Updated March 18, 2023
What is Data Modeling?
Does the following article provide an outline for Data Modeling? The method of creating a data store model is called data processing in a database. This introduces theoretical data objects and connections between different data objects. Data modeling is a data formulation process in a standardized format in an information system. It helps to analyze data, which helps to meet business needs quickly. Data modeling requires data modelers who work correctly with stakeholders and prospective IT users. Data modeling ends with the development of a model of data supporting the infrastructure for the business information system.
Understanding Data Modeling/Scope
It occurs at three different layers:
- Physical model: It is a schema that says how data is stored physically in the database.
- Conceptual model: It is the user’s view of the data, i.e., the high level that the user sees.
- Logical model: It sits between the physical and conceptual models, and it represents the data logically, separate from its physical stores.
Hierarchical Data Modeling: These models were used to replace file-based systems. The data was kept in a tree-like one with too many arrangements.
Relational Data Modeling: The hierarchical model helped us move from file-based systems, which reduced complexity but still, one had to know the specific physical data storage employed. The relational model, used by relational databases, stores data in tables, unlike the tree-like structure used by Hierarchical databases. In short, it reduced the complexity more when compared to the hierarchical model.
How does Data Modeling make Work so Easy/why Should we use it?
- It helps us in a visual representation of data and enforces business logic, regulations, policies, etc., on data.
- It guides scientists and analysts in designing and implementing database users.
- So, without data modeling, the job of analysts and scientists to implement the business requirements on a database becomes difficult.
Why do we need Data Modeling? What can you do with it?
The main goal of using it is:
- To ensure that all data objects are represented correctly, as if it is not done correctly, we would get incorrect results.
- It helps, as stated earlier, to design a database at conceptual, physical, and logical levels.
- It helps to design relational tables, primary keys, foreign keys, etc.
- Database developers can create a better physical database with a good model as it becomes a guiding tool for them.
- It helps to identify missing and redundant data.
- It helps us have a better IT infrastructure and easy and cheap maintenance when required in the long run though it’s initially time-consuming.
Working
Now let’s create a sample data model to understand how to work with a model.
To do this, we have to follow specific steps:
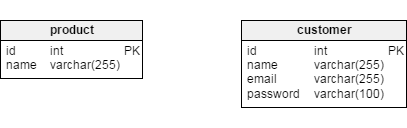
- First, we have to understand the requirements. In this case, we will create a model for an online store. So, keeping that in mind, we need two tables a) customers and b) products.
- The next step is to get the attributes of the tables or entities.
a. Customer table can have attributes like:
- Id
- Name
- Address
b. Product table can have attributes like:
- Id
- Name
In the customer table, we can have Id as the Primary key; similarly, Product Id in the Product table will be the primary key, as shown in the diagrams below.
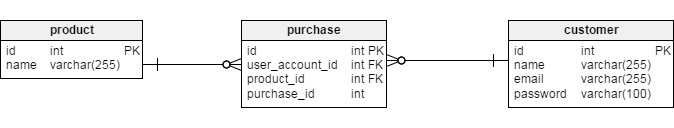
Now, we will design the relationship between these two tables. So to connect the customer and product table, we will create a table called purchase which will be like an order table (i.e., which customer ordered which product).
If you look at the figure above, the customer-purchase reference is OK because every purchase has one customer, and one customer has many purchases. So, this reference is OK. We have also taken user_account_id as a foreign key (the connection to the id in the customer key). Similarly product_id. The product-purchase reference still poses a problem, as one purchase can include several products, and the same product can be included in several purchases.
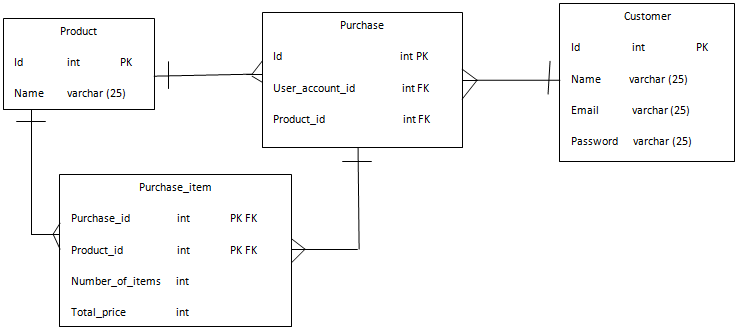
To overcome this, we will design an intermediary table known as purchase_item, connected with purchase and product. In the below figure, we can see the problem has been resolved.
Advantages
There are various advantages as follows:
- It helps businesses to communicate and plan across their organization.
- Recognition of the correct data source enables populating the model.
- defining relationships between tables, such as primary key, foreign key, etc.
Who is the Right Audience for Learning this Technology?
- It is essential. The right audiences for learning modeling techniques are individuals who are data architects and data analysts.
- Most individuals start as data analysts and then move up the ladder.
How will this Technology help you in Career Growth?
- According to Glassdoor, the average salary in the market for modelers is projected to earn about $78,601 on average.
- So you can see that it is a well-paid job.
- Most big companies invest in modelers as they are essential for keeping data integrity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can say that the model created by modelers ensures consistency in naming conventions, integrity, and data security because good data will enable businesses to correct and efficiently utilize their data.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Data Modeling. Here we discuss the introduction, scope, working, skills, advantages, and career growth in Data Modeling. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –