Updated June 16, 2023
Introduction to Array in Scala
Array, We all will be familiar with the term Array as we are using it since we started programming with java, and this collection is so much usable and code friendly that we all must have used it for our programming works.
So let us see if can we use this array with Scala programming. So Array is a collection of the same data type, so Scala also provides a Data Structure Array, which stores a fixed-size collection of elements of the same type. The same types come with as the same data type so it would be really easy to apply functions over the same data type. The index of Arrays starts with 0, and the last element is the no of elements – 1.
We can hold the data, traverse the elements in the Array, and perform operations over the array. We can iterate the array over the length. Scala supports both one-dimensional as well as multi-dimension arrays. A single dimension has one row over n columns and a two-dimension, it is actually a matrix of (n*m). Since Array is also like an object so, whenever an object is created using the “new,” new memory space is allocated in the heap, and a reference is returned.
Syntax for Array:
var nameofarray= new Array[datatype](size)nameofarray is the array name that we want to give to that array; the data type is the type of array data type we want to get, and the size of the Array we want to have.
Examples of Array in Scala
Following are the examples are given below:
Example:
var a = new Array[Int];
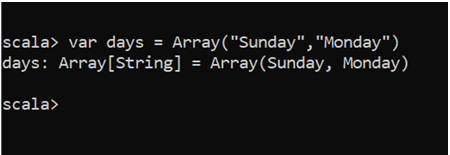
var days = Array("Sunday","Monday","Tuesday")Here we have created an array of 1 dimension named days with the days of the week.
1. Multidimensional Array
val nameofarray = Array.ofDim[data_type](number of rows, number of cols)
or
var nameofarray = Array(Array(elements), Array(elements))Above is the syntax for Multidimensional Array. Here Scala has a method Array.ofDim, that is used to create a multidimensional array. With this method, we can create up to five dimensions. The other we can do is the Array of Array method which can be used to create the multidimensional arrays.
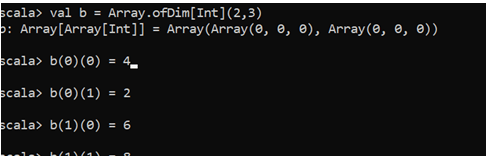
val b = Array.ofDim[Int](2,3)This will create a multi-dimension array, and we can add elements over the Array.
The same we can make it with the help of the Array of Array method.
Let us see how can we create that.
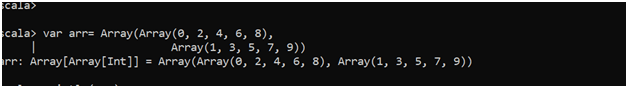
var arr = Array(Array(0,2,4,6,8),Array(1,3,5,7,9))This will create a multidimensional array, and we can perform operations over that.
2. Insertion of Elements in Array
We can insert elements in an Array, which can be used for Array functioning. We can append elements in the array. Also, while pointing the indices, we put the value over those indices in the array.
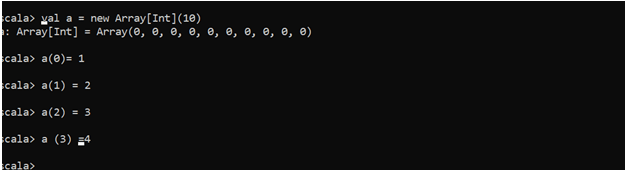
val a = new Array[Int](10)
a(0) = 1
a(1) = 2
a(2) =3
a(3) =4This will insert the element in the Array.
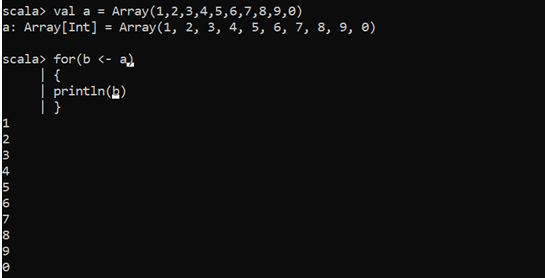
For iterating the elements, we can use for loop and print the elements in the array. With a simple for loop, we can iterate over the array and can traverse the elements in the array.
Val a = Array (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
for(m <- a)
{
println(m)
}This will print the elements in the array.
We can also concat or append two arrays, so that will merge the array value together. We can append the value in the array. +: This will append the value with the Array.
Let us see this with an example:
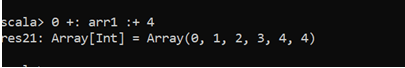
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
0 +: a :+ 6This will append the values in the arrays.
The result will be like:- 0,1,2,3,4,5,6
0 +: arr1 :+ 4Output:
For Multidimensional array, we can also do the same.
var arr = Array(Array("a", "b", "c"))Here we make a multidimensional array and append the other array value to it. ++ is used for appending the multidimensional array.
arr ++= Array(Array("d", "e"))3. Accessing Element in the Array
We can iterate the elements in Array and can check for all the values over the array. There are several methods with which we can iterate over the array. Let us look at some of them.
4. Iterating the Index
An array can be iterated over the elements with the help of the index they are stored in. The index number iteration gives the elements that are there over the array. So the index will be the length of the array that it is holding on, so just by iterating a loop from the index 0 as the index starts from 0 to going up to the array length, we can traverse the array element.
Let us look over an example:
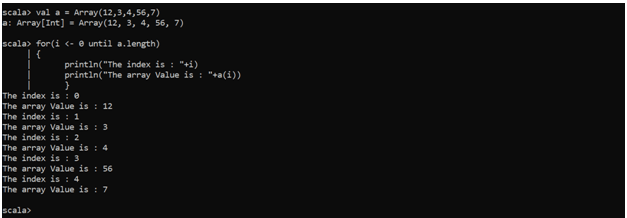
val a = Array(12,3,4,56,7)
for(i <- 0 until a.length)
{
println("The index is : "+i)
println("The array value is : "+a(i))
}Here we can see that with the index values, we traversed over the array and can fetch all the values over there. The other way out for traversing an array is iterating the elements itself .its, just like we are ignoring the index and directly traversing the elements themselves.
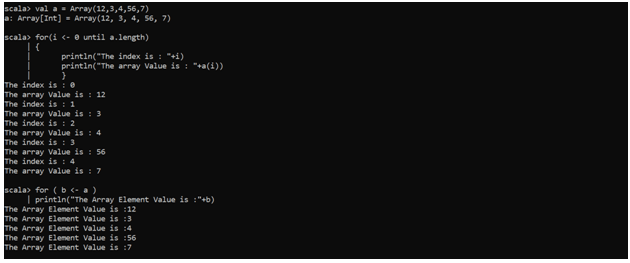
Let us have look over the same example we saw above and try to understand that:-
val a = Array(12,3,4,56,7)
for(i <- 0 until a.length)
{
println("The index is : "+i)
println("The array value is : "+a(i))
}
for( b <- a )
println("The Array Element Value is :"+b)Here we can see that we directly accessed all the elements that were in the Array, Ignoring the indexes alone.
5. Array Operations
Apart from adding values to traversing and iterating, there are many more operations over the array which we can apply to make the coding challenges easily solved.
Let us check on some operations over Array.
We can concat all the arrays into a simple array. A simple addition of an array over the other one is possible simply with ++ operation over the array.
Let us look over an example:
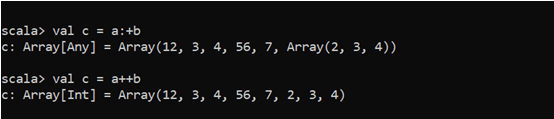
val c = a:+b
val c = a++bHere we can see that we can merge the array values over a single array and take it as one. The same as we can copy, and delete the elements.
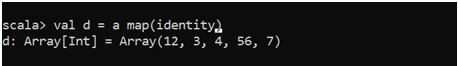
For copying the elements, we can simply map the identity of the array with a new one.
val d = a map(identity)We can do many things with the help of Array, making the work easier over the coding.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Array in Scala” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.