Updated March 24, 2023
Difference Between AMQP vs MQTT
The open-source protocols used for asynchronous queuing of messages deployed widely in the past decades are AMQP vs MQTT. Recently, it has adapted to its new update. AMQP has the intent to become a part of the International Standard Organization or International Electrochemical Commission and chosen by OASIS where MQTT has adopted Eclipse. AMQP executes its messaging queue using wire. Hence it is wire -ranged protocol that is transformed over the network as a torrent of byte values. MQTT is developed for limited devices with minimum bandwidth. It is a lightweight broadcasting system where the user can transfer and receive a message like a client.
Head to Head Comparison Between AMQP vs MQTT
Below are the top 14 differences between AMQP vs MQTT:
The Key Difference Between AMQP vs MQTT
Both AMQP and MQTT are employed in the Internet of Things. However, let us discuss the major differences:
- MQTT has client/broker architecture whereas AMQP has a client or broker and client or server architecture.
- MQTT follows the abstraction of publishing and subscribes whereas the AMQP follows response or request and Publish or subscribe methods.
- The header size of AMQP is 8bytes and MQTT is 2bytes. The message size of MQTT is small and defined whereas AMQP has negotiable and undefined.
- The method of MQTT is connected, publish, close, subscribe, and disconnect. AMQP follows Consume, deliver, publish, get, select, acknowledge, delete, recover, reject, open, and close.
- MQTT has partial support for cache and proxy whereas AMQP is offered full support.
- Both AMQP and MQTT follow TCP protocol, binary standard, and open source queuing system.
- The security offered AMQP is IPSec, SASL, TLS or SSL, and MQTT provides only TLS or SSL security standards. AMQP along with TCP uses SCTP for transmission purposes. OASIS supports both AMQP and MQTT.
- The quality of service delivered by MQTT is fire and forgets if QoS is 0. At least one if QoS is 1 and exactly one if QoS is 2. The quality of service offered by AMQP is to settle and unsettle format similar to MQTT.
AMPQ vs MQTT Comparison Table
Given below are the comparison between AMQP vs MQTT:
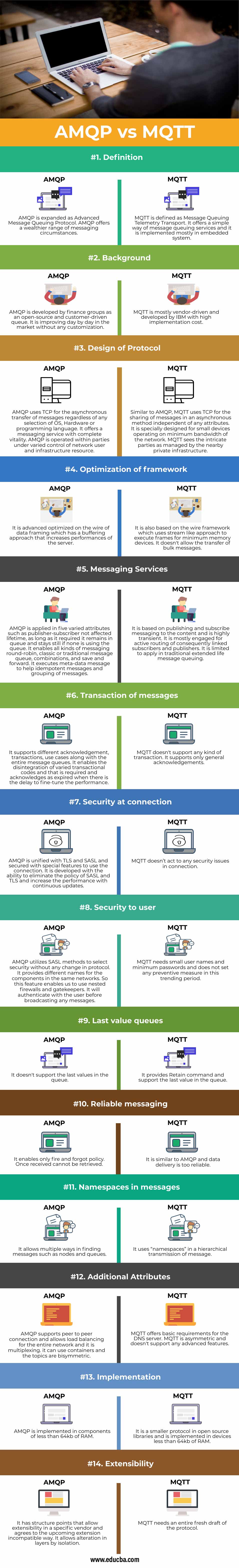
| Basis of Comparison | AMQP | MQTT |
| Definition | AMQP is expanded as Advanced Message Queuing Protocol. AMQP offers a wealthier range of messaging circumstances. | MQTT is defined as Message Queuing Telemetry Transport. It offers a simple way of message queuing services and it is implemented mostly in the embedded systems. |
| Background
|
AMQP is developed by finance groups as an open-source and customer-driven queue. It is improving day by day in the market without any customization. | MQTT is mostly vendor-driven and developed by IBM with high implementation costs. |
| Design of Protocol
|
AMQP uses TCP for the asynchronous transfer of messages regardless of any selection of OS, Hardware or programming language. It offers a messaging service with complete vitality. AMQP is operated within parties under varied control of network user and infrastructure resources. | Similar to AMQP, MQTT uses TCP for the sharing of messages in an asynchronous method independent of any attributes. It is specially designed for small devices operating on minimum bandwidth of the network. MQTT sees the intricate parties as managed by the nearby private infrastructure. |
| Optimization of framework
|
It is advanced optimized on the wire of data framing which has a buffering approach that increases performances of the server. | It is also based on the wire framework which uses stream like approach to execute frames for minimum memory devices. It doesn’t allow the transfer of bulk messages. |
| Messaging Services | AMQP is applied in five varied attributes such as publisher-subscriber not affected lifetime, as long as it required it remains in queue and stays still if none is using the queue. It enables all kinds of messaging round-robin, classic or traditional message queue, combinations, and save and forward. It executes meta-data message to help idempotent messages and grouping of messages. | It is based on publishing and subscribe messaging to the content and is highly transient. It is mostly engaged for active routing of consequently linked subscribers and publishers. It is limited to apply in traditional extended life message queuing. |
| Transaction of messages | It supports different acknowledgment, transactions, use cases along with the entire message queues. It enables the disintegration of varied transactional codes and that is required and acknowledges as expired when there is a delay to fine-tune the performance. | MQTT doesn’t support any kind of transaction. It supports only general acknowledgments. |
| Security at connection | AMQP is unified with TLS and SASL and secured with special features to use the connection. It is developed with the ability to eliminate the policy of SASL and TLS and increase the performance with continuous updates. | MQTT doesn’t act to any security issues in connection. |
| Security to user | AMQP utilizes SASL methods to select security without any change in protocol. It provides different names for the components in the same networks. So this feature enables us to use nested firewalls and gatekeepers. It will authenticate with the user before broadcasting any messages. | MQTT needs small user names and minimum passwords and does not set any preventive measure in this trending period. |
| Last value queues | It doesn’t support the last values in the queue. | It provides Retain command and support the last value in the queue. |
| Reliable messaging | It enables only fire and forgot policy. Once received cannot be retrieved. | It is similar to AMQP and data delivery is too reliable. |
| Namespaces in messages | It allows multiple ways in finding messages such as nodes and queues. | It uses “namespaces” in a hierarchical transmission of messages. |
| Additional Attributes | AMQP supports peer to peer connection and allows load balancing for the entire network and it is multiplexing. it can use containers and the topics are bisymmetric. | MQTT offers basic requirements for the DNS server. MQTT is asymmetric and doesn’t support any advanced features. |
| Implementation | AMQP is implemented in components of less than 64kb of RAM. | It is a smaller protocol in open source libraries and is implemented in devices less than 64kb of RAM |
| Extensibility | It has structure points that allow extensibility in a specific vendor and agrees to the upcoming extension incompatible way. It allows alteration in layers by isolation. | MQTT needs an entire fresh draft of the protocol. |
Conclusion
Though AMQP and MQTT have a lot of differences in their architecture and their protocols, they are being widely used in various applications like the internet of things. Being open-source protocols, both AMQP and MQTT can be employed in all applications based on the client requirement and the bandwidth that are available.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to AMQP vs MQTT. Here we discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–