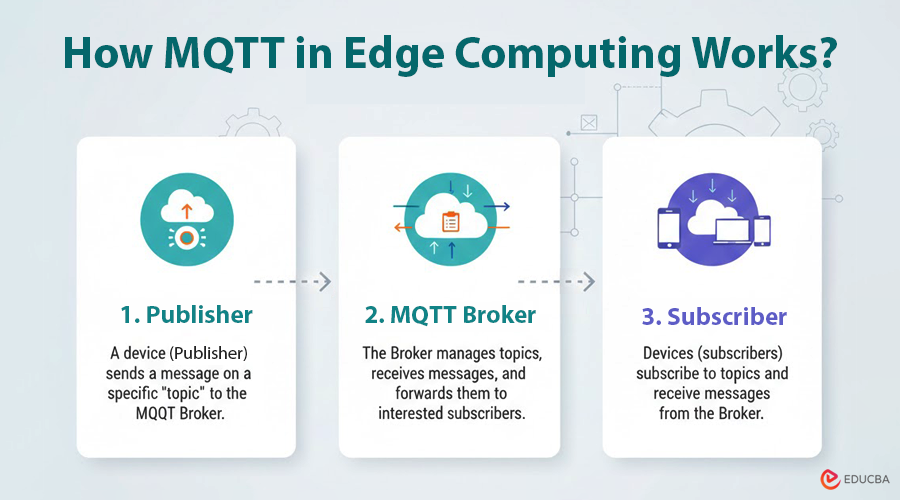
Introduction to MQTT in Edge Computing
In the rapidly evolving world of distributed systems and IoT, MQTT in Edge Computing has become a cornerstone for enabling efficient, real-time communication. MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is an ISO-standard, lightweight publish/subscribe messaging protocol designed for constrained devices and networks with high latency or unreliable connectivity. Its efficiency, reliability, and low overhead make it an ideal choice for edge computing, where data is processed close to its source to reduce delays, conserve bandwidth, and support faster, real-time decision-making.
As organizations increasingly adopt distributed architectures and IoT ecosystems, MQTT in Edge Computing provides a scalable, resilient, and high-performing framework for managing data communication across industries.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing refers to the architectural shift of processing data as close to the source as possible, such as industrial sensors, autonomous vehicles, smart grids, or consumer IoT devices, rather than sending everything to centralized cloud servers. This approach delivers key benefits like:
- Reduced latency: Faster processing for time-critical applications
- Efficient bandwidth use: Lower network load by filtering and pre-processing data locally
- Scalability: Support for massive IoT device ecosystems
- Improved reliability: Local decision-making, even with intermittent cloud connectivity.
At the heart of this paradigm lies the need for efficient communication among distributed components, an area where MQTT in Edge Computing demonstrates immense value.
Why MQTT Works Well at the Edge?
- Low overhead: Minimal packet structure reduces bandwidth consumption
- Quality of service levels: Three Quality of Service levels ensure message delivery reliability
- Publish/subscribe model: Decouples senders and receivers, fostering scalability
- Session persistence: Enables seamless reconnection after network disruptions
- Security support: Integrates with TLS/SSL for encrypted communication.
These features make MQTT a cornerstone protocol in modern distributed systems and a natural choice for MQTT in Edge Computing implementations.
Key Benefits of MQTT in Edge Computing Architectures
1. Real-Time Data Exchange
Edge systems often operate in environments where timely data is critical, such as predictive maintenance, autonomous control, or emergency response systems. MQTT’s efficient message routing and minimal overhead enable fast, reliable data propagation across edge nodes.
2. Fault Tolerance and Resilience
In edge scenarios, networks can be unpredictable. MQTT’s session persistence and reconnection strategies ensure that devices can recover from intermittent connectivity without losing context.
3. Scalability for Large IoT Deployments
The publish/subscribe design of MQTT allows thousands, or even millions, of devices to communicate without overwhelming centralized services. This is especially important in smart cities, industrial IoT, and distributed sensor networks.
4. Lower Bandwidth Usage
Because MQTT minimizes message size and allows selective data transmission, it conserves precious bandwidth, an advantage in remote or bandwidth-constrained locations.
Core Components of an MQTT-Driven Edge Architecture
An MQTT-based edge computing solution typically includes the following elements:
- Edge devices: Sensors, controllers, and embedded devices generating data
- Local MQTT broker: Manages message routing at the edge
- Edge analytics engines: Process data locally
- Cloud integration: For long-term storage, analytics, or orchestration
- Security services: For encryption, authentication, and access control.
Choosing the Right MQTT Platform
To successfully implement MQTT in Edge Computing, selecting a robust MQTT Platform is essential. A capable MQTT platform provides features such as scalable brokers, secure connectivity, flexible deployment options (edge, hybrid, cloud), and efficient monitoring and management tools.
How MQTT Enhances Edge Computing?
1. Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Factories rely on real-time data from sensors and machines to optimize production and detect anomalies. MQTT in Edge Computing enables local decision-making while synchronizing with centralized systems.
2. Smart Transportation
Connected vehicles process vast amounts of data with minimal delay. MQTT enables vehicle-to-infrastructure communication through lightweight messaging.
3. Healthcare Monitoring
Wearables and bedside monitors continuously transmit patient data. Edge analytics powered by MQTT ensures timely alerts while conserving network resources.
4. Smart Cities
From traffic signals to environmental sensors, smart cities generate a deluge of data. MQTT’s efficient messaging model handles this volume while enabling distributed processing at the edge.
Security Considerations for MQTT in Edge Computing
While MQTT is efficient, edge deployments must address:
- Encryption: Use TLS/SSL to protect messages in transit
- Authentication & authorization: Implement robust credential management
- Network security: Secure edge nodes behind firewalls or VPNs
- Monitoring & auditing: Track MQTT activity for anomalies.
Integrating security best practices ensures that MQTT in Edge Computing remains robust against threats.
Best Practices for Implementing MQTT at the Edge
- Deploy local MQTT brokers: Reduce latency and maintain autonomy
- Use quality of service levels thoughtfully: Balance delivery guarantees with performance
- Structure topics clearly: Ensure scalable and maintainable message flows
- Implement edge-to-cloud gateways: Bridge local systems with broader analytics or control planes
- Monitor performance: Track throughput, latency, and error rates to optimize deployments.
MQTT and Evolving Edge Technologies
As edge computing continues to grow, MQTT in Edge Computing will increasingly intersect with technologies such as:
- AI/ML at the edge: MQTT can deliver sensor insights for real-time inference
- 5G connectivity: Enhanced network performance will expand edge capabilities
- Serverless edge functions: Lightweight compute tied to MQTT events.
These trends further validate MQTT’s role in scalable, efficient distributed systems.
Final Thoughts
In the landscape of distributed architectures, MQTT in Edge Computing stands out as a reliable, lightweight, and scalable communication protocol. Its design fits modern edge deployments well, enabling real-time data exchange, strong reliability, and low network overhead. By using a reliable MQTT Platform and following best practices, organizations can fully benefit from edge computing across different industries.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide to the role of MQTT in Edge Computing helps you understand how businesses can achieve real-time data exchange, scalability, and reliable IoT communication. Explore these recommended articles for expert insights, practical strategies, and the latest trends in edge computing, IoT, and industrial automation.