Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction of SQL Views
Views in standard query language (SQL) are more or less like virtual tables through which a user can view and manipulate data. They are the results of a pre-stored source query on one or more data table that selects and stores records in a virtual table based on some conditions and joins. Views do not form part of the database schema. However, it reflects all the changes being made in the concerned tables.
In SQL, we can have two types of views, namely system-defined views and user-defined views. Within user-defined views, the two types of views that are widely known:
- Simple View: Simple views are views that are created on a single table. We can perform only basic SQL operations in simple views. That means, we cannot perform analytical and aggregate operations by grouping, sets, etc. in simple views. We can definitely perform insert, update, delete directly from a simple view, but for that, we must have the primary key column in the view.
- Complex View: Complex views as the name suggest are a bit complicated compared to simple views. Complex views are created on more than one database table. We can perform analytical and aggregate operations in complex views, but unlike simple views, we cannot perform insert, delete, and update directly from a complex view.
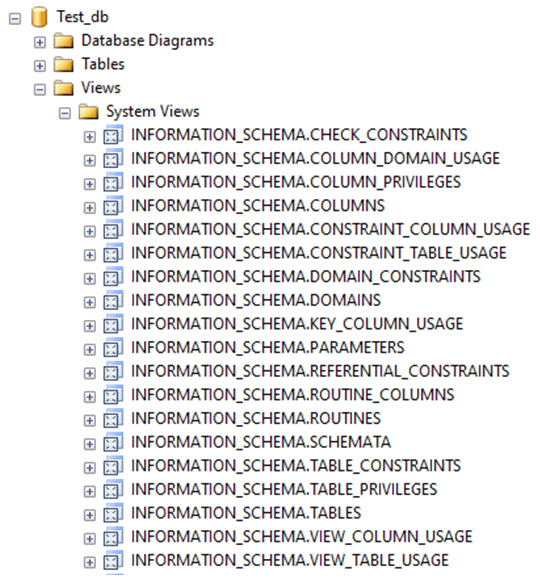
- In some databases like SQL server, we have some system-defined views too. They are views for routines, schemas, table_privileges, table_privileges, check_constraints, etc. They are automatically created when we create a database. Here is an image from SQL server management studio that gives us an understanding of what system views are:
- There are many more, but for this article, we have kept it short. Go check it out for yourself.
- Having discussed the types of views, in brief, let us go ahead and discuss the syntax used for creating a view in SQL.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for creating a view is as follows :
CREATE VIEW view_name AS query;The parameters used in the above-mentioned syntax are as follows :
- view_name: Name of the view
- query: Usually a select statement that sources data from database tables. The results of this query will be stored as a view.
The difference between simple and complex view comes in the query part of the syntax. If the query sources data from only one table and does not have any group by clauses, it will be our simple view. Otherwise, it will be known as a complex view. Going ahead, let us discuss a few examples to understand how views work in SQL and how to differentiate between a simple view and a complex view.
Examples of Types of SQL Views
To illustrate the creation of simple and complex views, we need to have a few base tables first. For this article, we will be using the following tables.
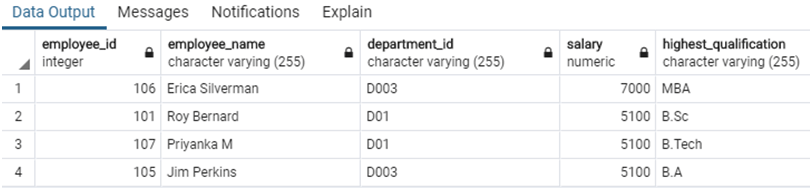
The data in the employee table looks something as follows :
SELECT * FROM employee;The data in our second table looks something as follows :
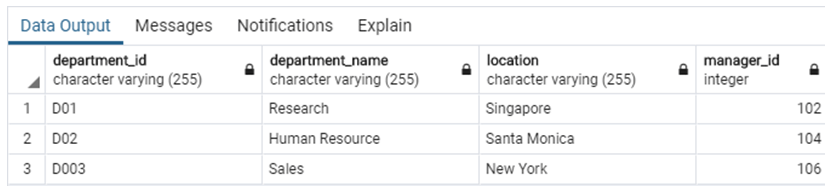
SELECT * FROM departments;Now we are all set to try a few examples based on views with the help of these tables.
Example #1
Create a view consisting of employee details for department ‘D01’.
CREATE VIEW employee_dept1_view AS
SELECT * FROM employee
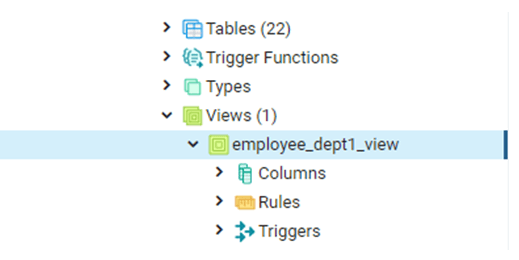
WHERE department_id = 'D01';The query executed successfully, and the view has been created. We can see the view in the concerned database. It will look something as follows :
In this case, we have created a simple view, for which the data is sourced from only 1 base table.
Example #2
Create a view based on the employee and department table with fields as employee_name, salary, highest_qualification, department_name and location.
CREATE VIEW employee_details AS
SELECT e.employee_name,
e.salary,
e.highest_qualification,
d.department_name,
d.location
FROM
employee as e JOIN departments as d
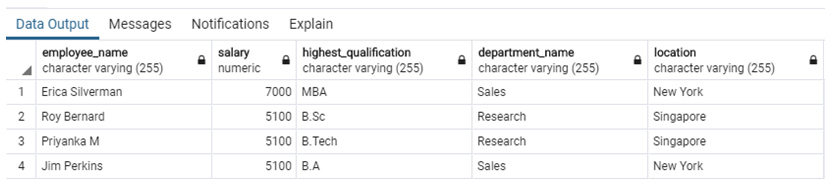
ON e.department_id = d.department_id;The view has been successfully created. Such views which are based on multiple tables are categorised as complex views. Here is a select query to give us a glimpse of records in the created view.
SELECT employee_name, salary, highest_qualification, department_name, location
FROM employee_details;Example #3
Create a view that contains records with maximum salary for each department.
CREATE VIEW employee_max AS
SELECT
d.department_id,
d.department_name,
MAX(e.salary)
FROM
employee as e JOIN departments as d
ON e.department_id = d.department_id
GROUP BY d.department_id,d.department_name;The view has been successfully created. Views with GROUP BY and aggregate functions are also categorised as complex views.
Let’s see what’s inside our newly created employee_max view with the help of a SELECT statement.
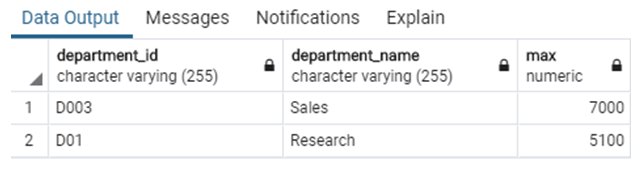
SELECT department_id, department_name, max
FROM employee_max;Conclusion
In this post, we have discussed the types of views in SQL. There are primarily two types of user-defined views in SQL, simple and complex views. Simple views are created on one database table, whereas complex views are created on more than one table.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Types of SQL Views” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.