Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Try-catch in PowerShell
A good practice while working on any script or program is to have a mechanism for error handling. Though it may take a little bit of additional time, its rewards are priceless. Try-catch in PowerShell in this article, it is not possible for any script or program to run without any error or issue 100% of the time. It is not necessary that an error always must occur because of logical errors in the script. Many external factors may also affect the successful running of the script. To avoid these kinds of surprises, it is better to implement the error handling mechanism.
There are two types of errors that can be occurring during script execution. They are terminating and non-terminating errors. As the name implies, terminating error will stop the program from further execution, whereas a non-terminating error will not stop the execution. An example of terminating error would be a syntax error whereas an example of non-terminating error would be missing a file.
Understanding Try-Catch
In PowerShell, the error handling is done through trial and catch blocks. The try block will have the code, that may likely throw an error. The catch block contains the code or action to be executed in case of an error that is thrown by the try block. Additionally, a final block can be used to free up the resources. Mostly, non-terminating errors can’t be handled in PowerShell. To handle such errors, they needed to be specifically converted to as a terminating error. This can be done using ErrorActionPreference.
Syntax:
The general syntax of the try-catch block is as follows
Try
{
//code1 that may generate exception
//code2 that may generate exception
//code3 that may generate exception
//to catch non-terminating error, convert them to terminating error
}
Catch(error)
{
//code to be executed
//multiple catch blocks can be included, or the same catch block can be used to catch multiple exceptions
// the error information is present inside the $_ variable
//The error can be logged to a text file or can trigger an email to inform some user about the error
}
Finally
{
//code to be executed
//this is an optional block of code
}
The syntax for Multiple Catch:
try
{
//code to be executed
}
catch [System.IO.DirectoryNotFoundException]
{
Write-Output "Directory Not Exception"
}
catch [System.IO.IOException]
{
Write-Output "Input/output Exception"
}
catch [System.IO.FileNotFoundException]
{
Write-Output "File Not Found Exception"
}
Parameters
Setting the Error action parameter can be done in many ways. The following are the possible values for the ErrorAction parameter.
- If -ErrorAction Stop: It throws the error and stops the execution of the program.
- If -ErrorAction Inquire/Continue: Throws error but continues with the execution of the program.
- If -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue: Error is not thrown, and the execution continues
- If – ErrorAction Ignore: Error is not thrown, and the execution continues
The difference between silently continue and ignore is that silently stores the error details in the $error variable whereas ignore doesn’t do that.
Examples of Try-catch in PowerShell
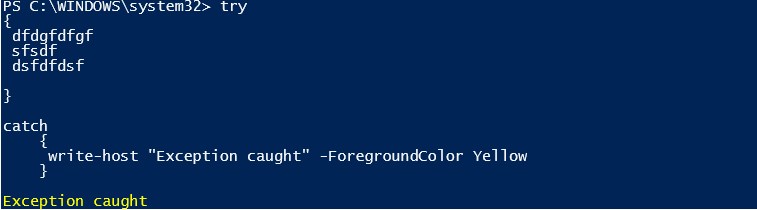
The below is a sample usage of Try, catch block:
Code:
try
{
dfdgfdfgf
sfsdf
dsfdfdsf
}
catch
{
write-host "Exception caught"
}
Output:
Example #1
Various parameters of ErrorActionPreference.
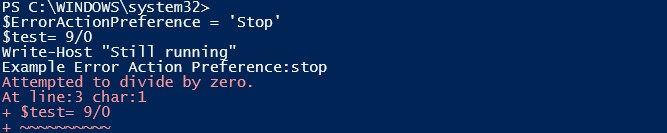
Code:
Write-Host "Example Error Action Preference: stop"
$ErrorActionPreference = 'Stop'
$test= 9/0
Write-Host "Still running"
Output:
As you can see, the execution is stopped immediately after an error has occurred.
Let’s change it to continue
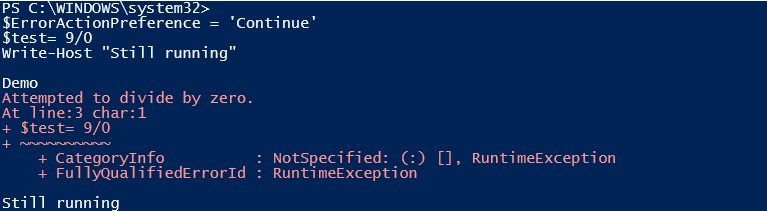
Code:
Write-Host " Demo"
$ErrorActionPreference = 'Continue'
$test= 9/0
Write-Host "Still running"
Output:
If you see in the above output, “Still running” is printed even after the occurrence of error
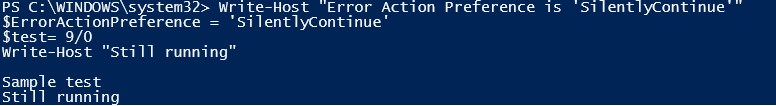
Let’s see the same input with ErrorActionSet set as ‘Silently continue’
Code:
Write-Host " Sample test"
$ErrorActionPreference = 'SilentlyContinue'
$test= 9/0
Write-Host "Still running"
Output:
As you can see, none of the errors are displayed on the screen and the execution is continued.
Example #2
Writing Error Message to Console.
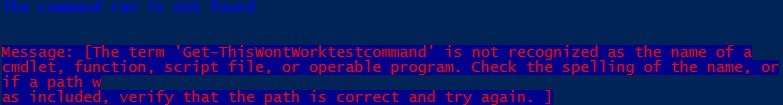
Code:
Try {
Get-ThisWontWorktestcommand
}
Catch {
Write-Host "The command ran is not found"`n -ForegroundColor Blue
Write-Host "Message: [$($_.Exception.Message)"] -ForegroundColor Red -BackgroundColor DarkBlue
}
Output:
Error Handling Best Practices
- If there is an exception that sits across your face, try to find a solution to avoid that completely instead of going for exception handling.
- Check the functionality of the code in case if the same error occurs frequently.
- Try to catch the specific type of exception that is trying block is going to return, in case of not knowing the type of exception that is going to occur create a generic catch block.
- Better to capture the exception message in an output file along with a timestamp and exception message.
- It is advisable not to create an empty catch block.
Conclusion
Thus, the article covered in detail about the try block feature in PowerShell. For any person aspiring to be a good developer in PowerShell, it is important that they have a very strong understanding of the error handling mechanism. In the case of automated jobs, without error handling mechanisms implemented in the code, it will be a nightmare for the administrator to understand what the issue is or when an issue has occurred.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Try-catch in PowerShell. Here we discuss the Understanding of Try-Catch, Error handling best practices along with the examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –