Updated March 17, 2023

Introduction to SQL Developer
SQL Developer provides a workspace for the development of the databases using the SQL programming, which is known as Integrated Development Environment or IDE. It is an open-source tool provided by Oracle that has a user-friendly Graphical User Interface (GUI) and supports all the other tools from Oracle. SQL is the widely used application software, as it facilitates various operations in one place, such as DBA processes, workspace to create and run queries, UI for report generation, etc.
Steps to Install SQL Developer
- You can install it from the Oracle website, but you need to have an account on it to create an account.
- Install the required version of the Oracle SQL Developer.
- Install Oracle Database 10g and Sample Schema.
- Unlock the HR user and log in as the SYS user and type command: alter user hr identified by hr account unlock.
- Download and unzip the files.zip that contains all required files to a local folder on your system.
The first task after installation is to create a connection to the Oracle Database using Oracle SQL Developer.
Steps to Create Database Connection
Following are the steps to create a database connection.
1. Open Oracle SQL Developer.
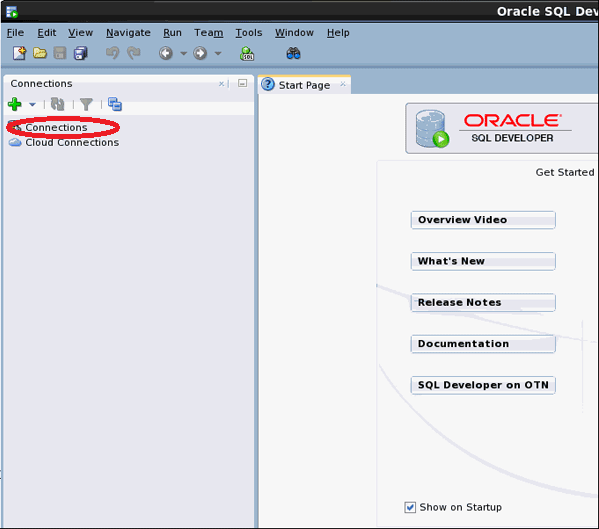
2. Now, under Connections, right-click on the Connections, and the Connection menu appears. Click on New Connection.
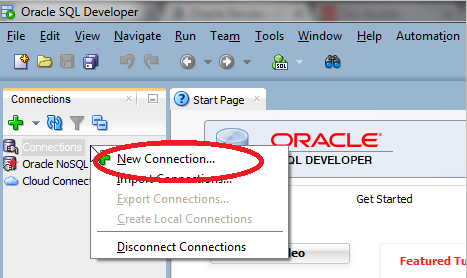
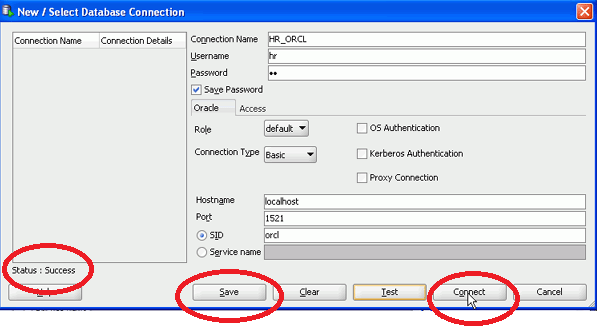
3. The New/Select Database Connection Dialog Box will appear.
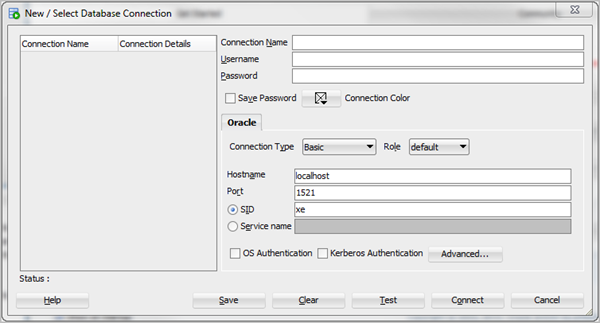
4. Enter the following details in the fields of the above-appeared dialog box.
- Connection Name: Name of Cloud Connection
- User Name: Database Username
- Password: Your choice (then check the checkbox Save Password)
- Hostname: Your local hostname
- SID: Your own SID
- Then click on Test
For example:
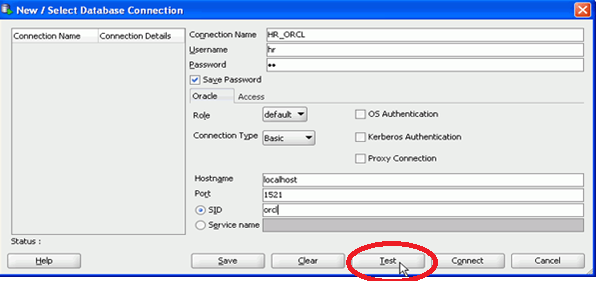
5. You can check the status of testing on the bottom left side. Then click connect and save.
6. The connection would be saved, and the new connection would appear under.
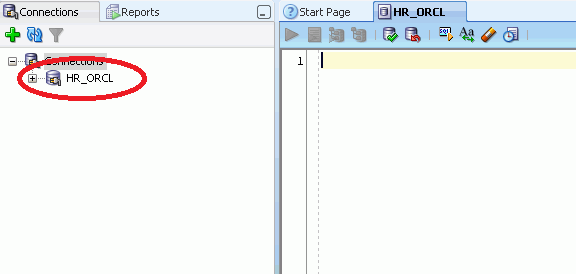
After creating a connection, you can use existing objects of Oracle SQL Developer or can create new also. Now let us see how to browse already existing objects.
Browsing Objects in Oracle SQL Developer
1. Expand the newly added connection.
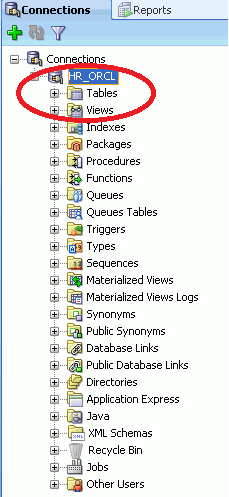
You can use any object like tables, views, indexes, packages, triggers, sequences, synonyms, directories, types, materialized views, functions, and many more. But we will see in brief how we can use tables.
2. Expand Tables.
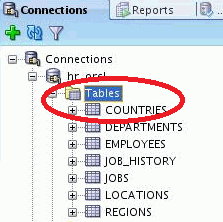
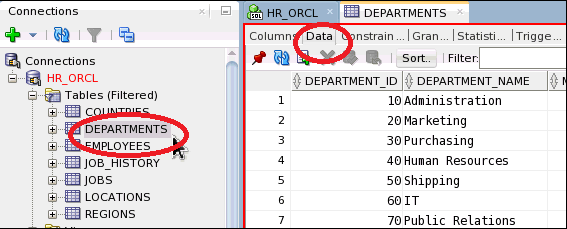
3. You can select any table from the list to view the table definition and click the Data tab.
In the figure below, we have selected the DEPARTMENTS table. You can then see the data present in the table.
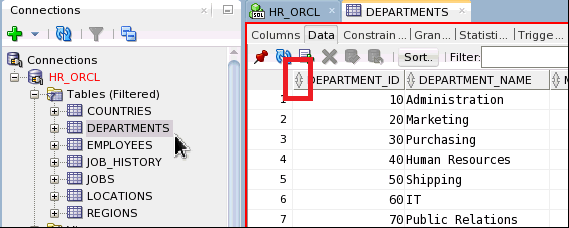
You can apply various operations on a table like sorting, filtering data, applying various constraints, and many more. For example, you can apply to sort by clicking the arrow icon next to the name of the column you want to sort.
Creating Objects in Oracle SQL Developer
You can create dialogs for each supported object type. Oracle SQL Developer also supports Temporary tables, External tables, lists, Partitioned tables, Index Organised tables, and many more object types.
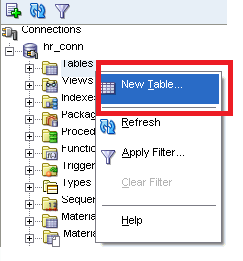
1. Right-click on.
2. Select a New Table.
3. Enter the Table Name and check the Advanced.
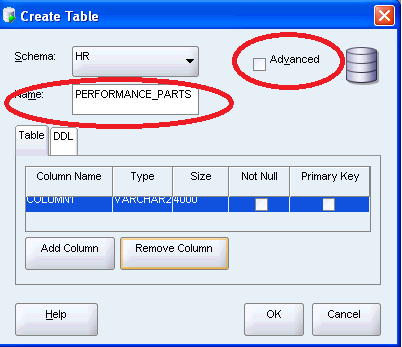
4. Enter information for the first column as mentioned below:
- Column Name: Performance_id
- Type: VARCHAR
- Size: 3
- Not Null: Select it
- Primary Key: Select it
5. Enter information for the second column as below:
- Column Name: Name
- Type: Varchar
- Size: 40
- Not Null: Select it
- Primary Key: Leave it
6. Similarly, enter information for as many columns as you require.
7. Click OK.
8. The new table would be created under TABLES.
9. To see it, you can expand the TABLES and then use them to perform SQL commands.
The Not Null and Primary Key is the integrity constraint which states what type of data can be inserted in each column. There are more integrity constraints that can be applied to restrict the type of data that is valid for a respective column.
Let us briefly see what these integrity constraints do.
There are basically five integrity constraints:
- NOT NULL: This constraint ensures that data must be present in that column. A null value cannot be inserted in that column.
- Unique: This constraint ensures that each value in the column must be unique, i.e., no repetition of values. This constraint can be applied on multiple columns together as a group called as Composite Unique. It does not say anything about Null value.
- Primary Key: This constraint ensures the properties of both NOT NULL and UNIQUE constraints, i.e. multiple rows cannot have the same value and prevent null value simultaneously.
- Foreign Key: This constraint states that for each value in the column on which the constraint is applied, there must be the same or matching values in other specified tables and columns. It is basically called referencing other tables.
- Check: This constraint is not used frequently, but it ensures that values must satisfy the specified condition. The condition can be the logical expression or comparison expression depending upon the need for the restrictions to be applied.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is SQL Developer? Here we discussed how to install and create a new database of SQL Developer respectively. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –

