Updated April 1, 2023
Definition of XML Parsers
XML parsers are also known as XML Processor is defined as splitting the information into some component parts means which read the XML file and stores all available functions in memory to the rest of the program code. The parser aims to check the syntax for a well- defined file and it is used all round in the software.If a user simply copies an XML file, then each program had to call parser to read the XML. The parser reads the document and analyses the structure of the document and data properties.
How does XML Parsers Work?
The main job of an XML parser is to access or modify the data in the document. The parser contains installed software packages for the client applications to interface with and also does the validation process of the XML Documents. Here the component parts are compared with the DTD or schema pattern for checking. It triggers the event when it finds opening and closing tags in a file while parsing line-by-line. Parser covers two sections: a lexer and parser. A lexer takes input characters from the file and produces tokens like (<, >, and tag names). The parser takes this token and constructs a tree-based syntax with respective to grammar With DOM the whole document is read, while in case of SAX parser reads node by node and throws parsing events.
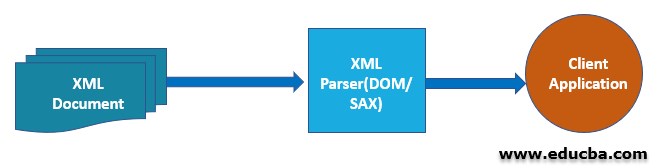
Fig: XML parser Process
The Parser could be categorized as validating and non- validating
- Validating Parser: It needs a Document type Declaration to parse and gives an error if the respective document doesn’t match with DTD and constraints.
- Non-Validating: This Parser eliminates DTD and the parser checks for the well-formed document.
Types of XML Parsers with Examples
This section talks about various types of parsers used recently in parsing XML document. They are:
- DOM Parser
- SAX Parser
- JDOM Parser
- stAX Parser
- Xpath Parser
The most important type is DOM and SAX which is explained detail in this article.
1. DOM Parser (Tree-Based)
Document Object Model is a W3C Standard and converts the XML document which is to parsed into a collection of objects and uses DOM API. It consists of a collection of nodes and is associated with other nodes in the tree. DOM is much easier to use as sorting and searching process is made faster.In DOM parser the content of the XML file is modified with Node and Node List. The Steps involved in Parsing with java:
- Getting document builder objects
- Taking XML document as input, parseit and return the class.
- Getting values of the input id through attributes and sub-elements.
- Display the results.
First is the XML file that generates the values which are going to be parse and java objects are constructed automatically.
Example
new.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<shops>
<supermarket>
<sid>201</sid>
<sname>sparc</sname>
<product> grocery</product>
<branch> two</branch>
<location> new york</location>
</supermarket>
<supermarket>
<sid>540</sid>
<sname> big basket</sname>
<product> grocery</product>
<branch> seven</branch>
<location>India</location>
</supermarket>
<supermarket>
<sid>301</sid>
<sname>Wallmart</sname>
<product> grocery</product>
<branch> fifteen</branch>
<location> France</location>
</supermarket>
</shops>
Read.java
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import java.io.File;
public class Read
{
public static void main(String argv[])
{
try
{
File file = new File("C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk-13.0.1\\par\\new.xml");
DocumentBuilderFactory docb = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder dbu = docb.newDocumentBuilder();
Document dt = dbu.parse(file);
dt.getDocumentElement().normalize();
System.out.println("Root: " + dt.getDocumentElement().getNodeName());
NodeList nd = dt.getElementsByTagName("supermarket");
for (int i = 0; i<nd.getLength(); i++)
{
Node node = nd.item(i);
System.out.println("\nNodeName :" + node.getNodeName());
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE)
{
Element el = (Element) node;
System.out.println("supermarket sid: "+ el.getElementsByTagName("sid").item(0).getTextContent());
System.out.println("sname: "+ el.getElementsByTagName("sname").item(0).getTextContent());
System.out.println("product: "+ el.getElementsByTagName("product").item(0).getTextContent());
System.out.println("branch: "+ el.getElementsByTagName("branch").item(0).getTextContent());
System.out.println("location: "+ el.getElementsByTagName("location").item(0).getTextContent());
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
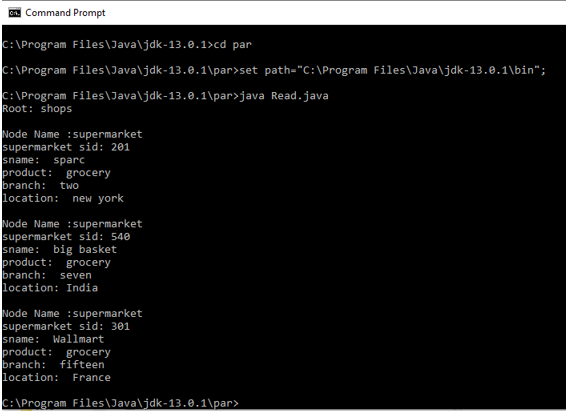
And here is the Output is shown for the XML File. Save XML and java file in the same folder during execution. In this article I have used java-jdk- 13.0.1 using command prompt. Save the respective folder in any drive and do the set path.
Output:
2. SAX Parser
SAX Is Simple API for XML and meant has Push Parseralso considered to be stream-oriented XML Parser. it is used in case of high- performance applications like where the XML file is too largeand comes with the community- based standard and requires less memory. The main task is to read the XML file and creates an event to do call functionor uses call back routines. The working of this parser is just like Event handler part of the java. it is necessary to register the handlers to parse the document for handing different events. SAX Parser uses three methods startElement() , endElement() , characters().
- startElement(): Is used to identify the element, start element is identified.
- endElement(): To stop the Supermarket tag in the example.
- character(): Is used to identify the character in the node
Next section shows an implementation of parsing using SAX with the java. Here we have XML file new.xml to parse and to create a list of supermarket object.
The xml file is the same file used in DOM Parser new.xml and next step generate Rsax.java file
Example
Rsax.java
import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParser;
import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParserFactory;
import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
public class Rsax
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
SAXParserFactory factory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
SAXParsersaxParser = factory.newSAXParser();
DefaultHandler handler = new DefaultHandler()
{
booleansid = false;
booleansname = false;
boolean product = false;
boolean branch = false;
boolean location = false;
public void startElement( String sg, String pp,String q, Attributes a) throws SAXException
{
System.out.println("Beginning Node :" + q);
if(q.equalsIgnoreCase("SID"))
{
sid=true;
}
if (q.equalsIgnoreCase("SNAME"))
{
sname = true;
}
if (q.equalsIgnoreCase("PRODUCT"))
{
product = true;
}
if (q.equalsIgnoreCase("BRANCH"))
{
branch = true;
}
if (q.equalsIgnoreCase("LOCATION"))
{
location = true;
}
}
public void endElement(String u, String l, String qNa) throws SAXException
{
System.out.println("LAst Node:" + qNa);
}
public void characters(char chr[], int st, int len) throws SAXException
{
if (sid)
{
System.out.println("SID : " + new String(chr, st, len));
sid = false;
}
if (sname)
{
System.out.println("Shop Name: " + new String(chr, st, len));
sname = false;
}
if (product)
{
System.out.println("Available Product: " + new String(chr, st, len));
product = false;
}
if (branch)
{
System.out.println("No.of Branches: " + new String(chr, st, len));
branch = false;
}
if (location)
{
System.out.println("Address : " + new String(chr, st, len));
location = false;
}
}
};
saxParser.parse("C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk-13.0.1\\par\\new.xml", handler);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
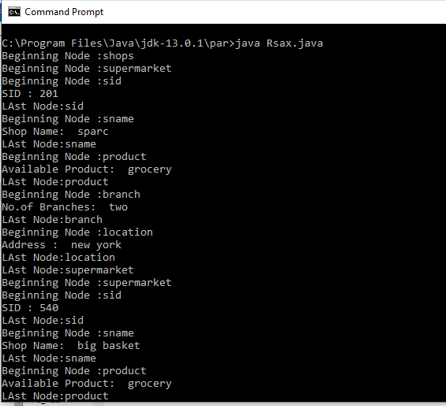
Output:
Conclusion
Therefore, we have discovered how to use XML parsers in Java with the powerful APIs in the applications.Also, we have seen the implementation of two parsers using java. When compared with DOM,sax parser uses arbitrary size to parse whereas DOM requires available memory to load the complete document.And Parsers differs based on the performance.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XML Parsers. Here we also discuss how does xml parsers work? along with examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –