Updated July 4, 2023
Definition of XML File
An Extensible Mark Up file is defined as a text-based language that carries data in the form of tags, not the format of the data. It is the most efficient way to store and move data online. XML file holds XML code, and the file is saved under the extension .xml. It is formatted with tags like HTML tags and other XML-based file types, including EDS, FDX, and DAE files. An XML file acts as a database to store the data. The most commonly used example of an XML-based file is RSS Feed.
Syntax:
A very Simple Syntax is given as
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<root>
<child>
</child>
</root>
How does File work in XML?
In this article, let’s see how to construct a simple XML file on our own. The XML file is plain text to store or transfer data on the internet. Web-based applications store information and transfer it through the web in XML format. Though XML file is meant for storage, their format of them is very important. For example, XML format is used for musical files.
The file works well in all editors. To view an XML file or to change the formats, it is recommended to use XML viewers Online. In the case of Text editors, an XML file is opened as a text file. Commonly used text editors are Notepad and WordPad to read an XML file. Well, known popular Online viewers are Code Beautify and JSON Formatter. The main reason for accessing XML files is good for data Storage. The hierarchical format of XML file includes:
- Child Element: The element inside another element.
- Global Element: Direct child element of the root tag. This Global element is referenced in XML Schema.
- Local Element: It is a nesting element.
Other elements are multiple-occurring and single-occurring elements.
These XML files could work on R programming and Java Programming, provided the packages must be installed.
Creating a File:
It is done by practicing our XML files in a text editor.
- Open the text editor file.
- And the first line of the file should include an XML declaration to tell the editor that it is an XML file.
- The next step is to create a root element that is the XML file’s main role. The root element should start with the start tag and end with the close tag.
- Followed by this is adding a child element.
The XML file is created by storing the information of a particular project in tags and saving the file using the file extension ‘.xml’. Let’s see the sample XML file to do the operations:
demo.xml
<shops>
<Type>
<No>1</No>
<NAME> riyaz</NAME>
<Street>620</Street>
<City>Bangalore</City>
</Type>
</shops>
Reading the XML file in R:
data <- xmlParse(file = "demo.xml")
print(data)
To check how XML file is loaded into Caching Database, we need the following attributes namely:
- FileName: Entering the full file Path to load it into the page.
- JPath/ Xpath: Defining the XML file to locate without Namespaces.
Few converters convert the XML file to other formats like HTML, CSS, and XSD.
Using a Text editor
As an XML file is a text file, we can open it in any editor, which helps to open and display the XML file Contents. In different programs, we can open an XML file. Formally, right-click the XML file -> open-> Menu -> choose any programs to open.
Using a Web browser to see the data in a File
To view the XML file in a Browser, it shows as a Document tree. The sample is shown below which it displayed in a different color. Although we can see them in blue text, still they are unclickable. To know exactly what these XML tags are, it is recommended to use XSLT to transform XML into various output formats.
Examples of XML File
This section covers how to create an XML file and let them execute in a Web browser.
Example #1
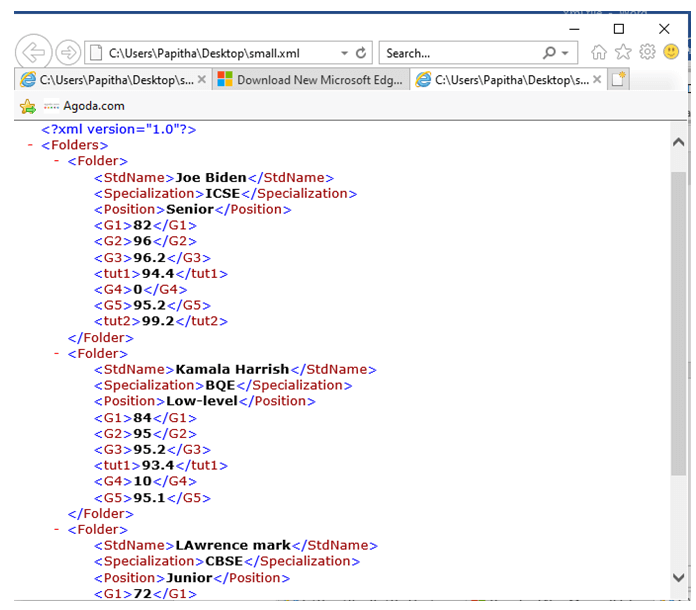
small.xml
<?xml version="1.0”?>
<Folders>
<Folder>
<StdName>Joe Biden</StdName>
<Specialization>ICSE</Specialization>
<Position>Senior</Position>
<G1>82</G1>
<G2>96</G2>
<G3>96.2</G3>
<tut1>94.4</tut1>
<G4>0</G4>
<G5>95.2</G5>
<tut2>99.2</tut2>
</Folder>
<Folder>
<StdName>Kamala Harish</StdName>
<Specialization>BQE</Specialization>
<Position>Low-level</Position>
<G1>84</G1>
<G2>95</G2>
<G3>95.2</G3>
<tut1>93.4</tut1>
<G4>10</G4>
<G5>95.1</G5>
</Folder>
<Folder>
<StdName>Lawrence mark</StdName>
<Specialization>CBSE</Specialization>
<Position>Junior</Position>
<G1>72</G1>
<G2>94</G2>
<G3>95.2</G3>
<tut1>93.4</tut1>
<G4>0</G4>
<G5>93.2</G5>
</Folder>
</Folders>
Explanation: This is how we created a file to work with which is a completed version XML file. Folders is a root element, and it contains sub-elements stdname, specialization. The folder is a parent element, stdname, specialization, G1..G5 are sibling elements. The following output shows the elements, structures, and attributes in an XML file.
Output:
Example #2 – Using DOCTYPE
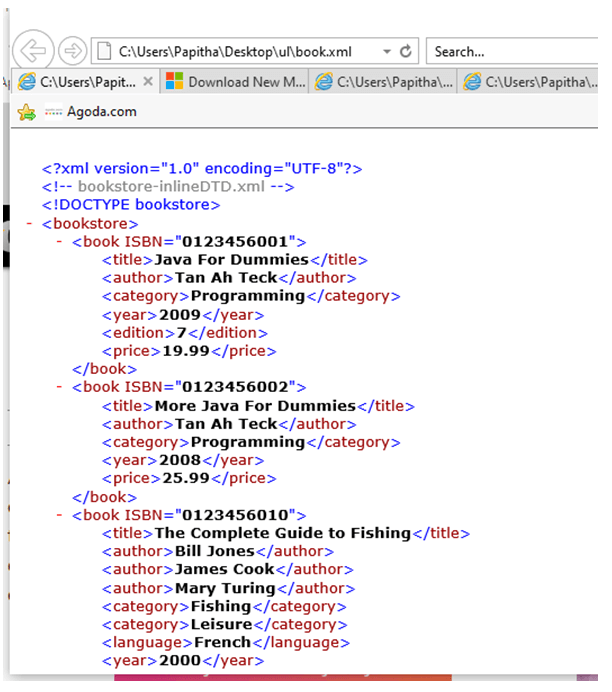
book.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE bookstore [
<!ELEMENT bookstore (book+)>
<!ELEMENT book (title, author+, category*, language?, year?, edition?, price)>
<!ATTLIST book ISBN CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ELEMENT title (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT author (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT category (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT language (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT year (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT edition (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT price (#PCDATA)>
]>
<bookstore>
<book ISBN="0123456001">
<title>Java For Dummies</title>
<author>Tan Ah Teck</author>
<category>Programming</category>
<year>2009</year>
<edition>7</edition>
<price>19.99</price>
</book>
<book ISBN="0123456002">
<title>More Java For Dummies</title>
<author>Tan Ah Teck</author>
<category>Programming</category>
<year>2008</year>
<price>25.99</price>
</book>
<book ISBN="0123456010">
<title>The Complete Guide to Fishing</title>
<author>Bill Jones</author>
<author>James Cook</author>
<author>Mary Turing</author>
<category>Fishing</category>
<category>Leisure</category>
<language>French</language>
<year>2000</year>
<edition>2</edition>
<price>49.99</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
Explanation: Above XML document displays a BookStore in an XML file.
Output:
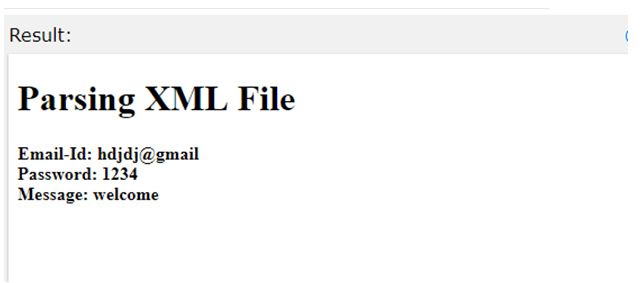
Example #3 – Parsing XML File
hello.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>Parsing XML File</h1>
<div>
<b>Email-Id:</b> <span id="Email-Id"></span><br>
<b>Password</b> <span id="Password"></span><br>
<b>Message:</b> <span id="message"></span>
</div>
<script>
var xmlh, xmlDo;
xmlh = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlh.open("GET", "hello.xml", false);
xmlh.send();
xmlDo = xmlh.responseXML;
document.getElementById("Email-Id").innerHTML=
xmlDo.getElementsByTagName("Email-Id")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.getElementById("Password").innerHTML=
xmlDo.getElementsByTagName("Password")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.getElementById("message").innerHTML=
xmlDo.getElementsByTagName("body")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation: The above code uses an XML document to Parse an individual XML file.
Output:
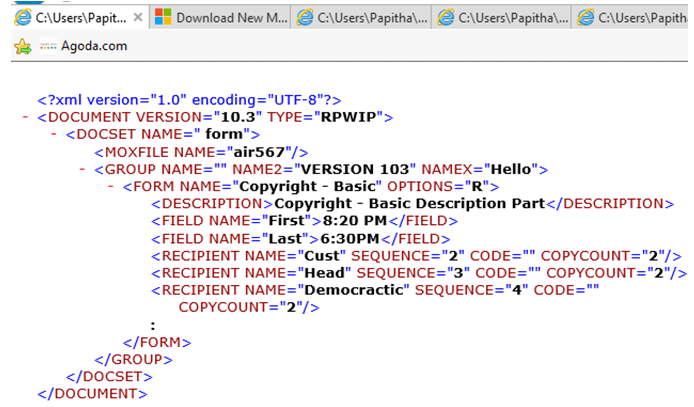
Example #4 – XML file in the format of DOCMAKER
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<DOCUMENT TYPE="RPWIP" VERSION="10.3">
<DOCSET NAME=" form">
<MOXFILE NAME="air567"/>
<GROUP NAME="" NAMEX="Hello" NAME2="VERSION 103">
<FORM NAME="Copyright - Basic" OPTIONS="R">
<DESCRIPTION>Copyright - Basic Description Part</DESCRIPTION>
<FIELD NAME="First">8:20 PM</FIELD>
<FIELD NAME="Last">6:30PM</FIELD>
<RECIPIENT NAME="Cust" COPYCOUNT="2" CODE="" SEQUENCE="2"/>
<RECIPIENT NAME="Head" COPYCOUNT="2" CODE=""
SEQUENCE="3"/>
<RECIPIENT NAME="Democractic" COPYCOUNT="2" CODE="" SEQUENCE="4"/>
:
</FORM>
</GROUP>
</DOCSET>
</DOCUMENT>
Explanation: The above code is done for the Document marker workstation, which lists a few tags for defining a .DAT file in DOCSET and field tags for forms and Group keys tags.
Output:
Conclusion
In the end, XML files practically model a hierarchical Database. Each Position specified in an XML hierarchy implements the relationships to other elements in the code. Therefore, in this article, we have seen how to work with files in .xml extensions and demo examples of various cases. This XML file could be implemented in Other programming Languages to retrieve the data from the XML document.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XML File. Here we also discuss the introduction and how file work in xml? along with different examples and code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –