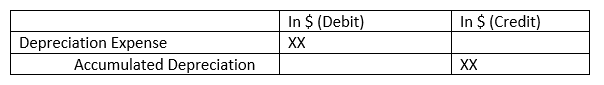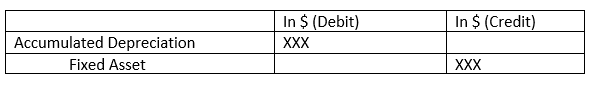Updated August 30, 2023
Key Highlights
- Accumulated depreciation is a way for businesses to track the decrease in the value of their assets over time.
- It applies to tangible assets like machinery and equipment and intangible assets like goodwill and patents.
- To find it, subtract the salvage value from the asset’s original cost, divide the result by the asset’s valuable life, and multiply by the number of years.
- It helps the company’s administration make informed decisions about when to replace and repair the assets.
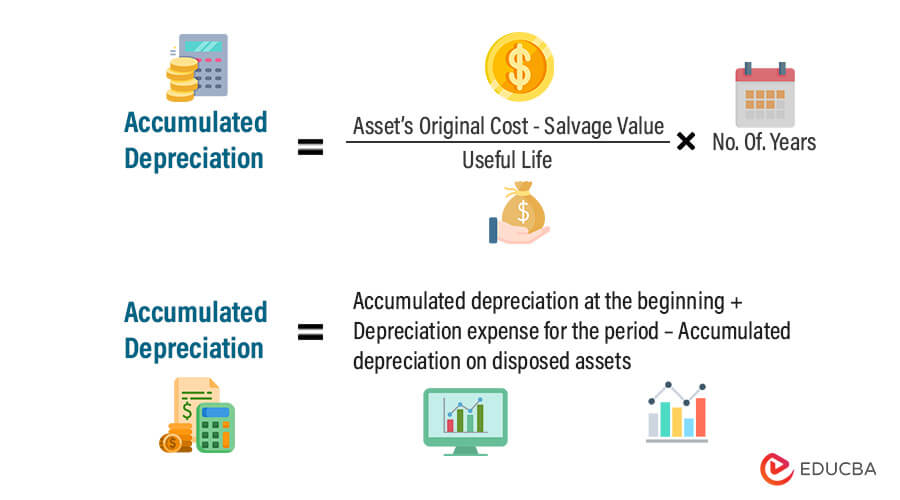
Formula
The two formulas to calculate accumulated depreciation are,
Where,
- The asset’s original cost is the initial cost at which one purchases the goods.
- The salvage cost of an asset is its book value after deducting all depreciation.
- Useful life is the product’s rough lifespan in years.
- The number of Years refers to the period the company has used the product.
Where,
- Depreciation at the beginning of the year refers to the depreciation of the asset until the beginning of the year.
- Depreciation for the period means the amount of asset depreciation in the particular year.
- Depreciation on disposed of assets refers to the depreciation associated with the company’s assets, either disposed of or sold.
How to Calculate the Accumulated Depreciation?
Step 1: Identify the Cost of the Fixed Asset on which Depreciation Needs to be Calculated
Step 2: Estimate the useful life of the fixed assets and calculate the depreciation amount to be reduced (salvage value) from the asset value each year.
Step 3: Use the formula to calculate the accumulated depreciation for any particular year.
Examples of Accumulated Depreciation Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Accumulated Depreciation Formula in a better manner.
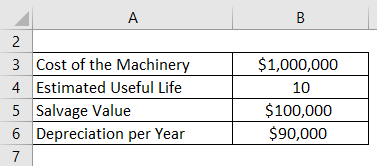
Example #1
Company ABC bought machinery worth $10,00,000, which is a fixed asset for the business. It has a useful life of 10 years and a salvage value of $1,00,000 at the end of its useful life. Depreciation for the company is calculated using the straight-line method, which is $90,000 per year for the next 10 years until the value of the machinery becomes $1,00,000. Each year the accumulated depreciation account will increase by $90,000 per year. Therefore, for example, at the end of 5 years, annual depreciation is $90,000 but the cumulative depreciation is 4,50,0000. This cumulative figure is the accumulated depreciation. It remains in the company’s accounts until the asset is sold.
Given,
Solution:
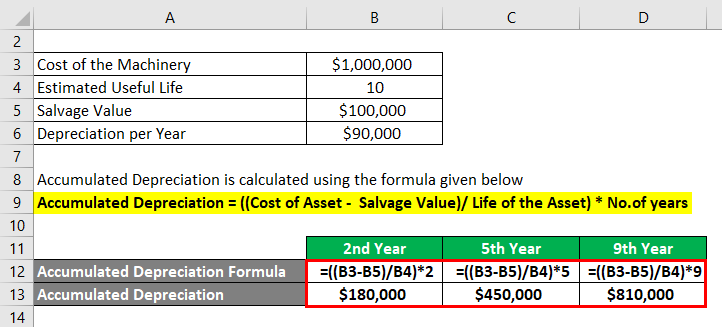
Accumulated Depreciation is calculated using the formula given below
Accumulated Depreciation = ((Cost of Asset – Salvage Value)/ Life of the Asset) x No.of years
For 2nd Year
- Accumulated Depreciation = (($1,000,000 – $1,00,000) / 10 ) x 2
- Accumulated Depreciation = $1,80,000
For 5th Year
- Accumulated Depreciation = (($1,000,000 – $1,00,000) / 10 ) x 5
- Accumulated Depreciation = $450,000
For 9th Year
- Accumulated Depreciation = (($1,000,000 – $1,00,000) / 10 ) x 9
- Accumulated Depreciation = $810,000
Note here, that we are considering only 1 machinery for the given company. In reality, there are additions to this value in terms of any improvements, upgradations, or just buying a new piece. Each would have a different useful life and therefore the depreciation for each need to be calculated separately with the method followed since its setup. Below is an extract for a real company:
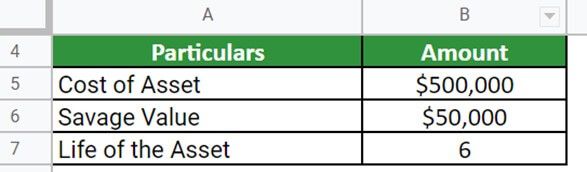
Example #2
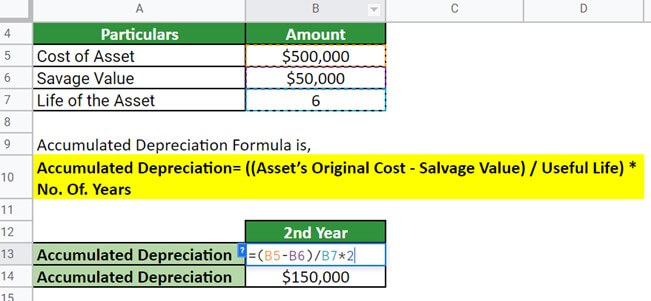
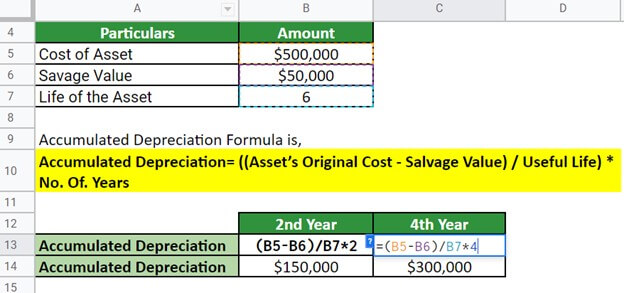
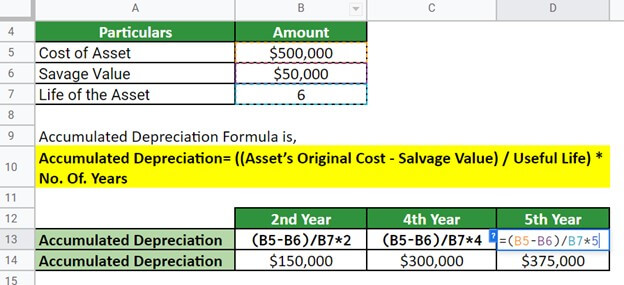
Lily purchased a new car worth $500,000. The company has a useful life of 6 years and a salvage value of $50,000 at the end of its useful life. Calculate the accumulated depreciation after 2,4, and 5 years of use.
Given,
Solution:
Let us calculate the depreciation for the year 2,
Similarly, for the year 4,
Next, for the year 5,
Thus, the accumulated depreciation after two, four, and five years of use would be $150,000, $300,000, and $375,000, respectively.
Example #3
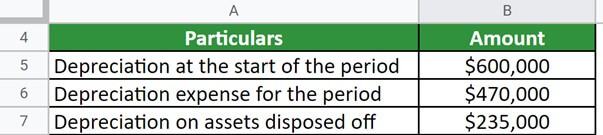
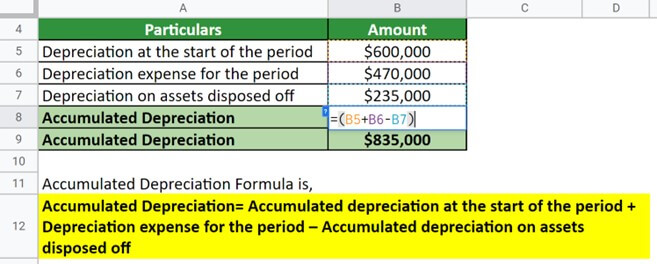
An US corporation ABZ purchases heavy industrial machinery for $2,500,000. At the beginning of the year, the depreciation was $600,000. During the period, the machinery’s value depreciated by $470,000. Value of the disposed assets is $235,000. Calculate the Accumulated depreciation.
Given,
Solution:
Implementing the formula,
Thus, the accumulated depreciation is $835,000 as a result of adding the aggregates of depreciation till the start of the period and during the period and then subtracting the depreciation of assets disposed of from the sum.
Journal Entry of Accumulated Depreciation
Whenever a company records depreciation as an expense, they must report the same amount as credit to accumulated depreciation.
The annual entry of the accumulated depreciation in the journal books will be as follows:
After the useful life of the machine, the journal entry will be,
Accumulated Depreciation on a Balance Sheet
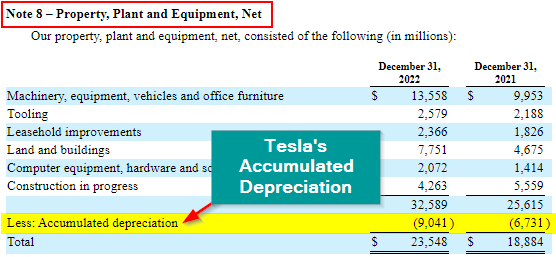
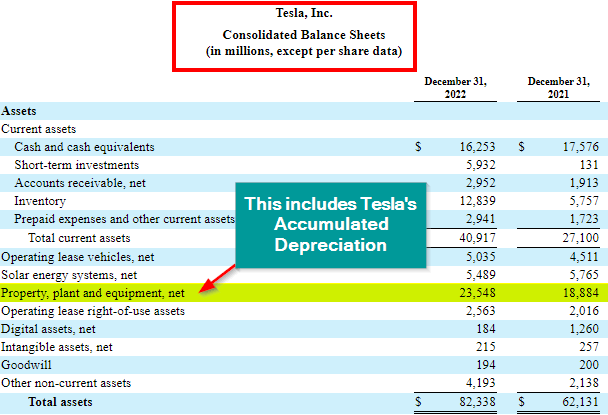
Businesses report their accumulated depreciation on the asset section of the balance sheet. Usually, it is reported under the term “Property, Plant, and equipment, net.”
For example, as we can see below in the Tesla 2022 annual report, the accumulated depreciation is added as a negative value under property, plant, equipment, net.
Here is the term reported in the balance sheet.
Methods
Straight-line Depreciation Method
- Multiply the valuable life of a fixed asset by the depreciable base to determine straight-line depreciation.
- The difference between an asset’s total expenditures and its anticipated salvage value at the end of its useful life is known as the depreciable base.
- The years that the asset will provide financial benefits indicate the useful life.
Decreasing Balance Method
- A decreasing balance approach accelerates the reporting of depreciation expenditure for assets in their early stages of useful life.
- It means they will incur less depreciation expense later in their useful lives.
Double-Declining Balance Depreciation Method
- The double declining balance (DDB) depreciation method is an accounting approach that involves depreciating some assets at twice the rate specified by straight-line depreciation.
- As a result, depreciation is most significant in the first year of ownership and gradually decreases over time.
Depreciation vs. Accumulated Depreciation
| Accumulated Depreciation | Depreciation |
| It is the total depreciation that has occurred up to a specific date since its purchase. | Depreciation is the decrease in value of an asset for a specific period. For example, 1 year. |
| Reported on the Balance sheet. | Recorded on the income statement. |
| Formula: ((Asset’s Original Cost – Salvage Value)/ Useful Life) x No. Of Years |
Formula: (Asset Cost – Residual Value) / Useful Life of Asset |
Importance
- To give an accurate record of an asset’s historical cost and depreciation over time.
- To provide a means of allocating the cost of a purchase over its useful life systematically and rationally.
- It reflects the wear and tear on an asset over time, which is a critical component of the asset’s value.
- It provides a way to match the cost of an asset to the income it generates, which is a crucial accounting principle.
- It helps companies make informed decisions about when to replace or repair assets.
- The company can use it in accounting for tax purposes, reducing their taxable income.
- It also aids in budgeting for future expenses for the replacement of assets.
Accumulated Depreciation Formula Calculator
You can use the following Accumulated Depreciation Formula Calculator
| Cost of Asset | |
| Salvage Value | |
| Life of the Asset | |
| No.of years | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | |
| Accumulated Depreciation = |
|
||||||||||
|
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Accumulated Depreciation Formula. Here we discuss how to calculate Accumulated Depreciation Formula along with practical examples. We also provide an Accumulated Depreciation calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –