop a Winning Brand Strategy
Developing a strong brand strategy requires clarity, research, and consistent execution. Follow these key steps to build a compelling and successful brand:
Step 1: Conduct a Brand Audit
Evaluate how your brand is currently perceived, encompassing its messaging, visuals, and customer interactions. Pinpoint the strengths and highlight areas that require enhancement.
Step 2: Research Competitors and Market Trends
Analyze your competitors’ positioning, messaging, and branding. Understand current market trends and customer expectations to find opportunities for differentiation.
Step 4: Define Your Brand Core
Clarify your mission, vision, and core values. This forms the foundation of your brand’s identity and influences every aspect of communication and culture.
Step 5: Develop Brand Positioning
Determine how you want your brand to be perceived by your target audience. Craft a unique value proposition that clearly distinguishes you from competitors.
Step 6: Create a Messaging Framework
Craft clear brand messages that reflect your promise, voice, and character. Maintain Consistency across every platform and customer interaction to deliver a unified brand experience.
Step 7: Design Visual Assets
Develop a unified visual identity by designing elements like your logo, color scheme, typography, and overall design style. Ensure that these visuals accurately reflect your brand’s character and resonate with your target audience.
Step 8: Launch Consistently and Monitor Performance
Roll out your brand across all channels—website, social media, packaging, customer service, etc. Track performance through brand awareness, engagement, and feedback to refine your strategy as needed.
Measuring Brand Strategy Success
To determine whether your brand strategy is effective, you need to track Performance using both qualitative and quantitative metrics. Here are key indicators to evaluate success:
1. Brand Awareness
Measure how well your audience recognizes and recalls your brand. Tools like surveys, social listening, and search volume trends can help assess visibility and top-of-mind presence.
2. Customer Loyalty
Track customer retention rates, repeat purchases, and referral activity to optimize your business. A strong brand encourages long-term relationships and organic growth through word-of-mouth.
3. Engagement
Track audience engagement with your content across various digital platforms. Engagement metrics, such as likes, shares, comments, time spent on the page, and click-through rates, indicate how well your brand message captures attention and resonates with viewers.
4. Perception Surveys
Conduct brand perception or sentiment surveys to understand how customers feel about your brand. These insights can highlight strengths and uncover areas for improvement.
5. Market Share and Revenue Growth
Monitor your brand’s share within its industry and its contribution to overall business revenue. An increase often reflects successful positioning and a preference for the brand.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Inconsistent branding – Confuses customers and weakens recognition.
- Targeting everyone – Leads to vague messaging; focus on a clear niche.
- Ignoring internal culture – Team misalignment affects brand delivery.
- Copying competitors – Dilutes uniqueness and originality.
- Not evolving – Outdated branding loses relevance.
Final Thoughts
A strong brand strategy goes beyond logos or taglines; it defines who you are, what you stand for, and how you are perceived. It helps build trust, stand out from the competition, and foster lasting customer relationships. In a crowded market, brands with clarity, purpose, and consistency are the ones that truly thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Q1. How long does it take to build an effective brand strategy?
Answer: Building a solid brand strategy can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the company’s size, the depth of market research, and the alignment across teams.
Q2. Who should be involved in developing a brand strategy?
Answer: Key stakeholders typically include company leadership, marketing teams, sales teams, product teams, and sometimes external brand consultants or agencies to bring in a fresh perspective.
Q3. How often should a brand strategy be updated?
Answer: Review your brand strategy annually, or whenever there is a significant market shift, business growth, or change in customer behavior, to ensure continued relevance.
Q4. How does storytelling fit into brand strategy?
Answer: Brand storytelling helps communicate your purpose, values, and personality in an engaging way. It adds emotional depth and makes your brand more relatable and memorable.
Q5. Is it necessary to trademark your brand elements?
Answer: Yes. Trademarking protects your brand assets, such as logos, names, or slogans, from being copied, helping to maintain uniqueness and legal security.
Recommended Articles
If you found this guide on brand strategy helpful, check out these related articles to enhance your knowledge of brand building, positioning, and long-term business growth.
