Updated April 18, 2023
Introduction to XML Tree
The tree structure is also referred to as an XML tree model or hierarchical model. It can be defined as a hierarchical data structure with two additional benefits: list and property simplify working with an XML document by providing full authentic access whenever needed to all part of the document. This tree structure data model is the graphical representation of node elements to express their relationship with the tree pattern. Unlike other trees, XML doesn’t show the content instantly; only the structure has been shown. The tree structure has root elements followed by child elements and sub-child elements. To Pick the single nodes or a set of nodes, it is ultimate using Xpath.XML Tree structures gives their hand in implementation with python, C# languages.
Syntax
The basic Syntax structure is drawn below:
Working of Tree
The tree is structured in a way similar to a tree connecting branches and leaves; the underlying tree structure forms an ancestor and descendant relationship. In this, the top element is placed at the root and the child elements are connected to the root element and certainly formed as element trees. As the tree has any number of child nodes (means any elements can have sub-elements). And again, the particular child nodes can behave as a root node, which can have any number of child nodes and so on until the depth. The tree structure enables the user to read the data in XML format. To understand the tree structure, it is necessary to read the basic XML terminologies and XML structure.
How to design a tree in XML?
At first, we shall see an XML document, and based on this; we can design a tree structure as the tree structure is the best supportive of XML language, which has the capability of deriving positions, powerfully combining hierarchical formats. We have some rules for designing a structure and a relationship between the two elements in XML Document. The rules are stated as follows:
Rule 1 – Descendants: If the XML element ‘X’ is contained by another element ‘Y’, X is Y’s descendant.
Rule 2 – Ancestors: If the XML element ‘X’ has element ‘Y’, then Y is the ancestors of X.
Rule 3 – The name of the label in the section data should be relative.
Examples of XML Document
Lets us first see the examples on the XML document
Example #1
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<SuperMarket>
<product id="001">
<productname>fssai dates</productname>
<productmfd> 12 october</productmfd>
<productexpdate> 4 january</productexpdate>
<mfdaddress>
<city>bangalore</city>
<state>karnataka</state>
<pincode>201301</pincode>
<landmark>Near waterpark</landmark>
</mfdaddress>
</product>
</SuperMarket>
In this example, the first line states version of the XML document as “1.0”. So, here <supermarket> is the root element followed by many child elements.
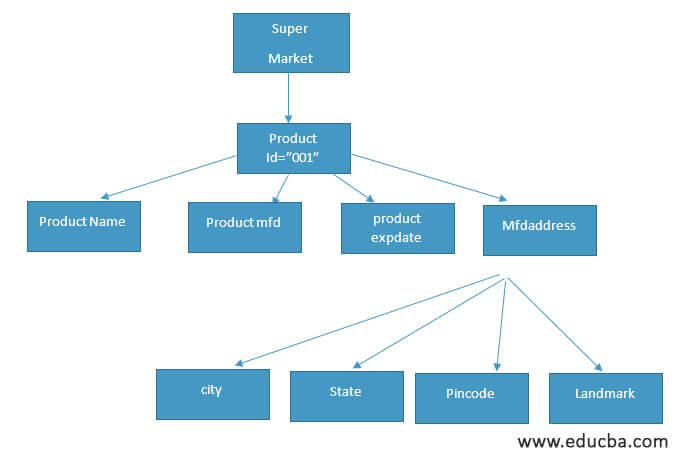
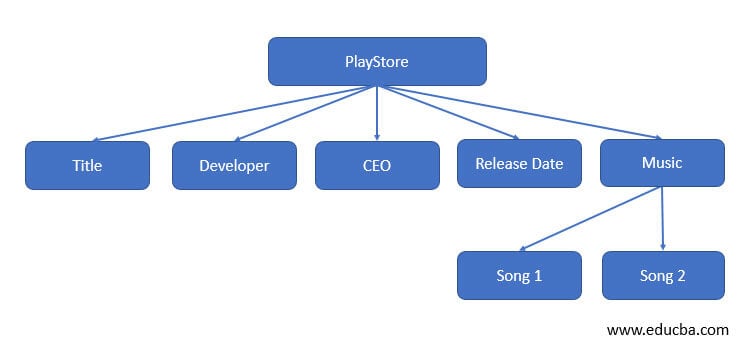
XML Tree
The Tree structure for the above xml document is shown below:where root node is <supermarket> , child element is <productname>,<product mfd>, < productexpdate> ,<mfdaddress> and the corresponding sub child element are <city>,<state>,<pincode>,<landmark>.
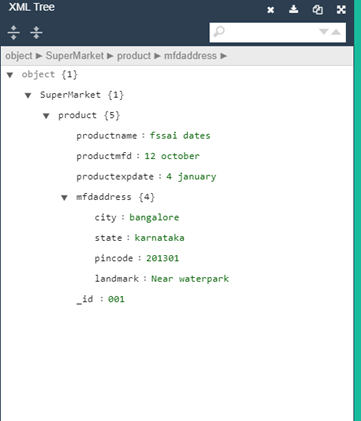
Computer Generated XML Tree in XML Viewer
When you click the down arrow, it elaborates to show the sub-child of the tree.
Example #2
Implementation with attributes and values in the Xml document.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<playstore app="game">
<title>Farmvillie- paris</title>
<developer>leonard britan</developer>
<CEO>mark kevin</CEO>
<released date="feb 23, 2001"></released>
<Music>
<Song no="1" duration="15:22">Wheels on the buse</Song>
<Song no="2" duration="16:25">Baby Shark</Song>
</Music>
</playstore>
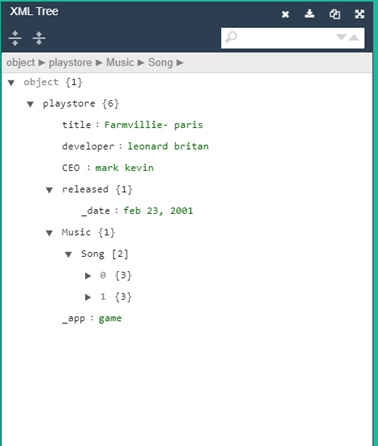
In the above code, <playstore> is the root node and category type =” game” is a node attribute and year date=” Feb 23 2001” is a node value. Here both the game id and song no has enclosed text and known to be text nodes. Representing the above information in a tree format like:
Result:
Example #3
Sample Implementation of the tree, which is parsed through Java.
Here we use several methods to create an element node, child node and text node and comment node like createElement(),appenrChild(),create TextNode() which is created in a text file.
import java.io.*;
import org.w3c.dom.*;
import javax.xml.parsers.*;
import javax.xml.transform.*;
import javax.xml.transform.dom.*;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory builderFactory =
DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder docBuilder =
builderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document dt = docBuilder.newDocument();
new Main().createXmlTree(dt);
}
public void createXmlTree(Document dt) throws Exception {
Element root = dt.createElement("CBSESchool");
dt.appendChild(root);
Element child = dt.createElement("Accrediation");
root.appendChild(child);
Element child1 = dt.createElement("SchoolName");
child.appendChild(child1);
Text text = dt.createTextNode("St.Francis International School");
child1.appendChild(text);
Comment comment = dt.createComment("Faculties in the School");
child.appendChild(comment);
Element element = dt.createElement("Faculties");
child.appendChild(element);
Text text1 = dt.createTextNode("Nithya Ananda");
element.appendChild(text1);
Element chilE = dt.createElement("FID");
chilE.setAttribute("name", "Nithya");
root.appendChild(chilE);
// adding a text element to the child
Text text12 = dt.createTextNode("Qualification");
chilE.appendChild(text12);
TransformerFactory factory = TransformerFactory.newInstance();
Transformer transformer = factory.newTransformer();
transformer.setOutputProperty(OutputKeys.INDENT, "yes");
StringWriter stw = new StringWriter();
StreamResult res = new StreamResult(stw);
DOMSource src = new DOMSource(dt);
transformer.transform(src, res);
String xmlString = stw.toString();
File file = new File("samplexml.xml");
BufferedWriter buf = new BufferedWriter
(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file)));
buf.write(xmlString);
buf.flush();
buf.close();
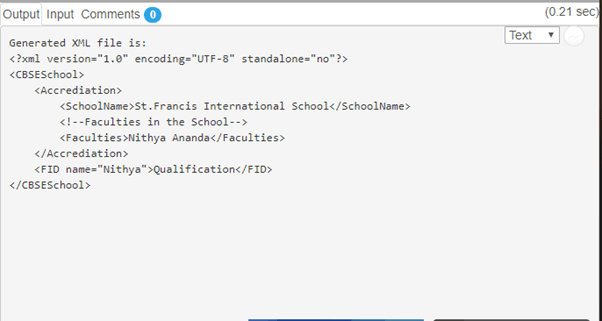
System.out.println("Generated XML file is:\n"
+ xmlString);
}
}
Result:
Conclusion
Therefore, we have gone through the tree, a family tree that provides easy access to manipulate the data within a tree in a flexible manner as it provides full access to the values in the XML document whenever it is needed. They form a huge foundation for a variety of data been used on the internet today. XML files are much handy to preserve program controls, and this tree provides great functionality to read the XML document. If the structure of the tree is constant, the complete XML tree is structured thoroughly.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XML Tree. Here we discuss How to design a tree in XML along with the working and examples on the XML document. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –