Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to T-SQL Union
The Union in the T-SQL is defined as, it is an operator that can be utilized to merge the output of two queries, but it cannot generate a separate row from columns and put together from two tables; it can accept three parameters such as expression, tables, and where conditions, and generate a set of output which can have several rows which are engaged in the union queries, the Union cannot allows the duplicate values and also it can describe that the different set of outputs can be merged and give back a single group of output sets.
Overview of T-SQL Union
The UNION operator is utilized to merge the output from two or more queries also; it can remove the matched rows between the distinct select statement; every SELECT statement under the UNION can have a similar amount of data in the output set, which means the order of columns which are present in each SELECT statement needs to be in equal order, and also needs to have equal data types.
Syntax:
SELECT declaration1, declaration2, ... declaration_n
FROM table1
[WHERE conditions]
UNION
SELECT declaration1, declaration2, ... declaration_n
FROM table2
[WHERE conditions];Parameters:
- Declaration: It is the column in which we can gain the data.
- Tables: We can access the records in which one table must have been selected from the FROM clause through the tables.
- WHERE conditions: This is the optional condition that must be fulfilled with the determined records.
All T-SQL Union
The Union can be used with various clauses:
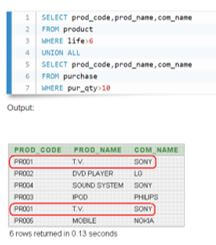
1. Union all with where
Let us see an example in which two queries have been put together using two various criteria having a ‘WHERE’ clause, then all the rows we get will show in the output set.
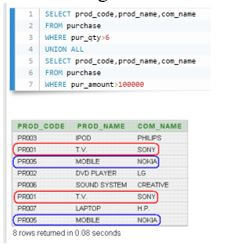
2. Union a table to itself
This example utilizes the two queries that have been put with two various criteria in the surviving table, so all the rows will be shown here.
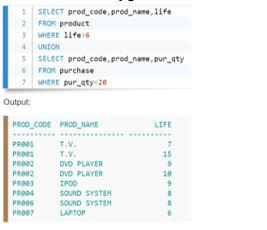
3. Union with different columns
In this example, we have utilized two queries put into two criteria and the various columns; the multiple columns in the two statements have the same data type for that column.
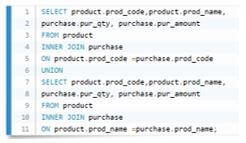
4. Union with inner join
In this case, we have tried to use a union that can be produced by using two queries in which queries can be the two joined statements.
Examples of T-SQL Union
Different examples are mentioned below:
1. By utilizing a simple Union
For the use of simple Union, let us first want a database, so in the below screenshot, we can see that the AdventureWorks database has been used.
Code:
IF OBJECT_ID ('dbo.Margin', 'V') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.Margin;
GOAfter that, we created a ‘Margin’ table.
Code:
SELECT DataItemID, Name
INTO dbo.Margin
FROM Data.DataItem
WHERE DataItemID IN (5, 6);
GOLet us see how the Union can work between two queries.
Code:
SELECT DataItemID, Name
FROM Data.DataItem
WHERE DataItemID NOT IN (5, 6)
UNION
SELECT DataItemID, Name
FROM dbo.Margin
ORDER BY Name;
GOIn the above example, we try to merge two data; in the first query, we try to extract data from the table, and in the second query, we try to extract data from the database.
2. To utilize the SELECT INTO with Union
First, we used the database Adventure works.
Code:
SELECT DataItemID, Name
INTO dbo.DataResults
FROM Dara.DataModel
WHERE DataItemID NOT IN (5, 6)
UNION
SELECT DataItemID, Name
FROM dbo.Margin;
GOIn the above example, we have used clause ‘INTO’ to define the table name ‘DataResults,’ which can handle output in which UNION can create columns from ‘DataItem’ and ‘Margin’ tables, and we have created the Margin table in the first example.
3. Union of two SELECT statements by using ORDER BY
As we have created the ‘Margin’ table in the first example.
Let us see the Union of the database and table using the ORDER BY clause.
Code:
SELECT DataItemID, Name
FROM Data.DataItem
WHERE DataItemID NOT IN (5, 6)
UNION
SELECT DataItemID, Name
FROM dbo.Margin
ORDER BY Name;
GOExample of utilizing three SELECT statements to see the result of ALL
Let us see examples of Union merging the output of three tables that may have the five rows of data; it utilizes the following AdventureWorks.
Code:
IF OBJECT_ID ('dbo.StudentOne', 'V') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.StudentOne;
GO
IF OBJECT_ID ('dbo.StudentTwo', 'V') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.StudentTwo;
GO
IF OBJECT_ID ('dbo.StudentThree', 'V') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.StudentThree;
GOLet us see an example that can utilize ‘UNION ALL’ to provide the matched records, and it will give back the number of records. In the second example, UNION has been without ALL and can remove the matched record from merging three select statements.
Code:
SELECT pp.LName, pp.FName, e.WorkTitle
INTO dbo.StudentOne
FROM Human.Human AS pp JOIN HR.Student AS e
ON e.TradeEntityID = pp.TradeEntityID
WHERE LName = 'James';
GO
SELECT pp.LName, pp.FName, e.JobTitle
INTO dbo.StudentTwo
FROM Human.Human AS pp JOIN HR.Student AS e
ON e.TradeEntityID = pp.TradeEntityID
WHERE LName = 'James';
GO
SELECT pp.LName, pp.FName, e.WorkTitle
INTO dbo.StudentThree
FROM Human.Human AS pp JOIN HR.Student AS e
ON e.TradeEntityID = pp.TradeEntityID
WHERE LName = 'James';
GOCode:
SELECT LName, FName, WorkTitle
FROM dbo.StudentOne
UNION ALL
SELECT LName, FName ,WorkTitle
FROM dbo.StudentTwo
UNION ALL
SELECT LName, FName,WorkTitle
FROM dbo.StudenteThree;
GO
SELECT LName, FName,WorkTitle
FROM dbo.StudentOne
UNION
SELECT LName, FName, WorkTitle
FROM dbo.StudentTwo
UNION
SELECT LName, FName, WorkTitle
FROM dbo.StduentThree;
GO
SELECT LName, FName,WorkTitle
FROM dbo.StudentOne
UNION ALL (
SELECT LName, FName, WorkTitle
FROM dbo.StudentTwo
UNION
SELECT LName, FName, WorkTitle
FROM dbo.StudentThree );
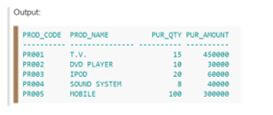
GOOutput:
In the above example, we have used three examples in which, from the second example, we are not allowed duplicate values, and UNION ALL can allow duplicates in the second example.
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the Union in T-SQL is the operator who can concatenate two queries together, and we get results in one set, so we have discussed the concept of Union and described the examples of it so it will help to understand the idea.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to T-SQL Union. We discuss the introduction, overview, all T-SQL unions, and examples for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –