Updated November 18, 2023
Advantages and Disadvantages of Robots- Introduction
Imagine machines that can move, see, and do things independently without constant human guidance – those are robots! They are like super-smart helpers that can follow instructions to complete tasks.
Robots may look like humans, animals, or just moving parts. They can be small, like tiny robots that help in surgeries, or big and strong, like those that help in factories to build cars. Moreover, robots are not just limited to factories and industries. For instance, they are making their mark in various fields. Some robots are exploring the ocean’s depths, reaching places humans can’t go. Others venture into outer space, assisting in space exploration.
We have ample proof that robots make life easy, but we also need to think about the challenging sides. So, let us see all the possible advantages and disadvantages of Robots.
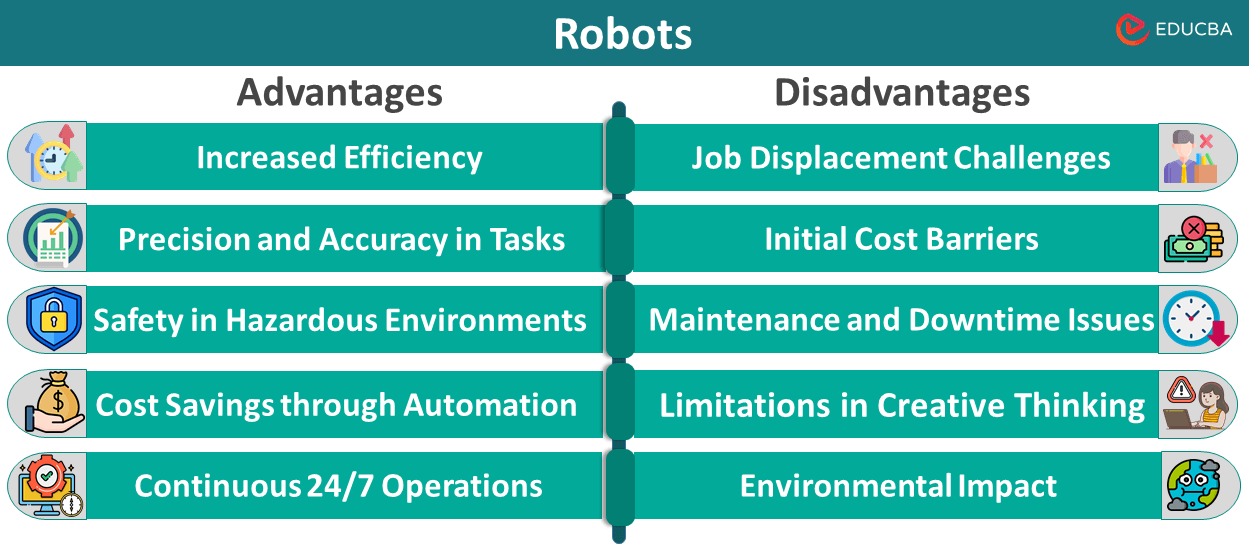
Advantages of Robots
Robots offer numerous advantages in a wide range of industries and applications. The following are some of the primary benefits of robots.
1. Increased Efficiency
Robots can perform tasks consistently without the need for breaks or rest, leading to increased efficiency in production processes.
2. Precision and Accuracy in Tasks
Robots can execute tasks with high precision, reducing errors and improving the quality of manufacturing and assembly processes.
3. Safety in Hazardous Environments
We can employ robots in hazardous environments to take on tasks that involve exposure to dangerous conditions, ensuring the safety of human workers.
4. Cost Savings through Automation
Over time, using robots can lead to cost savings through increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and minimized errors in production.
5. Continuous 24/7 Operations
Robots can operate continuously, enabling 24/7 production or service delivery without the constraints of human working hours.
6. Handling Repetitive Tasks Efficiently
Robots consistently handle repetitive tasks, freeing human workers to concentrate on more complex and creative aspects of their work.
7. Quick Data Collection and Analysis
Robots equipped with sensors and cameras can collect vast amounts of data in real-time. This data can be crucial for monitoring and improving processes, identifying issues, and making informed decisions.
8. Flexibility in Robotic Applications
Some robots are designed to be versatile and easily reprogrammable, allowing them to adapt to changing tasks and production requirements.
9. Consistency in Quality Output
Robots can consistently produce high-quality output without the variations that may occur in human-controlled processes.
10. Robots in Space Exploration
Robots play a crucial role in space exploration, conducting tasks in environments where human presence is challenging or impossible.
Disadvantages of Robots
Despite their many advantages, robots also present some potential disadvantages. Here are some of the key disadvantages of robots:
1. Job Displacement Challenges
Increased automation can lead to job displacement as robots take over tasks traditionally performed by humans.
2. Initial Cost Barriers
The upfront cost of acquiring and implementing robotic systems can be high, posing a barrier to entry for smaller businesses.
3. Maintenance and Downtime Issues
Robots require regular maintenance to ensure they work well. Sometimes, technical issues can arise, which requires skilled technicians to fix them. This can temporarily stop the production.
4. Limitations in Creative Thinking
Robots lack humans’ creative and intuitive thinking abilities, making them less suitable for tasks that require innovation and problem-solving.
5. Technology Dependence Risks
Heavy reliance on robotic systems can be risky. For instance, a failure in the technology can lead to disruptions in operations.
6. Environmental Impact
The production and disposal of robots can have environmental consequences. The use of non-renewable resources and disposal of electronic components can contribute to electronic waste, potentially harming the environment.
7. Versatility and Adaptability Limits
While robots excel at specific tasks, they may struggle with tasks that require human-like skill, adaptability, and complex decision-making.
8. Impact on Social Interaction
The increasing use of robots in certain roles, such as customer service, may reduce human-to-human interactions, potentially affecting social skills and relationships.
9. Increased Security Risks
Robots becoming more connected through the Internet of Things (IoT) may be vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Hacking into robotic systems can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and manipulation of their functions, posing security risks to industries and individuals.
10. Global Economic Differences
The adoption of robots may lead to economic differences between technologically advanced and less advanced regions, creating a digital divide.
These were all the advantages and disadvantages of robots.
Final Thoughts
In the future, the number of robots will likely increase, bringing both benefits and challenges. While robots can enhance efficiency, safety, and precision, there are concerns about job displacement, initial costs, and ethical considerations. Striking a balance between leveraging the advantages of robotics and addressing the associated challenges will be crucial. Therefore educating yourself on the advantages and disadvantages of robots is equally important.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on the Advantages and Disadvantages of Robots benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,