Updated May 19, 2023
Introduction to Types of Errors in C
Errors in C language are defined as an illegal operations performed by the user, resulting in the abnormal or abrupt working of the program logic. We cannot identify programming errors until we compile or execute the program. Some errors in C are hidden or prevent the program from being compiled or executed. So while executing our application successfully, we must remove the errors from the program.
Real-Time Scenario: We have an application for displaying the sum of the numbers while declaring variables; we have missed the semicolon or wrong syntax of the main method, resulting in an error while executing the application.
Advantage:
- Before compilation, we will eliminate all error issues.
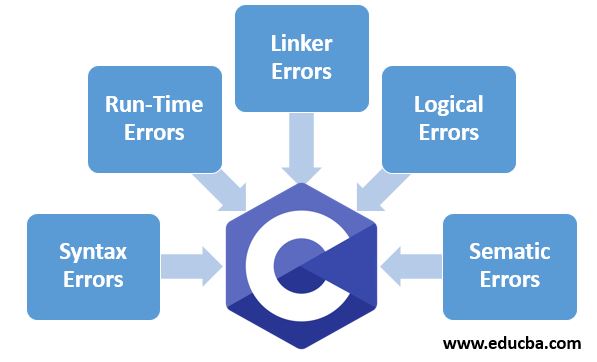
Types of Errors in C
C language broadly classified errors into five types. They are
1. Syntax Errors
Errors occur when you violate the rules of writing C syntax is said to be “Syntax errors.” This compiler error indicates that this must be fixed before the code will be compiled. The compiler identifies these errors as “compile-time errors.”
Syntax:
1.
void main()
{
int a //here semi colon(;)missed
}2.
void main()
{
int a;
//here parenthesis(}) missed2. Run-Time Errors
Errors which are occurred after a successful compilation of the program are said to be “run-time errors.” Number divisible by zero, array index out of bounds, string index out of bounds, etc., are the most frequent run-time errors. These errors can’t be very hard to detect at the compile time.
Syntax:
1.
void main()
{
int a=10;
int c=a/0;// Here number divisible zero error occurs
}2.
void main()
{
int a[3]={1,2,3};
int out=a[4];// Here array out of bounds error occurs
}3. Linker Errors
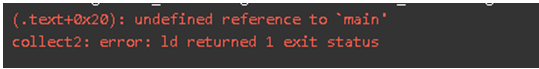
These errors are generated after compilation; we link the different object files with the main’s object using the Ctrl+F9 shortcut key. These errors occur when the executable program cannot be generated. This may be because of wrong function declaration, importing incorrect header files, etc. Most frequent linker error is writing Main() instead of a main() method.
Syntax:
void Main() // Here Main() method used instead of main() method
{
}4. Logical Errors
If our expectation is one thing and the resulting output is another, then that kind of error we call “Logical error.” Suppose we want the sum of the two numbers, but the given output is the multiplication of 2 digits; this is a Logical error. Detecting such errors is possible by performing line-by-line debugging.
Syntax:
void Main()
{
printf("%d",sum(10,20));
}
int sum(int a, int b)
{
return x*y;//expectation is sum but we are multiplying the numbers
}5. Semantic Errors
The C compiler generates this error only when the written code is in an incomprehensible format.
Syntax:
void main()
{
int x, y, z;
x + y = z; //semantic error }Examples of Types of Errors in C
Following are the examples are given below:
1. Syntax Error with Semicolon Example
Code:
#include<stdio.h> //Used to include basic c library files
void main() //Used to execute the C application
{
//declaring and defining the variables
int x = 10;
int y = 15;
//displaying the output
printf("%d", (x, y)) //Here semi-colon missed
}Output:
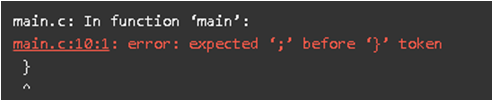
2. Syntax Error with Mustache Brace Example
Code:
#include<stdio.h> //Used to include basic c library files
void main() //Used to execute the C application
{
//declaring and defining the variables
int a = 100;
int b = 105;
//displaying the output
printf("%d %d",a,b);
//Here mustache brace missedOutput:
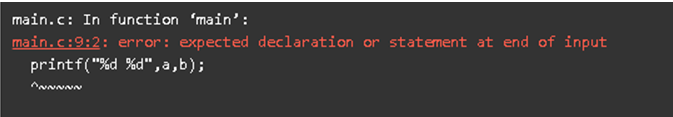
3. Run-Time Errors with Array Index out of Bounds Example
Code:
#include<stdio.h> //Used to include basic c library files
void main() //Used to execute the C application
{
//declaring and defining the array variables
int a[5] = {100,101,102,103,104};
int b[5] = {105,106,107,108,109};
//displaying the output
printf("%d\n",a[100]); //array index out of bounds run-time error
//in c this is not shown any error message it will just show out of bound values as 0
printf("%d\n",b[700]);//array index out of bounds run-time error
}Output:
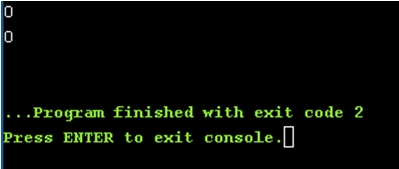
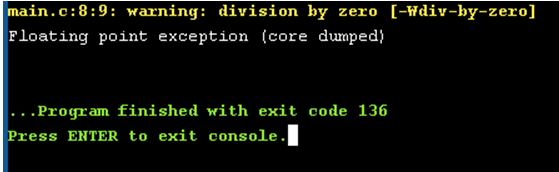
4. Run Time Error with Zero Divisible by Number Example
Code:
#include<stdio.h> //Used to include basic c library files
void main() //Used to execute the C application
{
//declaring and defining the variables
int x = 200;
int y = 400;
int a=x/10;
int b=y/0;
//displaying the output
printf("%d\n",a); // Here no divisible by zero error occurs
printf("%d\n",b); //divi by zero run time error
}Output:
5. Linker Error with Wrong Main() Method Syntax Example
Code:
#include<stdio.h> //Used to include basic c library files
void Main() //Linker error as wrong syntax of main method used
{
//declaring and defining the array variables
char a[] = "Amardeep";
char c[] = "Paramesh";
//displaying the output
printf("%s\n",a);
printf("%s\n",c);
}Output:
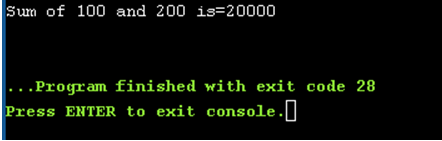
6. Logical Error Example
Code:
#include<stdio.h> //Used to include basic c library files
int sum(int a, int b);// Including method
void main()//main() method for executing the application
{
//declaring and defining the variables
int a=100;
int b=200;
//displaying the output
printf("Sum of %d and %d is=%d\n",a,b,sum(a,b));//sum(a,b) is calling method
}
//called method
int sum(int a, int b)
{
return a*b;//instead of sum here developer make a mistake by return multiplication logic
}Output:
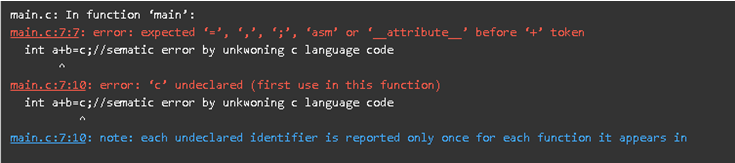
7. Sematic Error Example
Code:
#include<stdio.h> //Used to include basic c library files
void main() //main() method for executing the application
{
//declaring and defining the variables
int a=100;
int b=200;
int a+b=c;//sematic error by unkwoning c language code
//displaying the output
printf("%d %d",a,b);
}Output:
Conclusion
Errors in C language are occurred due to writing understandable statements passed to a compiler; then, the compiler throws some errors. These errors can be programmer mistakes or sometimes machine insufficient memory to load the code. Errors are mainly 5 types that are Syntax errors, Run-time errors, Linker errors, Logical errors, and Logical errors.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Types of Errors in C. Here we also discuss the Introduction and types of errors in c, along with different examples and code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –