Updated April 4, 2023
Introduction to XML boolean
XML boolean type is an XSD Simple Data types that represent True or False or Yes / No values as their types and assigned a value as 0 for false and 1 for true. A keyword bool defines it, and it is a simple resource which is referenced in the name attribute. Under a single XML file, we can combine many bool resources. As defined by W3C XML schema, all the standard data types are defined here; a short example is xsd: boolean.
Syntax of XML boolean
The general structure is given as:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<bool
name="b_name"
>[true | false]</bool>
</resources>
Following is a boolean declaration in schemas.
<xsd: attribute name = “Age” type=:xsd: Boolean”/>
Or
Xsd : boolean
The value of a boolean is an Integer value whose values are ‘0’ and ‘1’, representing logical yes or no. Capital Letters are avoided.
How boolean Type Work in XML?
This type is derived from the Simple Data type with the value spaces. The Boolean Datatype is primarily used for the binary logic purpose. This comes under the Miscellaneous datatypes.
The logical schema of the boolean is defined as below:
<xsd:attribute name="service" type="xsd:boolean"/
Following is an example in the XML document, this attribute is shown as with the elements:
<Employee service="false">
< Employee_name >Mac mike</ Employee_ name>
</ Employee>
Any modification to schema definition Object or user-defined schemas should use this type of data. Multi-value Boolean attributes are not supported here; only single-value is used.
An Xml file under the android application could be defined as:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<bool name="display_screen">true</bool>
<bool name="resolution adjust">true</bool>
</resources>
<xsd:simpleType name="trueOrFalse">
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:boolean">
<xsd:pattern value="true" />
<xsd:pattern value="false" />
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
The element may look like in xml:
<prize pattern="true"> 850 </prize>
The other pattern is like this:
<xs:simpleType name="boolean" id=”Boolean”>
<xs:restriction base="xs:anySimpleType">
<xs:whitespace="true" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
In the case of XML style sheet, it is specified as:
<xsl:template match="Items">
<p>Items in the stock:
<xsl:text> </xsl:text>
<xsl:value-of select="fn:boolean(@Item Numbers)"/>
</p>
</xsl:template
In XML schema, yes-no Boolean-like attributes are placed, and the expressions of Boolean values are restricted. The format is shown below with the Simple Data types enumeration concept.
<xs:simpleType name="y-n">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>in case of XSD yes-no format is used for values not an expressions.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:restriction base="xs:token">
<xs:enumeration value="yes" />
<xs:enumeration value="no" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
In the case of API, few fields entry are defined as Boolean Data Type, which may be redefined as int values or enumerations with lists. This happens when we have a greater number of true or false choices. In such a situation, it is preferred to use a compatibility level for the application.
Schema definition with nillable attribute.
<xsd:element name="conversion" type="xsd:boolean" nillable="true" default="false">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation>Conversion of the type</xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:element>
Examples of XML boolean
Given below are the examples of the type check on the input values for the well-formness of an XML document. Here the data values are mapped to the XML element.
Example #1
odrs.xsd
Code:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:token"/>
<xs:element name="qualification" type="xs:token"/>
<xs:element name="born" type="xs:date"/>
<xs:element name="dead" type="xs:date"/>
<xs:element name="isbn" type="xs:NMTOKEN"/>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID"/>
<xs:attribute name="available" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="lang" type="xs:language"/>
<xs:element name="title">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="xs:token">
<xs:attribute ref="lang"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="library">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="book" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="author">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="name"/>
<xs:element ref="born"/>
<xs:element ref="dead" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="book">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="isbn"/>
<xs:element ref="title"/>
<xs:element ref="author" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<xs:element ref="character" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="id"/>
<xs:attribute ref="available"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="character">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="name"/>
<xs:element ref="born"/>
<xs:element ref="qualification"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
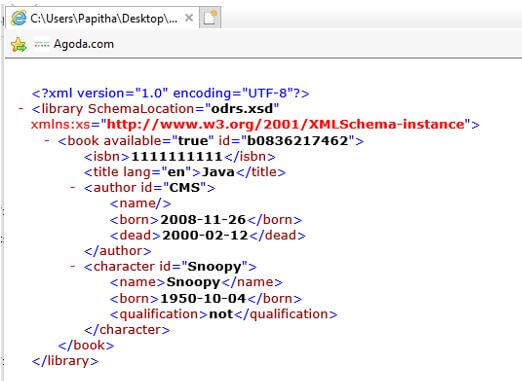
ord.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<libraryxmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" SchemaLocation="odrs.xsd">
<book id="b0836217462" available="true">
<isbn>1111111111</isbn>
<title lang="en">Java</title>
<author id="CMS">
<name></name>
<born>2008-11-26</born>
<dead>2000-02-12</dead>
</author>
<character id="Snoopy">
<name>Snoopy</name>
<born>1950-10-04</born>
<qualification>not</qualification>
</character>
</book>
</library>
Explanation:
- A Boolean value is encoded as true or false with the attribute type ‘name’ in the above example.
- When we execute an XML file, we get the following type Boolean in the output.
Output:
Example #2
perchema.xsd
Code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns="College" targetNamespace="College" elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="Faculty" type="FacultyType"/>
<xs:element name="Result">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="College" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="College">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="Faculty" type="FacultyType"/>
<xs:element name="Principal" type="FacultyType"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:element name="Dept" type="xs:boolean" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="noOfWorkers" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="FacultyType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="FullName" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="SurName" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="Address" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="Idno" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="YearsOfExperience" type="xs:int" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
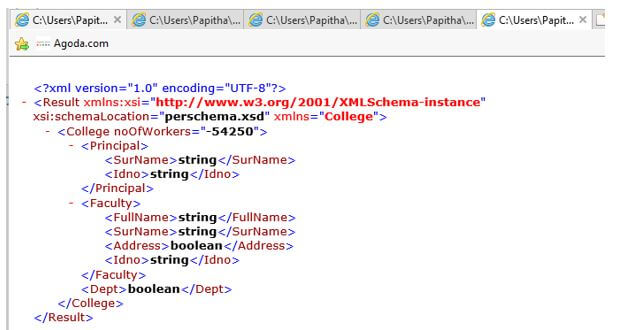
per.xml
Code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Result xmlns="College" xsi:schemaLocation="perschema.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<College noOfWorkers="-54250">
<Principal>
<SurName>string</SurName>
<Idno>string</Idno>
</Principal>
<Faculty>
<FullName>string</FullName>
<SurName>string</SurName>
<Address>boolean</Address>
<Idno>string</Idno>
</Faculty>
<Dept>boolean</Dept>
</College>
</Result>
Explanation:
- The bool value ‘yes’ or ‘no ‘given to the address tag element in the college file. The schema part defines the type of the address element.
Output:
Example #3
Airline System.
air.xsd
Code:
<xs:schema attributeFormDefault="unqualified" elementFormDefault="qualified" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element name="Backoff">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Airlines">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Airline" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Flight" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element type="xs:int" name="Ano"/>
<xs:element type="xs:short" name="Acode"/>
<xs:element type="xs:float" name="rREAL64" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element type="xs:string" name="sSTRING"/>
<xs:element type="xs:string" name="bBOOL"/>
<xs:element type="xs:short" name="Adev"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute type="xs:byte" name="Instance" use="optional"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Flight2" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element type="xs:string" name="sSTRING"/>
<xs:element type="xs:string" name="bBOOL"/>
<xs:element type="xs:byte" name="Adev"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute type="xs:byte" name="Instance" use="optional"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute type="xs:string" name="Name" use="optional"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
Airline.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<Backoff>
<Airlines>
<Airline Name=" Western">
<Flight Instance="1">
<Ano>123456789</Ano>
<Acode>5425</Acode>
<sSTRING>This is Adria Airways</sSTRING>
<bBOOL>true</bBOOL>
<Adev>200</Adev>
</Flight>
<Flight Instance="2">
<Ano>44582351</Ano>
<Acode>20215</Acode>
<rREAL64>234.56789</rREAL64>
<sSTRING>This is Air France</sSTRING>
<bBOOL>false</bBOOL>
<Adev>-10</Adev>
</Flight>
<Flight Instance="3">
<Ano>345678901</Ano>
<Acode>3456</Acode>
<sSTRING>This is Delta Airlines</sSTRING>
<bBOOL>true</bBOOL>
<Adev>250</Adev>
</Flight>
</Airline>
<Airline Name="Asia">
<Flight2 Instance="1">
<sSTRING>This is Emirates Airlines</sSTRING>
<bBOOL>false</bBOOL>
<Adev>-88</Adev>
</Flight2>
<Flight2 Instance="2">
<sSTRING>This is Malaysia Airlines</sSTRING>
<bBOOL>true</bBOOL>
<Adev>-19</Adev>
</Flight2>
</Airline>
</Airlines>
</Backoff>
Explanation:
- The above example chooses the bool value for the element tag flight with the values ‘true’ or ‘false’.
Conclusion
Hopefully, the information in this article on XML Boolean gives great ideas on binary logic and gives accurate direction with different patterned types. The data type which we have seen here are associated with XML Schema namespaces. The concept is much simple to understand the other features that the readers could explore.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XML boolean. Here we discuss the introduction, how boolean type work in XML? and examples, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –