Updated November 4, 2023
Introduction to Interface in Java
In Java, an interface is a blueprint that outlines a set of method signatures that a class must implement. It acts as a contract, ensuring that any class implementing the interface provides the specified methods. Interfaces are used to achieve multiple inheritance, which enables classes to inherit behaviors from various sources. They define a level of abstraction and play a crucial role in achieving polymorphism. This allows objects to be treated as instances of their implemented interfaces, which enhances code flexibility and reusability.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Syntax of Java Interface
- Why do we need it?
- How does the interface work in Java?
- How to Declare Interface in Java?
- Examples to Implement Interface in Java
Syntax of Java Interface
Below is the syntax:
public interface MyInterface {
// Declare constant variables (if any)
int MY_CONSTANT = 42;
// Declare abstract methods
void someMethod();
// Declare default method (optional)
default void defaultMethod() {
// Default method implementation
}
// Declare static method (optional)
static void staticMethod() {
// Static method implementation
}
}Parameters:
- MyInterface is the name of the interface.
- MY_CONSTANT is a placeholder for declaring constant variables.
- someMethod() is a placeholder for declaring abstract methods.
- defaultMethod() is a placeholder for declaring a default method (optional).
- staticMethod() is a placeholder for declaring a static method (optional).
You should replace these placeholders with your specific interface name, constants, method names, and their respective implementations as needed in your actual code.
Why do we need it?
Java interfaces are essential for:
- Achieving Multiple Inheritance: Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance of classes, but it allows various interface implementations. This helps a class inherit behaviors from multiple sources without the complexities of inheriting various classes.
- Defining a Contract: Interfaces define a contract that all classes must follow. This guarantees that classes implement certain methods, increasing code consistency.
- Polymorphism: Interfaces enable polymorphism, allowing objects to be treated as instances of their implemented interfaces. This enhances flexibility, code reusability, and loose coupling.
- Separation of Concerns: Interfaces promote a clear separation between what an object does (interface) and how it does it (class implementation). This separation improves code maintainability and modularity.
- API Design: Interfaces are crucial in designing APIs. They provide a clear structure for developers to follow, making it easier to understand and use libraries and frameworks.
Java interfaces facilitate code reusability, maintainability, and flexibility while ensuring adherence to a contract, making them a fundamental part of Java’s object-oriented programming paradigm.
How does the interface work in Java?
- Declaration: You define an interface using the interface keyword. Inside the interface, you specify a set of method signatures, which are abstract by default. These method signatures serve as the contract that implementing classes must fulfill.
- Implementation: Any class that wishes to adhere to the contract specified by an interface can implement that interface. To do so, the class uses the implements keyword, and it must provide concrete (non-abstract) implementations for all the methods declared in the interface.
- Polymorphism: When a class implements an interface, the objects in that class can be treated as interface instances. This forms the foundation of polymorphism in Java, allowing various classes to share the same interface and utilize it interchangeably.
- Multiple Inheritance: Interfaces enable numerous inheritance of behavior in Java. A class can implement multiple interfaces, inheriting the method contracts from all. This is a powerful way to combine different sets of behaviors in a class.
- Contractual Obligation: When a class implements an interface, it must provide the specified behavior. This requirement ensures consistency and facilitates code maintenance and extensibility.
- Default and Static Methods: Starting from Java 8, interfaces can also contain default methods with implementations and static methods, which offer more flexibility and backward compatibility.
How to Declare Interface in Java?
We can declare an interface by using the interface keyword and implement it by using the implement keyword.
Example:
interface Interf
{
void m1(); // by default public abstract void m1();
void m2();
}Implementation of Interface in Java
Implementation of an interface in Java is performed by using implements keywords.
interface Interfc {
void m1();
void m2();
}
abstract class ServiceProvider implements Interfc {
public void m1() {
// Concrete implementation for m1
}
public void m2() {
// Concrete implementation for m2
}
}Therefore, if a class implements an interface mandatorily, we should provide an implementation for every method of that interface; otherwise, that class must be declared as abstract. If an interface is getting implemented, it must declare the interface as public; otherwise, it will throw an error saying compile-time error.
Then there is one more essential aspect to be followed with interface declaration and implementation.
Examples to Implement Interface in Java
Following are the examples of implementing an interface in java with different scenarios:
Example #1
Code:
public interface Animal {
void animalRuns();
void sleep();
}
public class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void animalRuns() {
System.out.println("The cat says meow meow");
}
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("Cat sleeps");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat myCat = new Cat();
myCat.animalRuns();
myCat.sleep();
}
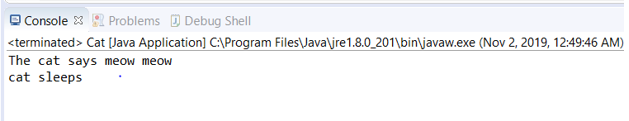
}Output:
The above output tries to prove the point that the interface must be implemented by another class using the implements keyword rather than using the extends keyword.
Example #2
Implementation of Multiple Interfaces:
Code:
public interface frstInterface {
void myMethod();
}
public interface secInterface {
void scnInterface();
}
public class DemoClass implements frstInterface, secInterface {
public void scnInterface() {
System.out.println("Some random Text");
}
public void myMethod() {
System.out.println("Some useful Text");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DemoClass myDemo = new DemoClass();
myDemo.myMethod();
myDemo.scnInterface();
}
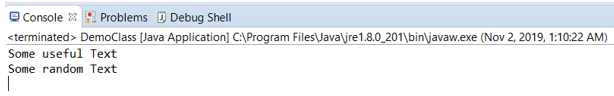
}Output:
Example #3
One interface can extend another interface also once a class can implement an interface.
Code:
public class TestImpl4 implements showble {
public interface Printable {
void print();
}
public interface showble extends Printable {
void show();
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("Welcome to the project");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestImpl4 obj = new TestImpl4();
obj.print();
obj.show();
}
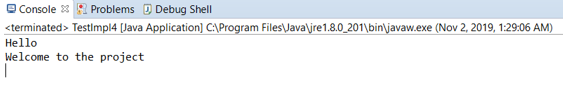
}Output:
Conclusion
Java interfaces act as a guide for classes, specifying a group of abstract methods that the classes must implement. They promote code flexibility, enabling various classes to adhere to a shared agreement. Interfaces facilitate the development of loosely interconnected and easily maintainable code, making them a vital component of Java’s object-oriented programming methodology.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Interface in Java” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.