Updated March 23, 2023

Introduction to Bitwise Operators in C++
Bit by bit operation is performed, and the operator that works on bits is called a bitwise operator. Using bitwise operators, there are no byte-level operations in programming; only bit-level calculations are performed in programming. The bits can be manipulated using various bitwise operators. The operations of bitwise operators can be done on integer and character datatypes only. Bitwise operators cannot be operated on the float and double. In C++, there are a total of six bitwise operators. The six bitwise operators are bitwise AND (&), bitwise OR (|), bitwise XOR (^), left shift (<<), right shift (>>), and bitwise NOT (~).
Operators of Bitwise in C++
In C++, there are a total of six bitwise operators. They are:
1. Bitwise AND (&)
In Bitwise AND (&) operation, two numbers are taken as operands and AND operation is performed on every bit of two numbers. If both the bits are one, the result of AND operation is one. If both the bits are zero, the result of AND operation is zero. If anyone of the bits is zero, the result of the AND operation is zero. Let’s take a simple example for bitwise AND operation.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unsigned int num1 = 10; // 10 = 0000 1010
unsigned int num3 = 12; // 12 = 0000 1100
int num2 = 0;
num2 = num1 & num3; // 8 = 0000 1000
cout << "Value of num2 is : " << num2 << endl ;
return 0;
}Output:

2. Bitwise OR (|)
In Bitwise OR (|) operation, two numbers are taken as operands and OR operation is performed on every bit of two numbers. If both the bits are one, the result of OR operation is one. If both the bits are zero, the result of OR operation is zero. If anyone of the bits is one, the result of OR operation is one. Let’s take a simple example for bitwise OR operation.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unsigned int num1 = 10; // 10 = 0000 1010
unsigned int num3 = 12; // 12 = 0000 1100
int num2 = 0;
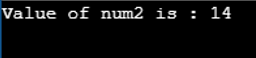
num2 = num1 | num3; // 14 = 0000 1110
cout << "Value of num2 is : " << num2 << endl ;
return 0;
}Output:
3. Bitwise XOR (^)
In Bitwise XOR (^) operation, two numbers are taken as operands, and XOR operation is performed on every bit of two numbers. If both the bits are zero, the result of the XOR operation is zero. If anyone of the bits is one or both the bits are one, the result of the XOR operation is one. Let’s take a simple example for bitwise XOR operation.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unsigned int num1 = 10; // 10 = 0000 1010
unsigned int num3 = 12; // 12 = 0000 1100
int num2 = 0;
num2 = num1 ^ num3; // 6 = 0000 0110
cout << "Value of num2 is : " << num2 << endl ;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
4. Left Shift (<<) operation
In Left Shift (<<) operation, two numbers are taken as operands. The first operand left shifts the bits, and the second operand decides the number of places to be shifted. Let’s take a simple example for left shift (<<) operation.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unsigned int num1 = 12; // 12 = 0000 1100
int num2 = 0;
num2 = num1 << 2; // 48 = 0011 0010
cout << "Value of num2 is: " << num2 << endl ;
return 0;
}Output:

5. Right Shift (>>) operation
In Right Shift (>>) operation, two numbers are taken as operands. The second operand decides the first operand right shifts the bits, and the number of places to be shifted. Let’s take a simple example of the right shift (>>) operation.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unsigned int num1 = 12; // 12 = 1100
int num2 = 0;
num2 = num1 >> 2; // 3 = 0011
cout << "Value of num2 is: " << num2 << endl ;
return 0;
}Output:

6. Bitwise NOT (~)
In the Bitwise NOT (~) operation, one number is taken as an operand, and all the bits of the number are inverted. Let’s take a simple example for Bitwise NOT (~) operation.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 12 = 0000 1100
unsigned int num1 = 12;
int num2 = 0;
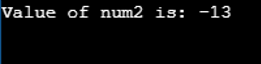
num2 = ~num1;
cout << "Value of num2 is: " << num2 << endl ;
return 0;
}Output:
7. All the bitwise operations
Let’s take a simple program including all the bitwise operations,
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
main() {
unsigned int a = 60; // 60 = 0011 1100
unsigned int b = 13; // 13 = 0000 1101
int c = 0;
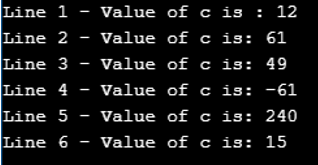
c = a & b; // 12 = 0000 1100
cout << "Line 1 - Value of c is : " << c << endl ;
c = a | b; // 61 = 0011 1101
cout << "Line 2 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ;
c = a ^ b; // 49 = 0011 0001
cout << "Line 3 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ;
c = ~a; // -61 = 1100 0011
cout << "Line 4 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ;
c = a << 2; // 240 = 1111 0000
cout << "Line 5 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ;
c = a >> 2; // 15 = 0000 1111
cout << "Line 6 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ;
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about different types of operands and operands in C++, their functionality and examples of how to use them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Bitwise Operators in C++. Here we discuss the different types of operands and operands in C++, their functionality and examples to use them. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


