Updated May 10, 2023

Introduction to Table in MySQL
Tables are the structured format of saving records in a database as this is easy to access and can be maintained by drawing relations between multiple tables. In the table in MySQL, there are two kinds of tables, called parent and child tables. There must be a primary key in each table that uniquely identifies each record. In the child table, the primary key is one attribute from the parent table, which may also be called a foreign key as this key establishes a relationship between 2 tables. If a common field exists between 2 tables, we can join both tables using multiple types of join commands like inner join, outer join, and left & right join. This table can consists many kind of datatypes as INT(), SMALLINT(), BIGINT(), CHAR(), VARCHAR(), DATE(), TIME(), TIMESTAMP(), BOOLEAN() etc. We can perform many table operations, such as joining, subquery, etc.
How to Create a Table in MySQL?
There are many kinds of SQL languages.
This is categorized into:
Creating a table, altering, and dropping a table comes under DDL.
| Commands | Description | Sample Query |
| CREATE | It is used to create a table or database. | CREATE table employee; |
| ALTER | Used to modify or change values in the table. | ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD COLUMN col_name; |
| RENAME | Rename the table or database name. | ALTER TABLE table_name
RENAME COLUMN col_name TO new_col_name; |
| DROP | This removes records of a table as well as the structure of a table. This can’t be rolled back/undo. | DROP TABLE IF EXISTS table_name; |
| TRUNCATE | This empties the records only and leaves the structure for future records. | TRUNCATE TABLE employee; |
Let’s create a customer table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE (IF NOT EXIST) 'tablename'
'Fieldname' datatype (optional parameter)
PRIMARY KEY ('Fieldname');OR
CREATE TABLE (IF NOT EXIST) 'Tablename'
'Fieldname' datatype PRIMARY KEY;- “CREATE TABLE” is responsible for creating a new table in the database.
- “IF NOT EXIST” is not mandatory to give. It checks whether the name we want to give to the new table already exists in the database.
- “Datatype” is referred to which kind of datatype we want to assign the attribute. E.g., numeric, string, date, etc.
- At the end of the line also, we can derive the constraints like primary key, unique key, not null, etc.
Best practices:
- We should use upper case for SQL keywords like SELECT, DELETE, DROP, etc.
- It would be best always to end the SQL query with a semicolon.
- We should always avoid spaces between the name of the table or field names. Instead, we should use underscore like student_table, customer_order, etc.
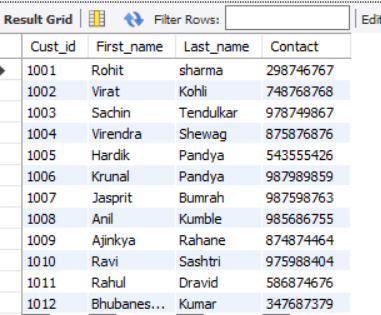
Let’s create the below ‘customer’ table in the database:
| Cust_id | First_name | Last_name | Contact |
| 1009 | Ajinkya | Rahane | 8746874464 |
| 1005 | Hardik | Pandya | 5435555426 |
| 1007 | Jasprit | Bumrah | 9875986763 |
| 1002 | Virat | Kohli | 7487687648 |
| 1010 | Ravi | Sashtri | 9759878404 |
| 1006 | Krunal | Pandya | 9874989859 |
| 1012 | Bhubaneswar | Kumar | 3547687379 |
| 1004 | Virendra | Shewag | 8765876876 |
| 1003 | Sachin | Tendulkar | 9878749867 |
| 1008 | Anil | Kumble | 9856876755 |
| 1001 | Rohit | Sharma | 2986746767 |
| 1011 | Rahul | Dravid | 5876874676 |
Step 1: Create the table with these fields.
Code:
CREATE TABLE customer (
Cust_id INT(10),
First_name VARCHAR(20) not null,
Last_name VARCHAR(20) not null,
Contact INT(10),
PRIMARY KEY (Cust_id)
);Step 2: Insert all records.
Code:
INSERT INTO customer
VALUES
(1009, 'Ajinkya','Rahane', 8746874464),
(1005, 'Hardik', 'Pandya', 5435555426),
(1007, 'Jasprit', 'Bumrah', 9875986763),
(1002, 'Virat', 'Kohli', 7487687648),
(1010, 'Ravi', 'Sashtri', 9759878404),
(1006, 'Krunal', 'Pandya', 9874989859),
(1012, 'Bhubaneswar', 'Kumar', 3547687379),
(1004, 'Virendra', 'Shewag', 8765876876),
(1003, 'Sachin', 'Tendulkar', 9878749867),
(1008, 'Anil', 'Kumble', 9856876755),
(1001, 'Rohit', 'Sharma', 2986746767),
(1011, 'Rahul', 'Dravid', 5876874676);Output:
How to Alter the Table in MySQL?
Alter is basically for manipulating a table, like adding a new column, changing the name of an existing column, dropping a current column, renaming the table name, and adding constraints.
Example #1
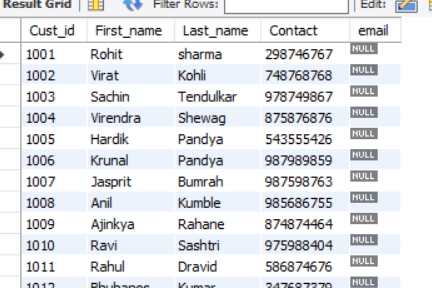
We are adding a new column.
Code:
ALTER TABLE customer
ADD COLUMN email VARCHAR(50);Output:
Example #2
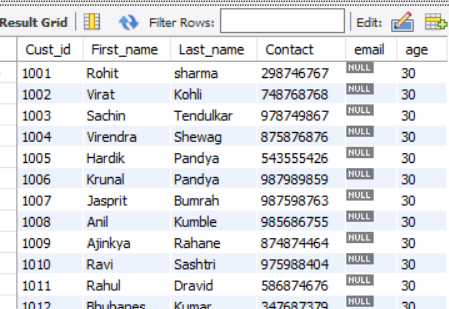
Code:
ALTER TABLE customer
ADD COLUMN age INT(5)
DEFAULT 30;Output:
Example #3
Code:
ALTER TABLE customer
DROP COLUMN email ;Output:
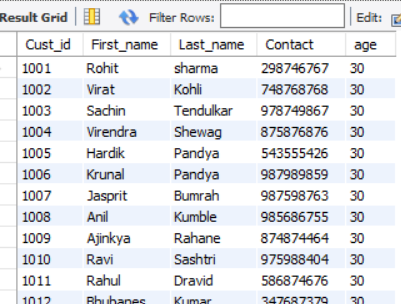
Example #4
Code:
ALTER TABLE customer
RENAME COLUMN Cust_id TO Customer_id;Output:
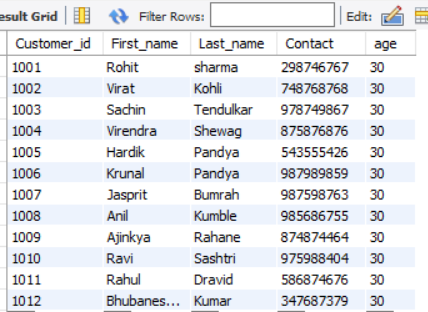
How to Delete a Table in MySQL?
There are three kinds of commands for deletion: DROP, TRUNCATE, and DELETE.
DROP table deletes the whole records as well as the structure/index of the table.
Syntax:
DROP TABLE Table_name;TRUNCATE table deletes only the records from the table by keeping the structure for further use.
Syntax:
TRUNCATE TABLE Table_name;DELETE is used with the WHERE clause to delete the records from the table.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM customer
WHERE first_name LIKE 'A%';Output:
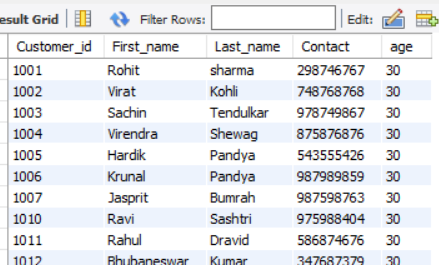
(It deleted all the records where first_name starts with ‘A’)
Conclusion
Those tables in SQL give advantages to keeping data in structural form so that we can use those records and perform many operations efficiently. A unique field can identify each row for better accessibility to particular records. In the database, using those tables, we can establish many relationships with different tables/data by creating some foreign keys. This helps us store large amounts of data with easy, secure, and faster accessibility.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Table in MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

