Updated April 20, 2023
Definition of XSLT substring
XSLT is defined as a manipulation language for XML documents. In such a case there is a function for searching a string for re-arranging the documents. Substring is primarily used to return a section of a string or truncating a string with the help of the length provided.XSLT is incorporated with XPath while manipulating strings of text when XSLT access. The Substring function takes a string as an argument with the numbers one or two and an optional length. The first character starts at the position ‘1’ not at ‘0’.
So, let’s get started with the working steps on this article.
Syntax:
String substring (string, num1,num2)
//substring (“6789”,2,3)
This returns 789
It returns a string value if the input is a string. To check for the position, it returns an integer. Each character is assigned a numeric position. The first character is assigned one and so on. If the third argument is not assigned, it returns the result of the substring starting at the position first.
The syntax for substring after
substring-after (string, string)
How does substring function work in XSLT?
XSLT doesn’t have any new function to search Strings in a reverse manner. We have substring function which creates two fields substring-before-last and substring-after-last.In XSLT it is defined as follows:
<xsl:value-of select="substring (string name ,0, MAX_LENGTH )"/>...
</xsl:when>
The following function returns ‘568 ‘for:
substring (“45689”, 2,3) // It implies that it selects sequential three digital starting at position 2.
Following are the types of substring provided in XSL.
fn: substring -after
This function returns the string value a part of an input string value after the first occurrence of the delimiter. A string that is declared should contain at least one single character. An empty string sequence is treated as an empty String. Let’s see an XPath example.
Substring(string,string)
|
Next example
| substring-after(‘search’, ‘h’) // This returns a zero value as it is an end of the character.
substring-after(“1985/02/06″,”19”) //call returns “85/02/06”: |
fn:substring-before
This returns a string value before a sub-string.
| Substring-before(‘xxx’,’yyy’)
Example: Substring-before(‘char – acter’ ,’-‘) // this returns a value char that is before ‘hypen’ substring-after(“1985/02/06″,”/”) //call returns “1985”: |
Therefore we are now familiar with their syntax and their sub-parts.Now let us move on to the implementation part.
Examples
Here we will be doing demo in different use cases of XML document to display the substring in the Output.
Example #1: A simple Document to demonstrate a Sub-String
Creating an XML file cosmetics and save it.
cosmetics.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="cos.xsl"?>
<Cosmetics >
<Categories cc = "1" >
<skin>Toners </skin>
<skin>Mists</skin>
<skin>Night Cream </skin>
</Categories>
<Categories cc = "2" >
<Personalcare>Rollers and Curlers </Personalcare>
<Personalcare>Hairfall and thining </Personalcare>
<Personalcare>Lotions and creams </Personalcare>
</Categories>
<Categories cc = "3" >
<Makeup>Face Primer </Makeup>
<Makeup>Highlighters </Makeup>
<Makeup>Contour </Makeup>
</Categories>
</Cosmetics>
In the same directory create cos.xsl file with the following content.
cos. xsl
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl = "http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform" version = "1.0" >
<xsl:output method = "text" />
<xsl:key name = "ooo" match = "Makeup"
use = "substring(.,3)" />
<xsl:template match = "/" >
<xsl:apply-templates select = "key('ooo','2')" />
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match = "Personalcare" >
<xsl:text >
</xsl:text>
<xsl:value-of select = "." />
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation
This demonstration shows how to apply XSLT to XML Document.
Output:
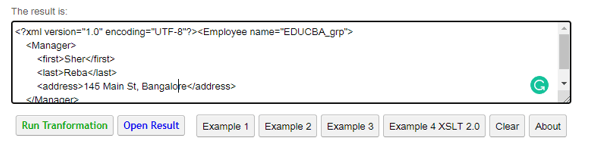
Example #2
.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Employee name="EDUCBA_grp">
<Manager>
<firstname>Sher Raj</firstname>
<lastname>Joy Reba</lastname>
<address>145 Main St, Bangalore</address>
</Manager>
</Employee>
.xsl
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="firstname">
<first>
<xsl:value-of select="substring-before(.,' ')" />
</first>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="lastname">
<last>
<xsl:value-of select="substring-after(.,' ')" />
</last>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="@* | node()">
<xsl:copy>
<xsl:apply-templates select="@* | node()" />
</xsl:copy>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation:
The above code selects appropriate nodes from the select and match type. Here the first and last name strings are retrieved before and after the sub-strings. The result is shown as:
Output:
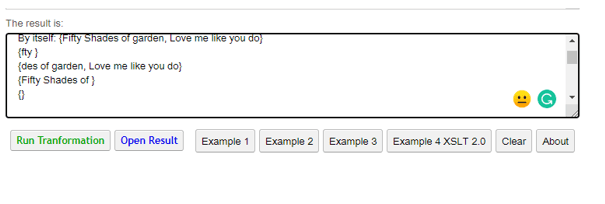
Example #3
.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<Song>
<Title>Fifty Shades of garden, Love me like you do</Title>
<Title>
Marshmello- Here with me Feet
</Title>
</Song>
.xslt
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="Title">
By itself: {<xsl:value-of select="."/>}
{<xsl:value-of select="substring(.,3,4)"/>}
{<xsl:value-of select="substring(.,10)"/>}
{<xsl:value-of select="substring-before(.,'garden')"/>}
{<xsl:value-of select="substring-after(.,'here')"/>}
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation
The above code uses a substring before and after types to display an XML document.
Output:
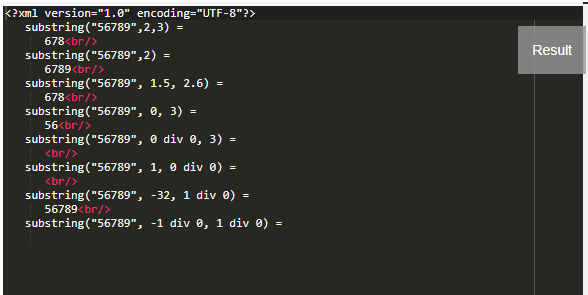
Example #4: Substring with numeric values truncation
sub.xsl
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="/">
Substring("56789",2,3) =
<xsl:value-of select='substring("56789",2,3)'/><br/>
substring("56789",2) =
<xsl:value-of select='substring("56789",2)'/><br/>
substring("56789", 1.5, 2.6) =
<xsl:value-of select='substring("56789", 1.5, 2.6)'/><br/>
substring("56789", 0, 3) =
<xsl:value-of select='substring("56789", 0, 3)'/><br/>
substring("56789", 0 div 0, 3) =
<xsl:value-of select='substring("56789", 0 div 0, 3)'/><br/>
substring("56789", 1, 0 div 0) =
<xsl:value-of select='substring("56789", 1, 0 div 0)'/><br/>
substring("56789", -32, 1 div 0) =
<xsl:value-of select='substring("56789", -42, 1 div 0)'/><br/>
substring("56789", -1 div 0, 1 div 0) =
<xsl:value-of select='substring("56789", -1 div 0, 1 div 0)'/>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation
The Processor Output is Shown as below
Output:
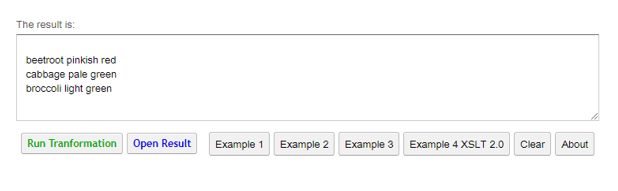
Example #5: Demonstration on Substring with values
veg.xml
<vegetables>
<colorveg>beetroot pinkish red</colorveg>
<colorveg>cabbage pale green</colorveg>
<colorveg>broccoli light green</colorveg>
</vegetables>
.xsl
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
version="1.0">
<xsl:output omit-xml-declaration="yes" />
<xsl:variable name="fieldWidth">12</xsl:variable>
<xsl:template match="colorveg">
<xsl:variable name="valueLength" select="string-length(.)" />
<xsl:variable name="padding" select="$fieldWidth - $valueLength" />
<xsl:value-of select="substring(' ',2,$padding)" />
<xsl:value-of select="." />
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation
The above code is a substring function assigned with variables. Here we have created two variables with substrings and the strings are extracted in the output as shown below from the respective XML document.
Output:
Example #6: Xslt-before demo
st.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<spensstore>
<store id="1">
<pname>cosmetics</pname>
<brand>MAC</brand>
<price>30.50</price>
</store>
<store id="2">
<pname>shampoo</pname>
<brand>Dove</brand>
<price>50.50</price>
</store>
<store id="3">
<pname>eatables</pname>
<brand>babyjunk</brand>
<price>41.50</price>
</store>
</spensstore>
ps.xsl
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="/">
<xsl:for-each select="//store">
<xsl:value-of select="substring-before(pname, 'bles')" />
</xsl:for-each>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation
The above XSL file takes an output method as HTML and followed by the select option in which the substring part of the string is truncated by ‘before’ keyword. Here the element pname is selected for the selection by which the value ‘bles’ is divided by the before-option. Therefore we will get the output as:
Output:
Conclusion
So, coming to the end of this article we have learnt more on substring functions. The very first thing we need to use is the XSLT basic coding. This helps in Performance analysis for the developers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XSLT substring. Here we discuss the definition, syntax, parameters, How does substring function work in XSLT? and examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –