Updated May 24, 2023
What is Abstract Class in Java?
The following article provides an outline for Abstract Class in Java. Abstract classes are like any other normal classes in Java. The significant difference between abstract and regular classes is creating the abstract class, we must use the ‘ABSTRACT’ keyword. It is a separation of class implementation. They used to define the very common features of its subclasses. Such a type of class is referred to as Abstract class. Most important, we cannot create an object of an abstract class.
Abstract classes can contain abstract as well as non-abstract methods. However, they cannot contain a body of the abstract method that the subclass can only provide. If the subclass does not implement the abstract method, then we must explicitly make it ABSTRACT. In other words, if a class contains an abstract method, it must define itself as ABSTRACT. We can group several Java classes using abstract classes, optimize the code, make the code more readable, and reduce redundancy. It also provides a template for future classes.
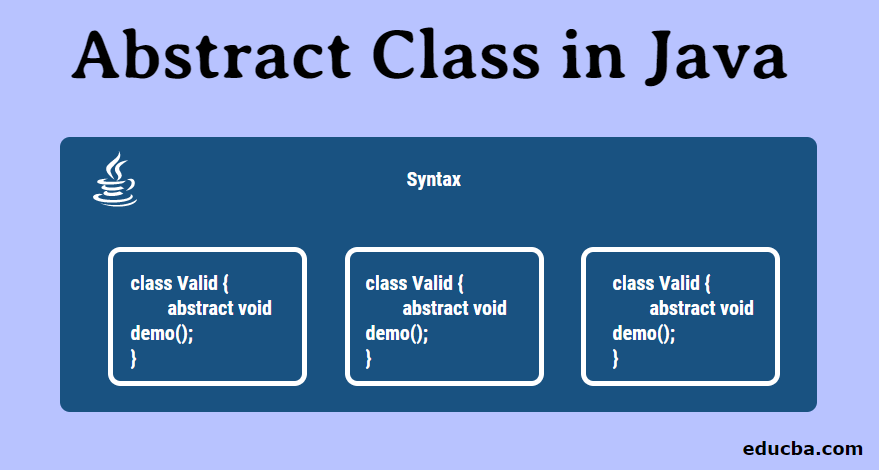
Syntax of Abstract Class in Java
The syntax of the abstract class is as follows:
How does Abstract Class Work in Java?
- An abstract class has an abstract method and a non-abstract method, i.e., an abstract method without a body, and they can have methods with implementation.
- An abstract class is used to provide the most common feature that is specific to different classes. Subclasses can implement those abstract methods differently according to their needs or requirement.
- We cannot create an object of an abstract class using the ‘new’ operator, but we can still define its constructor, which can only be invoked in the constructor of its subclass. A subclass constructor can access a superclass constructor to initialize its variable, which might be used in the subclass for further requirements.
Examples of Abstract Class in Java
The following examples are given below:
Human.java
package com.cont.article;
public abstract class Human
{
public abstract void whatTheylike();
public void doTheysleep()
{
System.out.println("Yes every human require sleep.");
}
}Human1.java
package com.cont.article;
public class Human1 extends Human
{
@Override
public void whatTheylike()
{
System.out.println("we like to have icecream.");
}
}Human2.java
package com.cont.article;
public class Human2 extends Human
{
@Override
public void whatTheylike()
{
System.out.println("we like to have coffee.");
}
}TestHuman.java
package com.cont.article;
public class TestHuman
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Human human1 = new Human1();
human1.whatTheylike();
Human human2 = new Human2();
human2.whatTheylike();
human1.doTheysleep();
human2.doTheysleep();
}
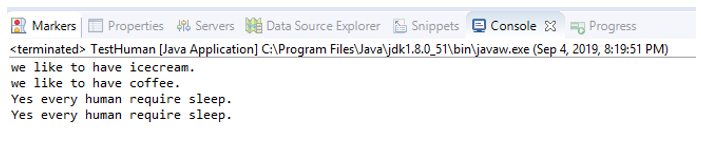
}Output:
In the above example, HUMAN is an abstract class that defines a human’s common needs, likes, and dislikes. There are different types of humans with different likes and dislikes. So every human can provide a specific implementation of what they like. That will be specific to them only.
The main advantage of abstract class is that we have a specific implementation of methods according to a requirement, reducing redundancy, increasing the readability of code, hiding the implementation of methods, and providing partial abstraction.
We can have one more example to understand when to use Abstract classes.
- We should use abstract classes to share common functionality with different classes with specific implementations.
- In abstract classes, fields should not be static and final; we can also have concrete, private, public, and protected methods.
Let’s say we have one Animal class. We have various animals on Earth, and they all differ from each other in some or major sense. Nevertheless, it will contain all the common features of all.
Now, this Animal class cannot have specific methods for every Animal. So by the concept of Abstract class, we can implement this functionality without redundant code.
All animals have different types of sounds, habits, etc. For example, dogs, cats, elephants, and snacks have different sounds. So for this, we can have a generic method in the parent class through which all other subclass or child class can provide their specific implementation.
In the parent class, i.e., Animal, we have one generic abstract method called their Sound (). So every child class needs to override this method and provide its specific implementation.
Abstract Class and Interface
Below are the distinctions between Abstract Class and Interface:
- Abstract class and interface are both used to achieve abstraction in Java. However, an abstract class provides partial abstraction, whereas an interface provides 100% or complete abstraction.
- By default, variables in an interface are final. But abstract class contains a non-final variable as well. Similarly, an abstract class can also have a static, non–static variable. But the interface will only include a final and static variable.
- Member variables of an abstract class can be private, public, and protected, but they are, by default, public in the interface.
- An abstract class can extend another Java class and implement multiple interfaces, but one interface can only extend another interface. Likewise, an abstract class can provide an implementation of an interface, but an interface cannot do so.
- We use implements and extend keywords to implement and extend interfaces and classes.
- We can modify or access an abstract class’s non-static and non-final variables through the method.
Conclusion
An abstract class is used to provide partial abstraction. An abstract class cannot be instantiated using the NEW keyword. An Abstract method has no body and always ends with a semicolon (;). Abstract class contains abstract and non-abstract methods. The subclass of an abstract superclass needs to implement all abstract methods; if it does not provide, then it has to declare itself as an abstract class. A subclass can be abstract even if the superclass is concrete. A non-abstract class cannot contain abstract methods. Also, the abstract method is non-static. Hence, abstract classes also have abstract and concrete methods, so they cannot provide 100% abstraction. It is a process of hiding the complex logic from the end-user and showing them only the services.
On the other hand, a subclass can be abstract even if its superclass is concrete and can also be used as a data type. An abstract class may have static fields and static methods. You can use these static members with a class reference.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Abstract Class in Java. Here we discuss how it functions, examples of abstract class in Java with the distinction between abstract class and interface. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –