Updated March 20, 2023
What is SVM Algorithm?
SVM stands for Support Vector Machine. SVM is a supervised machine learning algorithm that is commonly used for classification and regression challenges. Common applications of the SVM algorithm are Intrusion Detection System, Handwriting Recognition, Protein Structure Prediction, Detecting Steganography in digital images, etc.
In the SVM algorithm, each point is represented as a data item within the n-dimensional space where the value of each feature is the value of a specific coordinate.
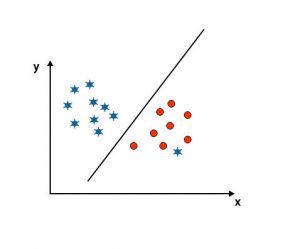
After plotting, classification has been performed by finding hype plane, which differentiates two classes. Refer to the below image to understand this concept.
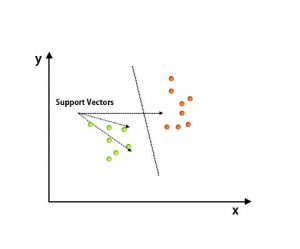
Support Vector Machine algorithm is mainly used to solve classification problems. Support vectors are nothing but the coordinates of each data item. Support Vector Machine is a frontier that differentiates two classes using hyper-plane.
How does the SVM algorithm work?
In the above section, we have discussed the differentiation of two classes using hyper-plane. Now we are going to see how does this SVM algorithm actually Works.
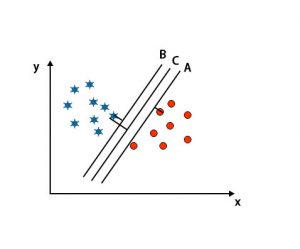
Scenario 1: Identify the right hyper-plane
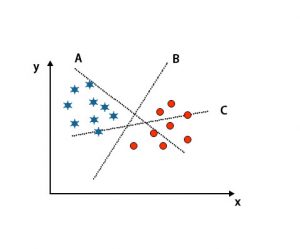
Here we have taken three hyper-planes, i.e., A, B and C. Now we have to identify the right hyper-plane to classify stars and circle.
To identify the right hyper-plane, we should know the thumb rule. Select hyper-plane which differentiates two classes. In the above-mentioned image, hyper-plane B differentiates two classes very well.
Scenario 2: Identify the right hyper-plane
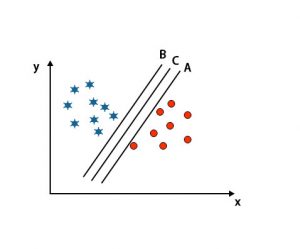
Here we have taken three hyper-planes, i.e. A, B, and C. These three hyper-planes are already differentiating classes very well.
In this scenario, we increase the distance between the nearest data points to identify the right hyper-plane. This distance is nothing but a margin. Refer to the below image.
In the above-mentioned image, the margin of hyper-plane C is higher than the hyper-plane A and hyper-plane B. So in this scenario, C is the right hyperplane. If we choose the hyperplane with a minimum margin, it can lead to misclassification. Hence we chose hyperplane C with maximum margin because of robustness.
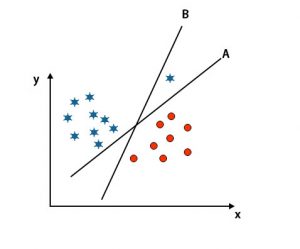
Scenario 3: Identify the right hyper-plane
Note: To identify the hyper-plane, follow the same rules as mentioned in the previous sections.
As you can see in the above-mentioned image, the margin of hyper-plane B is higher than the margin of hyper-plane A; that’s why some will select hyper-plane B as a right. But in the SVM algorithm, it selects that hyper-plane which classify classes accurate prior to maximizing margin. In this scenario, hyper-plane A has classified all accurately, and there is some error With the classification Of hyper-plane B. Therefore, A is the right hyper-plane.
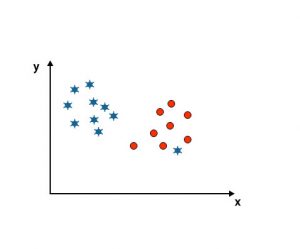
Scenario 4: Classify two classes
As you can see in the below-mentioned image, we are unable to differentiate two classes using a straight line because one star lies as an outlier in the other circle class.
Here, one star is in another class. For star class, this star is the outlier. Because of the robustness property of the SVM algorithm, it will find the right hyperplane with a higher margin ignoring an outlier.
Scenario 5: Fine hyper-plane to differentiate classes
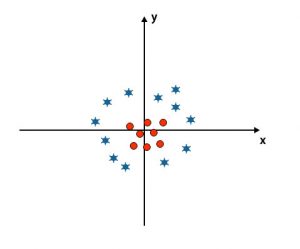
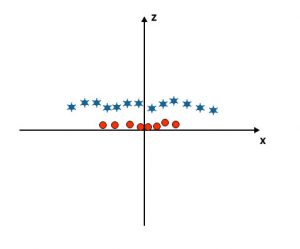
Till now, we have looked at the linear hyper-plane. In the below-mentioned image, we don’t have a linear hyper-plane between classes.
To classify these classes, SVM introduces some additional features. In this scenario, we are going to use this new feature z=x^2+y^2.
Plots all data points on the x and z-axis.
Note
- All the values on the z-axis should be positive because z is equaled to the sum of x squared and y squared.
- In the above-mentioned plot, red circles are closed to the origin of the x-axis and y-axis, leading the value of z to lower, and star is exactly the opposite of the circle, it is away from the origin of the x-axis and y-axis, leading to the value of z to high.
In the SVM algorithm, it is easy to classify using linear hyperplane between two classes. But the question that arises here is should we add this feature of SVM to identify hyper-plane. So the answer is no, to solve this problem, SVM has a technique that is commonly known as a kernel trick.
Kernel trick is the function that transforms data into a suitable form. There are various types of kernel functions used in the SVM algorithm, i.e. Polynomial, linear, non-linear, Radial Basis Function, etc. Here using kernel trick, low dimensional input space is converted into a higher-dimensional space.
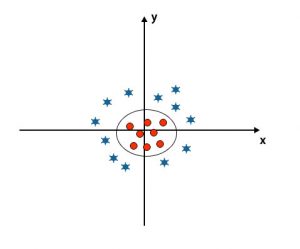
When we look at the hyperplane, the origin of the axis and y-axis looks like a circle. Refer to the below image.
Pros of SVM Algorithm
- Even if input data are non-linear and non-separable, SVMs generate accurate classification results because of their robustness.
- The decision function uses a subset of training points called support vectors; hence, it is memory efficient.
- It is useful to solve any complex problem with a suitable kernel function.
- In practice, SVM models are generalized, with less risk of overfitting in SVM.
- SVMs works great for text classification and when finding the best linear separator.
Cons
- It takes a long training time when working with large datasets.
- It is hard to understand the final model and individual impact.
Conclusion
It has been guided to Support Vector Machine Algorithm, which is a machine learning algorithm. This article discussed what the SVM algorithm, how it works, and Its advantages in detail is.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to SVM Algorithm. Here we discuss its working with a scenario, pros, and cons of SVM Algorithm respectively. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –