Updated June 23, 2023

Introduction to Android Architecture
Android is an operating system for Mobile devices (Smartphones and Tablets) and an open-source platform built on Linux OS. A conglomerate of Handset companies like Sony, Samsung, and Intel developed it. The Open Handset Alliance (OHA), led by Google, releases versions of the Android operating system (OS) for deployment on mobile devices.
Android Architecture provides an integrated approach for developers to develop mobile applications that can run on any device with Android OS installed in it, and it allows the applications component to be reused and obviate the need for redevelopment. Android source codes are offered under the category of open-source license on multiple websites. Google hosts most of it under Apache License 2.0 and kernel under General public license 2.0. It also provides a robust run-time environment for the execution of apps with a powerful interaction with peripheral devices and other apps.
What is Android Architecture?
Before studying Architecture, let us go through some of the features of the Android Operating system.
- Android OS can be customized as needed, and hence we can notice many avatars of this OS are deployed in different mobile devices with multiple unique features.
- It supports all mobile connectivity technologies, viz., Wi-Fi, CDMA, GSM, NFC, Bluetooth, etc., and basic functionalities like telephony, SMS, and data transfer. With this connectivity, data can be transferred back and forth between devices thru various apps.
- It provides Interfaces (APIs) that support location-dependent services such as GPS.
- SQLite database provides storage functionalities needed by Android. Being a lightweight database, it enables simpler storage and quicker data retrieval.
- It supports all versions of multimedia files (Audio/Video) and integrates a Microphone, Camera, Accelerometer, and speaker for effective management of recording and playback operations.
- Developers can use HTML5 and CSS3 to create an intuitive and impressive front-end screen.
- It allows multiple windows to be active simultaneously, performing different tasks.
- Graphics 2D/3D are supported.
- Supports NFC technology that connects two NFC-enabled devices by touching each other.
- Other features include multi-language support, User-adjustable widgets, and Google Cloud messaging.
Architecture:
It consists of several software modules to support the functioning of mobile devices. These software modules mainly contain the kernel and set of Libraries that facilitate mobile application development, and they form part of the runtime, application framework, and the actual application.
The application modules are grouped into five sections under four different layers.
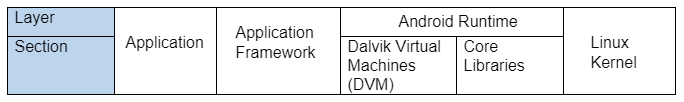
Android runtime layer has two sections, namely DVM and Libraries, and all the layers have only one section each.
1. Application Layer
The application layer is the topmost layer in the architecture, and it is the front end for the users. Native applications developed using Android architecture and third-party applications are installed in this layer. Applications from this layer get executed with the help of the run time layer using the classes and services provided by the framework layer. Example of Application is Email, Contacts, Calendar, Camera, Time, Music, Gallery, Phone, SMS, Alarm, Home, and Clock.
2. Applications Framework Layer
The applications Framework layer holds the classes needed to develop applications in the Android platform. It enables access to hardware, handles the user interface, and manages resources for an application. The services provided by this layer are made available to the application layer for development as a class. Some of the components in the framework layer are NFC service, Notification Manager, Activity Manager, Telephony service, Package Manager, and view system, and used in application development as needed.
3. Android Runtime Layer
Android Runtime layer is vital to this OS, containing sections like Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM) and Core libraries. This environment provides basic power to the applications with the help of libraries. Dalvik virtual machine exploits the basic inherent power of Java language in managing memory and multi-threading options to provide multiple instances to Android OS and ensure that it runs effectively. It leans on Kernel for threading and OS-level functionalities. This layer provides the services of Zygote to handle the forking of the new process, Android debug bridge, etc. Core Libraries provide features of Java language for the development of applications in Android OS.
4. Kernel Layer
The kernel layer is the bottom-most layer, and it interfaces basic hardware functionalities with the rest of the OS layers described above. It deals with drivers of display units, cameras, Bluetooth, memory units, and Audio/Video devices and ensures the smooth functioning of Android devices. In addition, it does centralized management of Memory, Power, and resource allocation/de-allocation for the device.
Framework of Android Architecture
The application framework provides Java classes for application development. Developers use these Java classes during coding. This component provides the following services.
- Activity Manager: Manages the application’s lifecycle and tracks all the activities.
- Content Provider: Facilitates sharing data with external applications.
- Resource Manager: Enables applications to use other resources like color settings, user interactions and strings.
- Notification Manager: Manages alerts and notifications to users on the status of application execution.
- View system: Provides various view options for creating user interaction.
Android Architecture Libraries
Some of the components in this library are:
1. Media framework to manage Audio and video recording and playing.
2. Surface Manager to monitor display functionalities and text manipulation during display.
3. SQLite for Database management.
4. SGL & OpenGL for managing 2D/3D graphics.
5. Freetype supports the front end.
6. Web-Kit supports browser functionalities.
7. Readily available Widgets such as buttons, layouts, radio buttons, and lists.
8. SSL provides internal security.
9. Interfaces and other services:
- Access to OS services for communication across processes.
- Access to App model templates for easy development
- Enables content access and interactions across applications.
Conclusion
In summary, Android Architecture provides a robust framework, interfaces, and libraries for developing and executing superior applications on mobile devices. It fully uses unique features of Android, such as Open source, Community support, Effective marketing, Low cost of development, a Rich environment for app development, and Solid inter-app and intra-app interfaces.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Android Architecture. Here we discuss the introduction, architecture, framework, and Android architecture libraries. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


