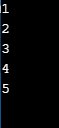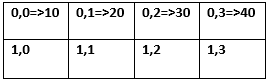Updated November 22, 2023
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- How to Declare Arrays in Java?
- How to Initialize Arrays in Java Programming?
- How to Access Array Elements?
- Types of Arrays in Java
- Array Methods in Java with Examples
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Arrays in Java
Introduction to Arrays in Java
Java is a versatile programming language renowned for its object-oriented paradigm, making it widely adopted in the IT sector. With various data types, Java supports both primitive and non-primitive types. Arrays, a fundamental data structure in Java, store a fixed-size sequential collection of homogeneous elements.
The Java.util.Arrays class provides useful methods for manipulating arrays, including obtaining array indices and checking array equality. To set values at specific indices, arrays offer an efficient means of organizing data uniformly.
Java provides the sort method for sorting arrays in ascending order, and for large arrays on multiprocessor systems, parallel sorting methods enhance performance. As static data structures, arrays excel at storing multiple values of the same type. In Java, arrays can be passed as parameters to methods, offering flexibility in handling and processing data efficiently.
Code:
class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[] = {3, 1, 2, 5, 4};
sum(a);
}
public static void sum(int[] a)
{
// getting sum of array values
int total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
total+=a[i];
System.out.println("sum of array values : " + total);
}
}Output:
How to Declare Arrays in Java?
An array is a data structure representing a collection of elements, where each element must be of the same data type. It is a way of storing and organizing data in a single variable. For example, if we have a class of students, and each student has an ID, we can use an array to store these IDs as a homogeneous set of data values within a single variable.
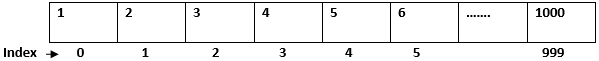
Suppose 100 students are there. Look at below; we will declare a variable for each.
int student1 = 1;
int student2 = 2;
int student3 = 3;
int student4 = 4;
.
.
.
Int student5 = 5;Huh… it’s still ok. But what if you have 1000 students? It is very tedious and time-consuming to declare a variable 1000 times.
So what’s the solution then? Yes, and the answer is Array. Let’s see how can we declare an array.
In Array, we can put values in a single variable.
Ex:
int student[] = new int[1000];We will see it clearly in the following diagram:
Student[]
Here, in a single variable, we can store the number of values we want. A variable is nothing but a reference to the memory location.
If you have seen carefully, we declared the array with the new keyword. Generally, we are using a new keyword to create objects. That means in Java; arrays are objects.
Hey, hold on, what? Object. That means there should be a class that already exists to make its object. Yes, we have one superclass for it, and that is the object class. The array always extends the class object. Arrays always occupy heap memory. Not only Array objects but all the objects in Java are stored in heap memory. So we have only one reference to all values. By this, we used memory efficiently. An array is a common topic in nearly all languages. Once we understand the core concept of the array, then we can easily tackle it.
How to Initialize Arrays in Java Programming?
Initialization is nothing but the process of assigning value to the variable. There are multiple ways to initialize arrays in Java.
The first way is as shown in the above example while declaring the Array.
Ex:
int student[] = new int[1000];The next thing is we can initialize the array while declaring it as follows:
Ex:
int student[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ….1000};While working with the array, we may get the exception. If you have learned about error handling in Java, then you must know the exception. The exception is nothing but the error that is known at runtime and gets handled efficiently. For the array, we have an Array Index out-of-bounds exception.
How to Access Array Elements?
Till now, we have learned how to declare and initialize the array. Now the time is to move forward. Let’s consider you have an array the same as above, i.e. student array.
Now, we want a particular value to access for doing some programming. How to get the value of a particular element in the array.
In Array, we have the concept of index no.
For example, look at the below diagram.
Index no starts with zero(0).
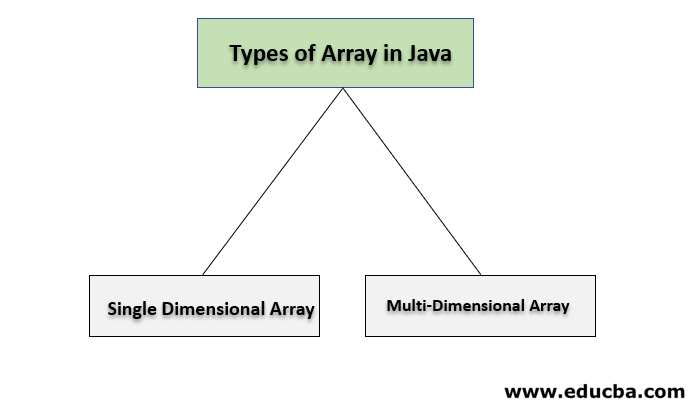
Types of Arrays in Java
Before getting into the types of arrays, let’s understand some basic concepts.
The elements in the array allocated by new will automatically get initialized by zero (for numeric types), false (for boolean), or null (for reference types). There are default array values in Java. Obtaining an array is a two-step process. You need to declare a variable of the array type. Then, you need to allocate the memory for that which will hold the array using a new keyword, and it will assign it to the array variable. So, we can say that in Java, all arrays are dynamically allocated.
There are two types of arrays as follows:
1. Single Dimensional Array
Single dimensional consists of the 1D array. It may have a single row or a single column.
We can declare a single-dimensional array as below:
int[] a; OR int a[]; OR int []a; OR int[]a;But the most preferred way is int[] a; Do remember that we are not declaring the size of the array here. Ex: int[5] a; is not valid in Java. At the time of declaration, we are not giving the size of an array.
Now, we will look at the declaration and creation of the array:
int[] a; //Declaration of the arraya = new int[5] //Creation of arrayAt the time of array creation, providing the size of an array is very important.
We can declare and create an array in a single line as below:
int[] a = new int[3];Now let’s look at how to initialize the array. Suppose you have to add some values in an array. Then you will add it to a particular index number as below:
a[0] = 1; // We are adding 1 at 0th position in array
a[1] = 25; // We are adding 25 at 1th position in array
a[2] = 32; // We are adding 32 at 2th position in arrayNow you have seen how to initialize the array. But what if I gave the index no, which does not exist on the array?
Ex:
a[10] = 11; // suppose we had array of 5 onlyAt this time, it throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException. You cannot add values beyond the size of an array.
Now, We can declare, create, and initialize the array in a single line as below:
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5}; //Declare, create, initializeOR
int[] a = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5};Now, let’s see how can we retrieve elements from a single-dimensional array:
How to Print Values of Array?
We will use for loop here:
Example:
public class Demo2{
public static void main (String args[]){
int[] a = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5};
for(int i=0; i<=a.length-1;i++)
{
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
}Output:
In the above example, we can loop over the array values.
2. Multi-Dimensional Array
The multi-dimensional array consists of 2d and 3d arrays. It has multiple rows and multiple columns. We also called it an Array of Arrays. We can also call them jagged arrays. Now let’s look at the array declaration. I mean 2-D array declaration. Above, we have seen how to declare a one-dimensional array. Now we are going to see the 2-D array. Same as we read a single-dimensional array using its length variable within a for-loop, we can read a 2-dimensional array using its length variable within two for-loops. Suppose the length variable of a single-dimensional array gives the total number of values that a single-dimensional array can hold. The length variable of a 2-dimensional array gives the total number of arrays that a 2-dimensional array can hold.
The multi-dimensional array can be that array of arrays.
int [][] a; //here we declared array aNow, same as above, what we did with a one-dimensional array. After declaring the array, we need to create an array. Look at the below example.
a = new int[2][4];After this, we are going to initialize an array.
We will understand this with the below diagram more clearly.
By the above diagram, we can easily initialize the array elements.
a[0][0] = 10
a[0][1] = 20
a[0][2] = 30
a[0][3] = 40
Look at the following diagram above values get inside a given position. We can easily initialize the array with rows and columns.
Now, All the processes like declaration, creation, and initialization can be done in a single line as below. Please look at the below syntax carefully. First, we will see the declaration and creation in one line:
int[][] a = new int[2][3];Now we will see all three processes declaring, creating, and initializing the array.
int[][] a = {{10,20,30},{100,200,300}};Look at the following program to be more precise:
Code:
public class MyArray {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] a = {{10,20,30},{100,200,300}};
System.out.print(a[1][2]);
}
}Output:
Try the small programs in the array. Manipulate the values. By making hands dirty while programming most of the small things, you will understand.
Array Methods in Java with Examples
The class Arrays belongs to java.util package has numerous static methods that are useful in filling, sorting, searching, and many other things in arrays.
They are as follows:
1. static <T> List<T> asList (T… a)
asList method is used to return the fixed-size list that mentioned Arrays back.
Code:
// Program to showcase asList() method
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Fetching Array
int Arr[] = { 10, 30, 35, 52, 75 };
// Converting elements into list
System.out.println("The Integer Array as a List = "+ Arrays.asList(Arr));
}
}Output:
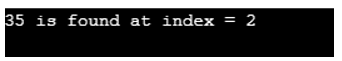
2. static int binarySearch(itemToSearch)
This method would search for a mentioned element in the array through the Binary Search algorithm.
Code:
// Program to showcase binarySearch() method
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Fetching Array
int Arr[] = { 10, 30, 35, 52, 75 };
Arrays.sort(Arr);
int ele = 35;
System.out.println (ele + " is found at index = "
+ Arrays.binarySearch(Arr, ele));
}
}Output:
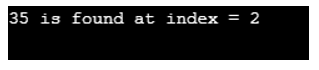
3. static <T> int binarySearch(T[] an int fromIndex, int toIndex, T key, Comparator<T> c)
This method would search the range of the mentioned array for a specified object using a binary search algorithm.
Code:
// Program to showcase binarySearch() method
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Fetching Array
int Arr[] = { 10, 30, 35, 52, 75 };
Arrays.sort(Arr);
int ele = 35;
System.out.println ( ele + " is found at index = " + Arrays.binarySearch(Arr, 1, 3, ele));
}
}Output:
4. compareUnsigned(arr 1, arr 2)
The compareUnsigned method would compare two arrays passed as parameters in a lexicographical style and treat them as unsigned. This method of Integer class would compare two integer values treating them as unsigned and then returning zero in case x equals y.
Code:
// Program to showcase compareUnsigned() method
import java.lang.Integer;
class Arrays {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int m = 10;
int n = 20;
// as 10 less than 20, the output would be a value less than zero
System.out.println(Integer.compareUnsigned(m, n));
int x = 8;
int y = 8;
// as 8 equals 8, Output would be zero
System.out.println(Integer.compareUnsigned(x, y));
int e = 25;
int f = 8;
// as 25 is greater than 8, Output would be a value greater than zero
System.out.println(Integer.compareUnsigned(e, f));
int o = 15;
int p = -7;
/* as 15 is greater than -7 but -7 would be treated as an unsigned number
which will be greater than 15
Output would be a value less than zero */
System.out.println(Integer.compareUnsigned(o, p));
}
}Output:
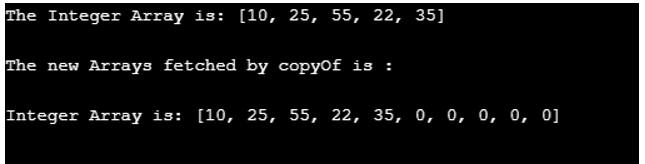
5. copyOf(original array, new length)
Copy method copies the mentioned array, truncates it, or pads it with a default value, but only if necessary so that copy has got the mentioned length.
Code:
// Java program to showcase Arrays.copyOf() method
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Fetching Array
int Arr[] = { 10, 25, 55, 22, 35};
// Printing the elements in a single line
System.out.println("The Integer Array is: " + Arrays.toString(Arr));
System.out.println("\nThe new Arrays fetched by copyOf is :\n");
System.out.println("Integer Array is: " + Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOf(Arr, 10)));
}
}Output:
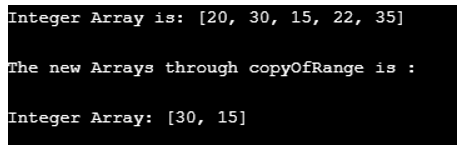
6. copyOfRange(the previous array, startIndex, finishIndex)
The copyOfRange method would copy the mentioned array’s range into a new Array.
Code:
// Java program to showcase Arrays.copyOf() method
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Array{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Fetching Array
int Arr[] = {20, 30, 15, 22, 35 };
// Printing the elements in a single line
System.out.println("Integer Array is: " + Arrays.toString(Arr));
System.out.println("\nThe new Arrays through copyOfRange is :\n");
System.out.println("Integer Array: " + Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOfRange(Arr, 1, 3)));
}
}Output:
7. static boolean deepEquals(Object[] m1, Object[] m2)
The DeepEquals method would return true if the two mentioned arrays are deeply equal to the other array.
Code:
// Java program to showcase method Arrays.deepEquals()
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Array{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Fetching first Array
int Arr[][] = { {10, 20, 35, 82, 95} };
// Fetching second Array
int Arr2[][] = { { 10, 15, 22 } };
// Comparing both arrays
System.out.println("Arrays when compared: " + Arrays.deepEquals(Arr, Arr2));
}
}Output:
8. static int deepHashCode(Object[] a): deepHashCode
The method would return the hash code depending upon the “deep contents” of the mentioned arrays.
Code:
// Java program to showcase Arrays.deepHashCode() method
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Fetching first Array
int Arr[][] = { { 10, 20, 15, 22, 35} };
// Getting deep hashCode of arrays
System.out.println(Arrays.deepHashCode(Arr));
}
}Output:
Advantages and Disadvantages of Arrays in Java
Below we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- An array can store multiple values in a single variable.
- Arrays are fast as compared to primitive data types.
- We can store objects in an array.
- Members of the array are stored in consecutive memory locations.
Disadvantages
- The array has a fixed-size
- We cannot increase or decrease the size of the array at runtime.
- In an array, memory wastage can be more.
- We can store similar data type items only.
- While adding or removing items in the middle of the array affects the performance of the array.
Arrays in Java are the data structures used to store elements of the homogeneous data type. The advantage of arrays is that the elements in the array can be accessed using its index number. This makes it easy to perform sorting, fetching, searching, and other preferred operations on those elements in arrays considerably fast. The array is such a small concept and can be covered in a small stipulated time. When we are preparing for the exam or an interview at that time, make sure you have seen and implemented all the concepts discussed above.
Conclusion
In Java programming, arrays are fundamental data structures that store sequentially elements of the same type. They offer efficient manipulation and retrieval. Understanding arrays is crucial for managing collections of data. Java’s array functionality simplifies complex operations, making it a cornerstone for building robust and scalable applications.
FAQs
Q1. What is the length of an array in Java?
Answer: The length of an array in Java is determined by the length property. For example:
int[] numbers = new int[5];
int length = numbers.length; // This will be 5Q2. Can an array have a negative index in Java?
Answer: No, array indices in Java must be non-negative integers. Accessing an element with a negative index or an index beyond the array size will result in an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
Q3. What is the difference between arrays and ArrayList in Java?
Answer: Arrays have a fixed size, and their size cannot be changed once initialized. ArrayLists, on the other hand, can dynamically grow or shrink in size.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Arrays in Java” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.