What is Zero-Party Data?
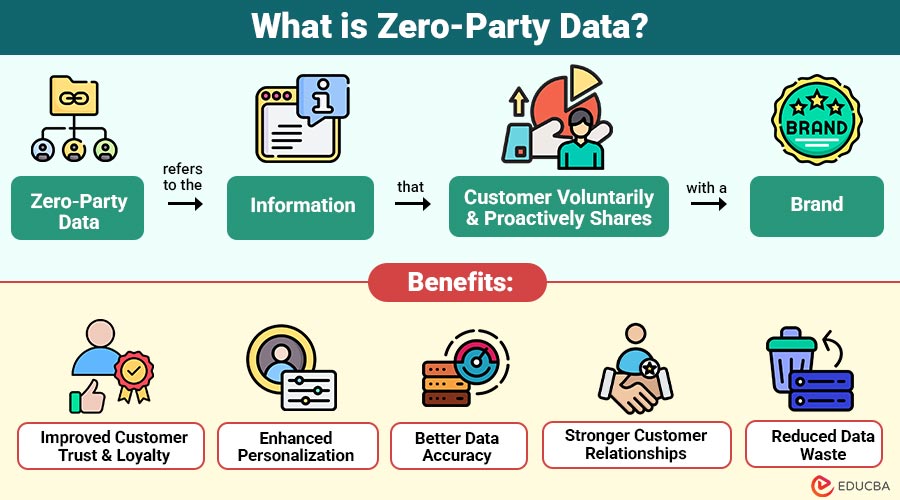
Zero-party data refers to the information that customer voluntarily and proactively shares with a brand. This data is not inferred, tracked, or purchased; instead, it is directly provided by the customer in exchange for better, more personalized experiences.
For example, a customer might complete a survey on their product preferences, indicate their favorite color during sign-up, or specify communication preferences via email. This data is explicit and consensual, making it highly reliable and privacy-friendly.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Why Zero-Party Data Matters?
- How to Collect Zero-Party Data?
- Benefits
- Challenges
- How Businesses Use Zero-Party Data?
- Real-World Examples
- Best Practices
Key Takeaways:
- Zero-party data is voluntarily shared by customers, enabling accurate personalization while respecting privacy and compliance regulations.
- Collecting zero-party data builds trust, improves customer engagement, and strengthens long-term loyalty and brand relationships.
- Businesses use quizzes, surveys, preference centers, and loyalty programs to gather explicit customer insights effectively.
- Proper implementation requires transparency, value exchange, secure storage, seamless integration, optional sharing, and continuous optimization for success.
Why Zero-Party Data Matters?
With the rise of privacy regulations like General Data Protection Regulation and California Consumer Privacy Act, traditional data collection methods like third-party cookies are becoming obsolete. Consumers now demand transparency and choice in how their data is used. Zero-party data addresses this new reality by building mutual trust. It gives customers a voice in personalization while ensuring brands operate ethically within privacy frameworks.
Key reasons why it matters:
Collecting zero-party data should always be transparent, ethical, and engaging. Here are effective methods businesses can use:
1. Preference Centers
Centralized platforms allowing users to select communication channels, product preferences, and content types to create a fully personalized experience.
2. Interactive Quizzes
Engaging quizzes designed to collect user responses, preferences, and opinions, helping businesses recommend products, services, or personalized content effectively.
3. Surveys and Polls
Structured tools that gather voluntary customer feedback, opinions, or suggestions to understand preferences and improve products or services accordingly.
4. Loyalty Programs
Reward-based systems motivating users to provide personal insights, complete profiles, or share preferences in exchange for points or benefits.
5. Contests and Giveaways
Promotional campaigns that encourage users to share opinions or information, increasing engagement while offering prizes or incentives.
6. Onboarding Forms
Initial signup forms that collect users’ interests, preferences, and personal details to deliver a tailored, personalized experience from the start.
Benefits of Zero-Party Data
Here are some of the main benefits:
1. Improved Customer Trust and Loyalty
By asking customers directly for their preferences, brands demonstrate respect for privacy. This transparency builds credibility and long-term loyalty.
2. Enhanced Personalization
Since zero-party data reflects real customer intent, it enables hyper-personalized product recommendations, offers, and messaging—leading to better engagement.
3. Better Data Accuracy
It is information that customers give directly, so it’s accurate and doesn’t rely on guesses or assumptions.
4. Stronger Customer Relationships
Engaging users through surveys, quizzes, or preference centers opens two-way communication, making customers feel valued and heard.
5. Reduced Data Waste
Companies collect only the information they need, minimizing irrelevant or outdated data and optimizing storage costs.
Challenges of Zero-Party Data
While zero-party data offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges that businesses must manage carefully:
1. Customer Engagement Barrier
Users may hesitate to provide personal information unless there is a clear incentive, reducing participation in data collection initiatives.
2. Data Volume Limitations
Because zero-party data relies on voluntary user input, the overall data quantity can be smaller than other sources.
3. Integration Complexity
Integrating with pre-existing databases, systems, or marketing platforms can be difficult technically and needs prior preparation.
4. Need for Value Exchange
Consumers anticipate receiving concrete rewards for disclosing their information, such as exclusive access, tailored experiences, or discounts.
How Businesses Use Zero-Party Data?
Here are some practical ways companies leverage zero-party data:
1. Personalized Marketing Campaigns
Businesses leverage customers’ explicitly shared preferences to create highly relevant emails, product recommendations, and promotional offers that drive engagement and sales.
2. Product Development
Insights collected from user feedback, quizzes, and surveys help companies identify innovative product ideas, enhancements, and features aligned with customer desires.
3. Customer Experience Enhancement
Companies optimize websites, app layouts, content, and promotional offers based on users’ stated preferences to improve overall satisfaction and usability.
4. Predictive Engagement
It works together with AI tools to help brands better understand what customers want and when they want it, leading to more accurate and personalized interactions.
5. Segmentation and Targeting
Marketers use explicitly shared customer information to create precise audience segments, such as eco-conscious versus trend-focused users, for targeted campaigns.
Real-World Examples
Here are some notable examples of how companies use zero-party data effectively:
1. Sephora’s Beauty Quiz
Sephora collects users’ skin type, tone, and preferences through quizzes, recommending products and improving customer satisfaction using zero-party data.
2. Spotify Wrapped
Spotify’s “Wrapped” campaign uses each listener’s favorite songs and listening habits to create fun, personalized yearly summaries that users can view and share, helping keep them more engaged and connected with the app.
3. Netflix Recommendations
Netflix gathers user ratings and preferred genres voluntarily, using this zero-party data to provide tailored recommendations and improve content discovery.
4. Nike Membership App
Nike asks users to share fitness goals and interests within the app to deliver customized workouts, products, and personalized experiences.
Best Practices
Here are the best practices for data effectively:
1. Be Transparent
Users should be completely informed about the collection, storage, and use of their data in order to build trust and encourage voluntary participation.
2. Offer Value
Provide meaningful incentives, personalized experiences, or rewards so users feel motivated to share preferences willingly and confidently.
3. Ensure Data Security
Protect user data using encryption, secure storage, and compliance with privacy regulations to prevent unauthorized access or breaches.
4. Integrate Seamlessly
Use with CRM, email, and analytics tools to manage customer information easily, automate tasks, and give personalized experiences.
5. Keep it Optional
Always allow users to modify, update, or delete their preferences, ensuring they maintain full control over their personal data.
6. Test and Optimize
Regularly analyze engagement metrics, refine collection methods, and adjust strategies to maximize data accuracy and customer satisfaction.
Final Thoughts
Zero-party data represents a transformative shift in the digital marketing landscape—from intrusive tracking to consensual collaboration. It empowers customers to share their preferences willingly while allowing brands to deliver personalized experiences with integrity and compliance. By adopting strategies, businesses not only respect privacy laws but also foster trust, engagement, and long-term loyalty—creating a win-win relationship between brands and consumers in the data-driven future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is zero-party data better than first-party data?
Answer: Yes. While first-party data is collected passively, zero-party data is shared intentionally by the user, making it more accurate and privacy-compliant.
Q2. How can small businesses collect zero-party data?
Answer: They can use surveys, quizzes, email sign-ups, and preference forms to gather customer input directly.
Q3. Is zero-party data GDPR-compliant?
Answer: Absolutely. Since it relies on explicit consent, it aligns perfectly with GDPR and similar data protection regulations.
Q4. Can zero-party data replace third-party cookies?
Answer: Yes, it offers a privacy-first alternative by enabling personalization without tracking users across websites.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Zero-Party Data” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.