Updated April 1, 2023
Introduction to asp.net core environment variables
ASP.NET Core Environment Variables uses the variable called ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT, which points towards the runtime environment. The value of this variable may be something as per the requirement but usually be a Production, Staging, and Development. The Environment variable defines the runtime environment for which the application runs. The value is not case-sensitive for Windows and Mac OS, but for Linux, it is case-sensitive.
ASP.NET Core Environment Variable Overviews
The ASP.NET Core supplies a selection to manage various environments for an Application. Before deploying the application to production or actual users, the Enterprise or Professional Application has several domains or phases (stages). Staging, Production, and Development Environments are just a few examples. The Environment variable defines the runtime environment for which the application runs.
The ASP.NET Core Application uses an Environment Variable called ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT, indicating the application is presently running. You can afford any of the values to the variable as per the need, but generally, the environmental importance of Development, Production, or Staging can be used. The environment name is not case sensitive; let us consider one example; if we set the variable to Development or DEVELOPMENT or development, the concluding result will be the same.
In ASP.NET Core, enhanced support for managing applications around several environments like production, staging, and development will be provided. The Environment Variables are mainly used to specify the Environment application executing, enabling the application to configure it.
For the conventional purpose, there will be used by three values; those variables can be set to any of the values you prefer: Development, Production, or Staging.
Development
This process will be used during the application development; while using Visual Studio, the setting will be denoted in the project’s debug, like IIS Express.
Staging
The Staging Environment is a Pre-Production Environment used for testing after the application before the deployment.
Production
The Production Environment is used while the application executes during the live process where the end-user works on it. This process is configured for application Robustness based on performance, safety, and security. Some settings of production will be varied from development they are,
- Allow the Production Logging and Controlling
- Caching- turn on
- Diagnostic Error Pages –turn off
- Make sure entire client-side resources which are safely served from CDN.
Lets the following code:
- It calls to UserDeveloperExceptionPage when ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT is set to development.
- It calls to UserExceptionHandler when the value of ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT sets to Production, Staging, or Staging_2.
- It injects to IWebHostEnvironment into the Startup.Configure. This method is functional when the app needs altering Startup.Configure a few environments with minor code differences as per the environment.
ASP.NET Core Environment Variable Command
To set the hosting environment by using the commands, depending on configuring the WebHostBuilder, we can specify the environment by offering the command line argument. To make use of ConfigurationBuilder makes use of the AddCommandLine() extension method from Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.CommandLine package. Now then pass the configuration to WebHostBuilder by using the UseConfiguration(config):
Var config= new ConfigurationBuilder()
.AddCommandLine(args).Build();
Var host=new WebHostBuilder().UserConfiguration (config)
. UseContentRoot (Directory.GetCurrentDirectory ())
. UseKestrel()
. UseIISIntegration()
. UseStartup<Startup>().Build().
. Build();It enables to specify the environment hosting during runtime by using the environment argument, àdotnet run – environment "Staging"Project in the solution explorer and select Properties.
ASP.NET Core uses the Environment Variable called ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT, which indicates the runtime environment. The value of this variable may be something as per the requirement but usually be a Production, Staging, and Development. The Environment variable defines the runtime environment for which the application runs. The value is not case-sensitive for Windows and Mac OS, but for Linux, it is case-sensitive.
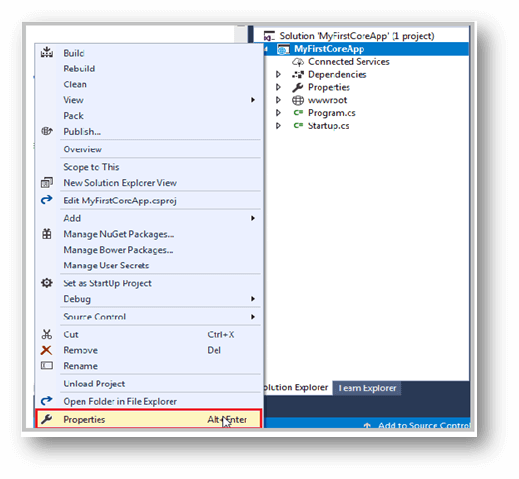
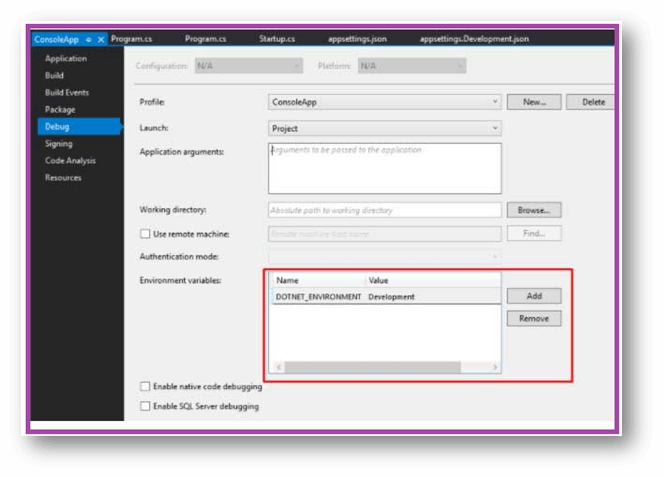
Look at the following screens, Open Visual Studio, and set ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT in debug tab of Project Properties. Just open the Project Properties just by right-clicking the project in the Solution Explorer and choosing the Properties,
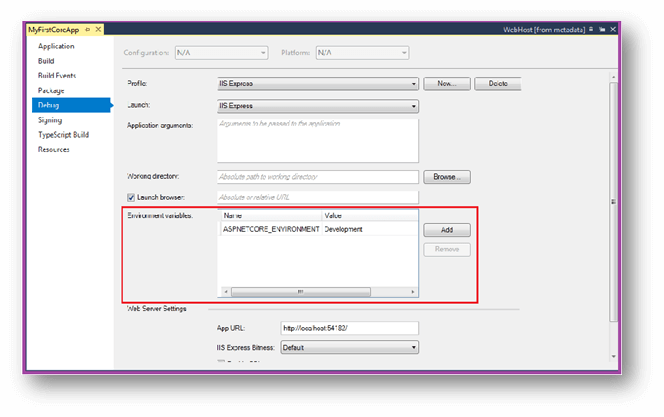
Once opening the Project Properties, it will open the Properties Page, click on the Debug tab and look at the Environment Variables as shown below,
- It contains the Profile Settings
- It is used only on the Local Development Machine
- It is not deployed
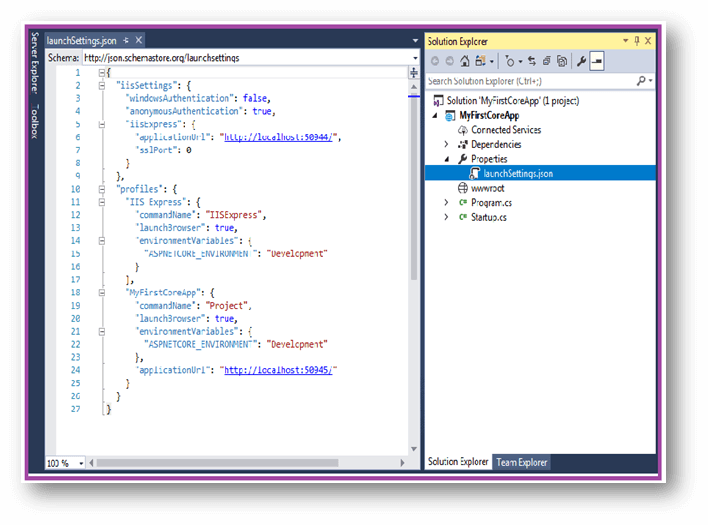
Look at the following JSON, which depicts the launchSetting.json file for ASP.NET Core Web Project, which is named EnvironmentSample created with Visual Studio or dotnet new,
JSON Code – launchSetting.jsonWe can also make a change directly in the Environment Variable in launchSetting.json.
How asp.NET Core Support Environment Configurations
The Environment variable defines the runtime environment for which the application runs. It makes it available with the Static Class to access the Environment Variables Environment in System NameSpace. Let’s see the following variable as given below,
using System;
namespace Application
{
class SampleProgram
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
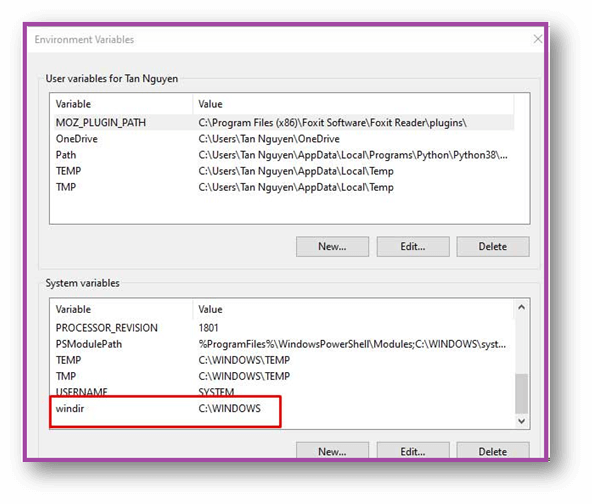
var environment = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("windir");
Console.WriteLine("windir path: " + environment);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
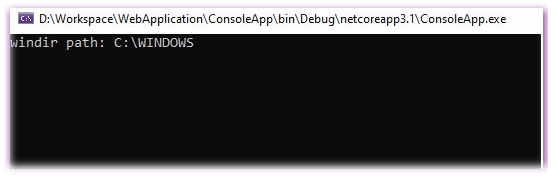
}Output:
You can see the value of the “windir” Environment Variable through the “C:\WINDOWS.”
While using the VISUAL STUDIO, the Environment Variable can be denoted during the Development Process in the Projects’ Debug File; let’s see the following example as shown.
ASP.NET Core Environment Variable Examples
The ASP.NET Core supplies a selection to manage various environments for an Application. To get the value of the Environment Variable in the code to execute with the extra code based on some value. IHostingEnvironment Service, which includes the EnvironmentName Property, which contains the value of the ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT variable, also consists of the extension methods to verify the environments like IsDevelopment(), IsEnvironm’ent (), IsStaging (), and ISProduction(). Let’s look at the sample code below as shown,
Sample Code
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsEnvironment("Development"))
{
// Development Environment - Code Execution
}
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
// Development Environment - Code Execution
}
if (env.IsStaging())
{
// Staging Environment - Code Execution
}
if (env.IsProduction())
{
// Production Environment - Code Execution
}
}Conclusion
This article shows the asp.net core environment variables, which indicate during the runtime environment. The environment variable defines the runtime environment for which the application runs. I hope the article helps you to understand the concept.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “asp.net core environment variables” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.