Updated March 14, 2023
Introduction to Switch Statement in C
Before we learn what is Switch statement in C, let us first understand what C. C is, a procedure-oriented programming language developed by Dennis Ritchie. The basic purpose behind developing the C language was to use it as a programming language of the system, i.e. to program an operating system. Many languages borrow their syntax from this C language. C++, for instance, is an extension or can be considered as an upgraded version of the C programming language.
What is Switch Statement in C?
Consider a case where you have been given a bunch of keys of different sizes. Now you are asked to open a door using one of the keys from this bunch. So what will be your approach towards this problem? It is simple, and you guessed it right, you will pick one key and try to unlock the door using it. If this key does not open the door, you try with another key. The process continues until you’ve finally found the key which unlocks the door. After the key is found and the door is unlocked, you stop. In case if you are able to find the key on the first attempt, you will not keep on trying with the other keys after that, correct?
Similar is the case with the switch statement. This example can help you easily understand the basic definition and flow of the switch statement. The basic flow and functionality of the switch statement remain the same in all the programming languages. The difference can be seen only in the general syntax based on the programming language being used.
In a very basic term, a switch statement evaluates an expression, tests it, and compares it against the several cases written in the code. As soon as the match with any case is found, the control enters into this case and starts executing the statements written within this case until a break statement is encountered. As soon as a break statement appears, the switch statement terminates, and the program control exits the switch.
It might sometimes happen that no case matches up with the value of the expression. For such cases, we mention a default case that will always execute in case if no match is found. The cases in a block of the switch statement are represented by different numbers or strings, which is known as an identifier. The value of the expression or the value provided by the user is compared with these cases until the match is found.
The syntax for switch statement in C programming language is given below:
Syntax :
switch( expression )
{
case value1:
//Block of code;
break;
case value2:
//Block of code;
break;
case valueN:
//Block of code
break;
default:
//Block of code
break;Example:
This example will give more clarity about the use of switch statement.
Code:
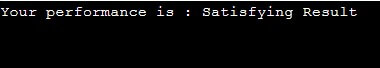
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
char grade_report = 'D';
printf("Your performance is : ");
switch(grade_report) {
case 'A' :
printf("Outstanding Result!\n" );
break;
case 'B' :
printf("Excellent Result!\n" );
break;
case 'C' :
printf("Good Result\n" );
break;
case 'D' :
printf("Satisfying Result\n" );
break;
case 'F' :
printf("Poor Result\n" );
break;
default :
printf("You did not appear for exam\n" );
}
return 0;
}Output:
Flowchart of Switch Statement
Given below is the flowchart of switch statement:
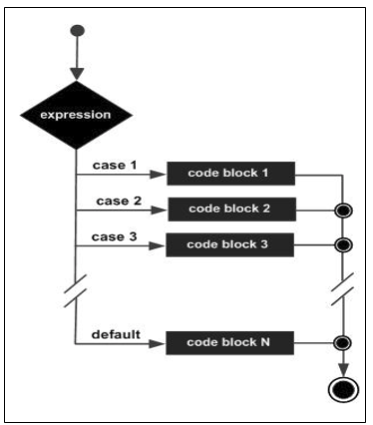
How does Switch Statement work in C?
Let us understand the flow of control depicted in the flowchart above in order to gain a better understanding of the flow of execution.
An expression is passed with the switch statement, which is equal to one of the values of the cases. In case the value is not equal, the default case is executed. The value of this expression is then compared with the case identifier or the first case. If the first case matches, then the block of code associated with the first case is executed.
Once the break is encountered, the execution stops, and you will exit the switch statement. However, if the case does not match, the execution flows to the next case. If this case matches, then the second code block executes; otherwise, the flow checks the next case in a similar way. Finally, if no case matches, then the default code block is executed.
Examples for Switch Statement in C
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
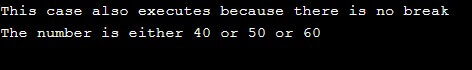
This example depicts the use of the break statement in the switch. If the break statement is not specified after the case, the execution flow will continue until it encounters the break statement.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int range_of_number=50;
switch (range_of_number) {
case 10:
case 20:
case 30:
printf("The number is 10 or 20 or 30 ");
break;
case 50:
case 55:printf("This case also executes because there is no break ");
printf("\n");
case 60:
printf("The number is either 40 or 50 or 60");
break;
default:
printf("The number is greater than 60");}}Output:
Example #2
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 10, y = 5;
switch(x==y && x+y<10)
{
case 1:
printf("hi");
break;
case 0:
printf("bye");
break;
default:
printf(" Hello bye ");
} }Output :

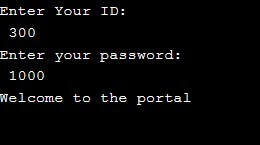
Example #3
Nested Switch Statement.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int ID = 300;
int password = 1000;
printf("Enter Your ID:\n ");
scanf("%d", & ID);
switch (ID) {
case 300:
printf("Enter your password:\n ");
scanf("%d", & password);
switch (password) {
case 1000:
printf("Welcome to the portal\n");
break;
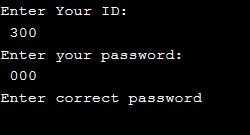
default:
printf("Enter correct password");
break;
}
break;
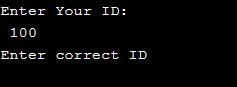
default:
printf("Enter correct ID");
break;
}
}Output :
This will depend upon the values entered by the user.
Output 1 :
Output 2:
Output 3:
Conclusion
Switch case statements are a controlled statement that is regarded as a substitute for if-else statements. It is a multiway branch statement that provides a way to organize the flow of execution to parts of code based on the value of the expression.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Switch Statement in C. Here we also discuss the basic concept and how switch statement works in C, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


