Updated March 21, 2023
Introduction to Templates in C++
When it comes to powerful features in any programming language C++ is considered as the first priority. Templates are example of powerful C++ feature. It’s a code written in a way to make it independent of the data type. The template is a formula for creating generic functions or classes. Generic programming is used where generic types are used as arguments in algorithms for compatibility with different data types. You don’t have to write the code again and again for performing the same operation just for a change in the data type of a function or class.
Types of Templates in C++
There are basically two types of templates in the C++ programming language.
Let’s have a look at them:
1. Function Templates
As we are using generic programming therefore this function templates is just a normal function with only one key difference. Normal function can work only with defined data type inside the function whereas function template is designed in such a way that makes it independent of the data types, in fact, these templates can work with any data type you want.
The general syntax for defining a function template is:
template <class F>
F function_name ( F args ) {
Function body
}Here, F is the template argument and class is a keyword. F can accept different data types.
Here is the C++ program to demonstrate the function template in programming.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename F>
void swapping(F &arg1, F &arg2)
{
F temporary;
temporary = arg1;
arg1 = arg2;
arg2 = temporary;
}
int main()
{
int x = 100, y = 200;
double p = 100.53, q = 435.54;
char ch1 = 'A', ch2 = 'Z';
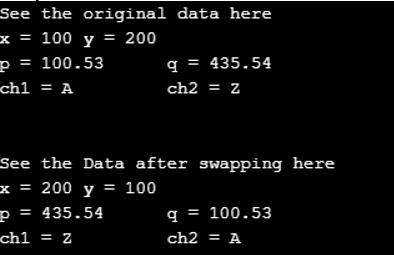
cout << "See the original data here\n";
cout << "x = " << x << "\ty = " << y<<endl;
cout << "p = " << p << "\tq = " << q<<endl;
cout << "ch1 = " << ch1 << "\t\tch2 = " << ch2<<endl;
swapping(x, y);
swapping(p, q);
swapping(ch1, ch2);
cout << "\n\nSee the Data after swapping here\n"
cout << "x = " << x << "\ty = " << y<<endl;
cout << "p = " << p << "\tq = " << q<<endl;
cout << "ch1 = " << ch1 << "\t\tch2 = " << ch2<<endl;
return 0;
}Output:
2. Class Templates
As we are using generic programming therefore this class templates is also similar to function templates. It’s like a normal class with only one key difference. Normally we declare a class so that it can work only with defined data type inside the class whereas class template is designed in such a way that makes it independent of the data types, in fact, these templates can work with any data type you want.
Instead of creating a new class every time for using a functionality based on a particular data type it is better to define a generic class template that is compatible with maximum data types. Class templates help us in code reusability which makes our program perform faster and produce better efficiency.
The general syntax for defining a class template is:
template <class F>
class Class_Name
{
... ..
public:
F variable;
F function_name(F arg);
... ..
};Here F is the template argument for data type used, class_name can be according to your choice and a member variable name variable and a function with function_name is defined inside the class.
Here is the C++ program to demonstrate the class template in programming.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class F>
class Calci
{
private:
F x, y;
public:
Calci(F p, F q)
{
x = p;
y = q;
}
void showresult()
{
cout << "The Numbers are: " << x << " and " << y << "." << endl;
cout << "Addition is: " << add() << endl;
cout << "Subtraction is: " << subtract() << endl;
cout << "Product is: " << multiply() << endl;
cout << "Division is: " << divide() << endl;
}
F add() { return x + y; }
F subtract() { return x - y; }
F multiply() { return x * y; }
F divide() { return x / y; }
};
int main()
{
Calci<int> intCalc(2, 1);
Calci<float> floatCalc(2.4, 1.2);
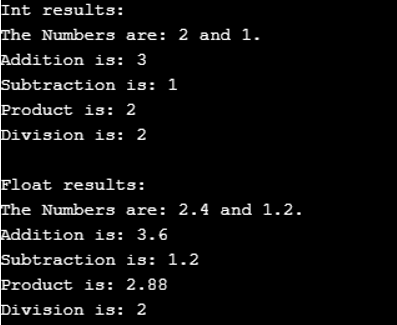
cout << "Int results:" << endl;
intCalc.showresult();
cout << endl << "Float results:" << endl;
floatCalc.showresult();
return 0;
}Output:
3. Variadic Templates
Only templates can take a variable number of arguments as the arguments are resolved at runtime and are type-safe. It is a better template to use as compared to others because the rest of the templates can only take fix number of arguments.
Here is the C++ program to demonstrate the Variadic template.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
template<typename F>
F aggregate(F val) {
return val;
}
template<typename F, typename... Args>
F aggregate(F first, Args... args) {
return first + aggregate(args...);
}
int main()
{
long total = aggregate(11, 72, 83, 78, 37);
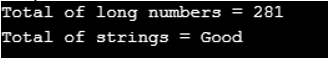
cout<<"Total of long numbers = "<<total<<endl;
string s1 = "G", s2 = "o", s3 = "o", s4 = "d";
string s_concat = aggregate(s1, s2, s3, s4);
cout << "Total of strings = "<<s_concat;
}Output:
Aggregate is the variadic function so we need a base function that can implement a base case after that we can implement variadic function at top of the functions. Once you write the template for the function that is implementing the base case we write a variadic function to implement it as a general case. This functionality is similar to recursion. The output we see is the aggregation of all the long integers and characters we have passed in the above C++ code.
Conclusion
The templates feature in the programming plays a vital role in making a program efficient in terms of performance and memory space because of the code reusability feature. Template functions can be easily overloaded as you can define a cluster of classes and functions for handling multiple data types.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Templates in C++. Here we discuss the basic concept, 3 different types of templates in C++ along with the respective examples. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –