Updated June 29, 2023
Introduction to ASP.NET Core Middleware
ASP.NET Core brings in an innovative concept called Middleware. They are software modules collected together to the application pipeline to handle the responses and requests passed. The ASP.NET Core Middleware maintains how the application responds to HTTP requests. Middleware is the key part of authenticating and authorizing a user to achieve exact actions. It also manages the application if there any error has occurred. Every part of Middleware in ASP.NET Core is an object, and every part has a particular purposeful role.
What is ASP.NET Core Middleware?
- ASP.NET Core Middleware is a software component composed of the application pipeline to handle the requests and responses. Middleware is a component or class implemented on every request in the ASP.NET Core application. Therefore, every component decided to select whether to pass the request to the subsequent component in the pipeline.
- Consider we have the middleware component to handle the errors. Another middleware authenticates a user, and another serves static files like CSS Files, Images, JavaScript files, etc.
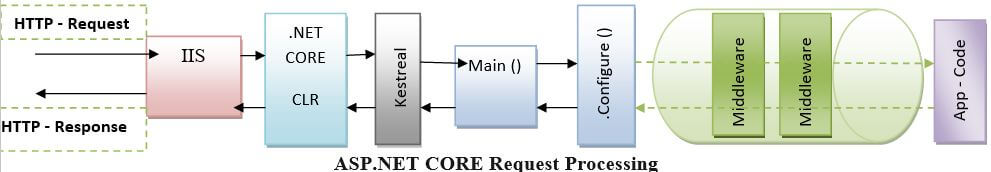
ASP.NET Core Request Processing
In ASP.NET, request pipelines are called HttpHandlers and HttpModules, similar to the middleware. Both require configuring and implementing every request. ASP.NET Core Middleware maintains how the application responds to HTTP requests. Middleware is the key part of authenticating and authorizing a user to achieve specific actions.
In general, there is numerous Middleware in ASP.NET Core Web-Application. The middleware are in two types. It may be its custom middleware or a framework middleware added through NuGet. In the requested pipeline, we can position the middleware order-wise. Each middleware adds and alters the HTTP Request and preferably passes the controls to the subsequent middleware component.
The Middleware built the requesting pipeline describing the ASP.NET CORE Request Processing.
How to Add Another ASP.NET Core Middleware?
ASP.NET Core Middleware maintains how the application responds to HTTP requests. Thus, middleware is the key part of authenticating and authorizing a user to achieve specific actions.
Let’s see the following steps to include the additional middleware.
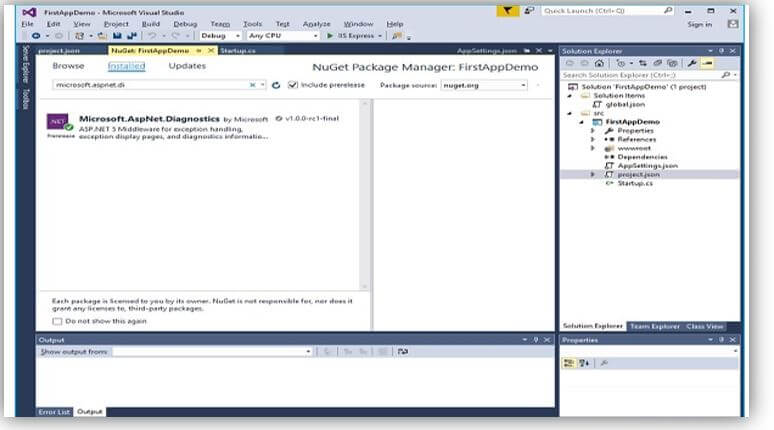
- To add the Middleware, we must right-click the project and choose the Manage NuGet Packages.
- Then look for Microsoft.AspNet.Diagnostics that’s the real ASP.NET Core Middleware for exception display pages, diagnostics information, and exception handling. This selected package includes various parts of Middleware we can make use of.
- Install that package if it is not installed in your project.
- To install the package called Microsoft.AspNet.Diagnostics, if it’s not already installed in the project.
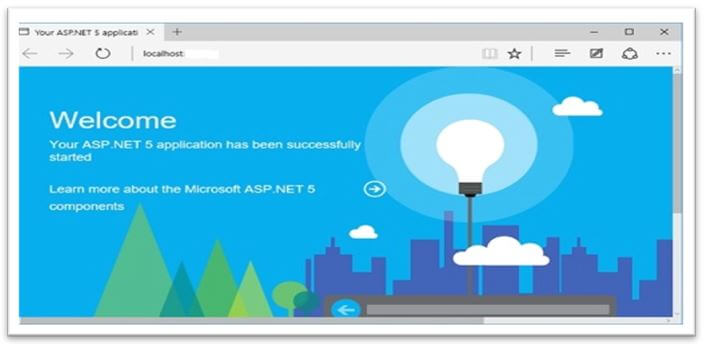
- And then, go to the Configure() method and invoke the app.UseWelcomePage Middleware.
// the Configure () method will be called during runtime
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseIISPlatformHandler();
app.UseWelcomePage();
// by using the method to configure the HTTP Request pipeline
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
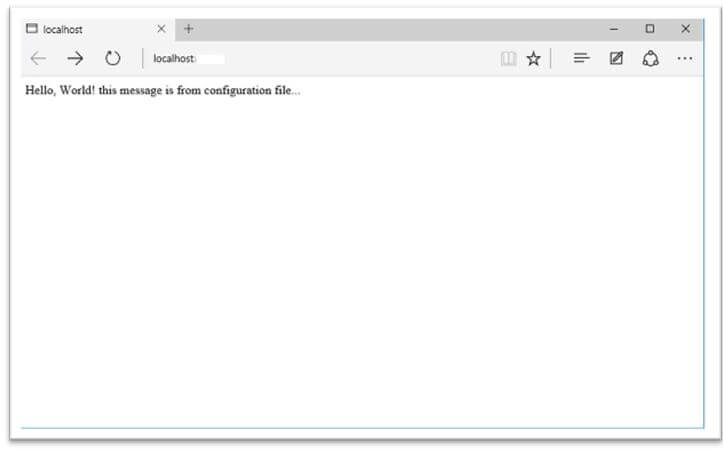
var msg = Configuration["Message"];
await context.Response.WriteAsync(msg);
});
}
}- Finally, execute the application and see the screen as follows.
The above screen is just the welcome page; let’s use the RuntimeInfoPage by giving the following code.
// the Configure () method will be called during runtime
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseIISPlatformHandler();
app.UseRuntimeInfoPage(); //here the UseRuntimeInfoPage() method
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
var msg = Configuration["message"];
await context.Response.WriteAsync(msg);
});
} // by using the method to configure the HTTP Request pipeline- Update the Startup.cscode page, save it, refresh the browser, and see the following screen.
The RuntimeInfoPage is the Middleware that responds to specific URL requests. If the incoming request does not match the URL, then the middleware part passes the request to the next portion of the Middleware. And then, the request passes through the IISPlatformHandler Middleware; after that, it goes to the UseRuntimeInfoPage() Middleware. Finally, it will go to the app. Run and displays the string.
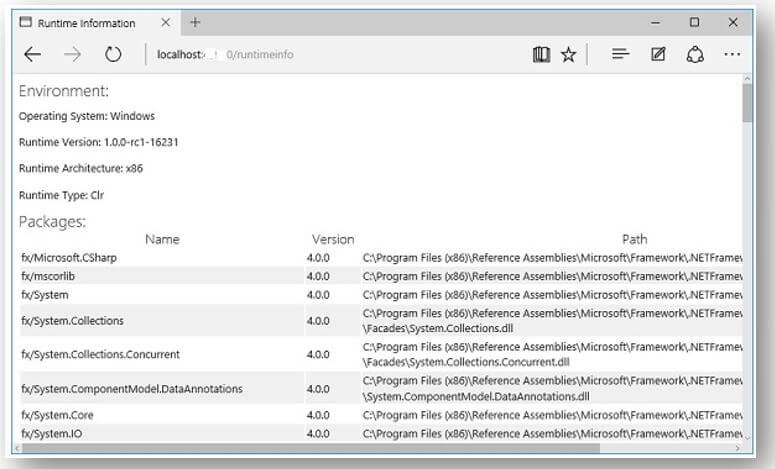
- Finally, add the “/runtimeinfo” at the end of the URL and now look at the page generated by that RuntimeInfoPage Middleware.
And then, look at the response, which gives a few details on the Runtime Environment like Operating System, Runtime Versions, their type, Architecture, and the entire packages you were using and so on.
Run Method
The Run Extension method includes the Middleware; let’s see the following format method used for Run Method ().
public static void Run(this IApplicationBuilder app, RequestDelegate handler)This Run Method () is an extension method on the IApplicationBuilder and also accepts the attribute of RequestDelegate. This RequestDelegate is a type of delegate method that handles the request.
Let’s see the following RequestDelegate format as follows.
public delegate Task RequestDelegate(HttpContext context);The Run method() accepts the method as an attribute, and its syntax matches the RequestDelegate. So the method agrees with the HTTPContext attribute and returns the task. So we can use either a particular Lambda Expression or a particular Function in Run Method().
Let’s make the asynchronous using the await and async to enhance the performance and scalability.
app.Run(async context => await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!"));
//or else make use of
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!");
});Example of ASP.NET Core Middleware
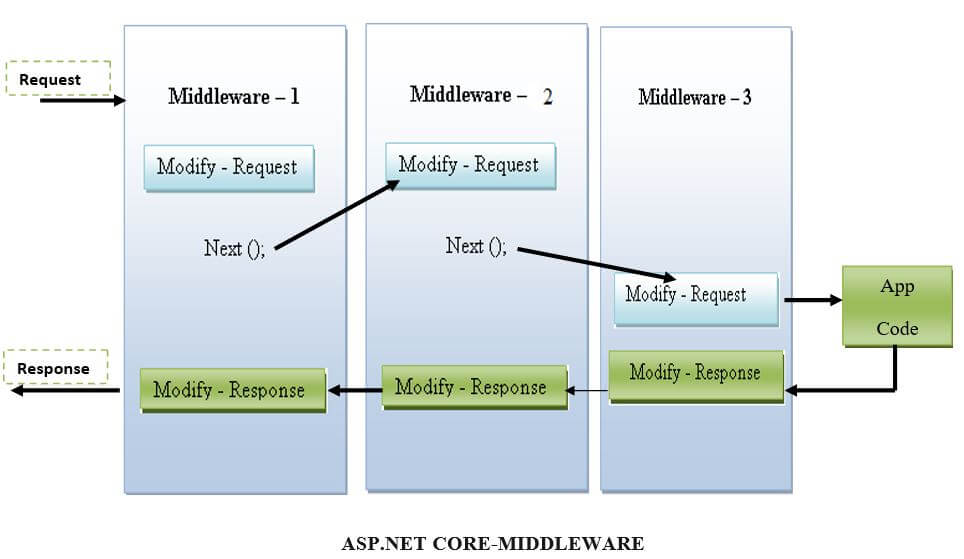
Middleware is a component or class implemented on every request in the ASP.NET Core application. ASP.NET Core Middleware is a software component composed of the application pipeline to handle the requests and responses. Every component decided to select whether to pass the request to the subsequent component in the pipeline.
Let’s see the following diagram, which describes the implementation of middleware components.
Conclusion
This article shows how the ASP.NET Core Middleware components handle the request processing pipeline and how it controls our application’s HTTP request responses. Every middleware component in ASP.NET Core has to access the incoming requests and outgoing responses.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “ASP.NET Core Middleware” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.