Updated July 12, 2023
Definition of Straight Line Depreciation Method
Straight line depreciation method is one of the methods used for depreciating the asset where the amount of depreciation is the same throughout the life of the asset, which is to be charged per year in the company’s income statement.
The amount of depreciation is calculated by dividing the difference between the asset’s value and the salvage value by the asset’s life.
Explanation
It is one of the methods for charging depreciation. In Straight line depreciation method, the depreciation charged amount is constant throughout the asset’s life. Generally, it is calculated as the value of an asset less its salvage value divided by the life of the asset or the prescribed rate is determined for depreciating under the straight-line method, say an asset is of cost $ 100,000, and depreciation is to be charged at 10% over 10 years. So, the depreciation will be $ 10,000 every year. This method is considered the easiest method of charging depreciation, and the calculation of this method is also easy. On both tangible and intangible assets, straight-line depreciation can be charged. Amortization can also be done on a straight-line basis.
The Formula for Straight Line Depreciation Method
The formula for calculating Straight line depreciation method is as under:
The asset’s value is the value at which the asset is recorded in the balance sheet. It is generally called the historical cost of the asset.
Salvage value is the estimated value that can be realized at the end of the asset’s life. It is the minimum value which is like the sale of scrap. The asset’s life is the expected life through which the asset is expected to generate revenue.
How to Calculate Straight Line Depreciation Method?
Here are the steps for calculating the straight-line depreciation on the assets:
- Step 1: Determine the value of the asset. It is the asset’s historical cost or the asset’s value shown in the balance sheet.
- Step 2: Determine the Salvage Value of the asset. It is the estimated realizable value at the end of the asset’s life. The valuer determines it, which is the minimum value the seller can get at the end of the asset’s life.
- Step 3: Determine the life of the Asset. The registered valuer also determines it. The life of an asset is the years up to which the asset can generate revenue for the organization.
- Step 4: Calculate the Depreciation by applying the formula:
Depreciation = (Value of Asset – Salvage Value) / Life of Asset
The depreciation so calculated is to be charged over the life and debited to the profit and loss account.
Example of Straight Line Depreciation Method
ABX Ltd. has purchased 2 assets costing $ 500,000 and $ 700,000. The salvage value of Asset 1 is $ 5,000, and asset 2 is $ 10,000. The life of both assets is 10 years. Asset one is sold at $ 100,000 at the beginning of the 7th year. Calculate the depreciation and determine the profit or loss on the asset’s sale. Calculate the Value of the asset at the beginning of year 7.
Solution:
Calculation of Depreciation as per Straight line method on Asset 1
| Particulars | Value |
| Value of Asset | $500,000.00 |
| Less: Salvage value | $5,000.00 |
| Life of Asset (In years) | 10 |
| Depreciation | 49,500.00 |
Depreciation is calculated as
Depreciation = Value of Asset – Salvage Value / Life of Asset
- Depreciation = (500,000-5,000)/10
- Depreciation = $49,500
Calculation of Depreciation as per Straight line method on Asset 2
| Particulars | Value |
| Value of Asset | $700,000.00 |
| Less: Salvage value | $10,000.00 |
| Life of Asset (In years) | 10 |
| Depreciation | 69,000.00 |
Depreciation is calculated as
Depreciation = Value of Asset – Salvage Value / Life of Asset
- Depreciation = (700,000-10,000)/10
- Depreciation = $69,000
Calculation of Written down value at the beginning of year 7
| Particulars | Asset 1 | Asset 2 |
| Value of asset | 500,000.00 | 700,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation for Year 1 | -49,500.00 | -69,000.00 |
| WDV at year 2 | 450,500.00 | 631,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation for Year 2 | -49,500.00 | -69,000.00 |
| WDV at year 3 | 401,000.00 | 562,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation for Year 3 | -49,500.00 | -69,000.00 |
| WDV at year 4 | 351,500.00 | 493,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation for Year 4 | -49,500.00 | -69,000.00 |
| WDV at year 5 | 302,000.00 | 424,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation for Year 5 | -49,500.00 | -69,000.00 |
| WDV at year 6 | 252,500.00 | 355,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation for Year 6 | -49,500.00 | -69,000.00 |
| WDV at year 7 | 203,000.00 | 286,000.00 |
Calculation of loss on sale of the asset
| Particulars | Amount |
| WDV of Asset 1 at the beginning of year 7 | 203,000.00 |
| Less: Sale Value | -100,000.00 |
| Loss on Sale of Asset | 103,000.00 |
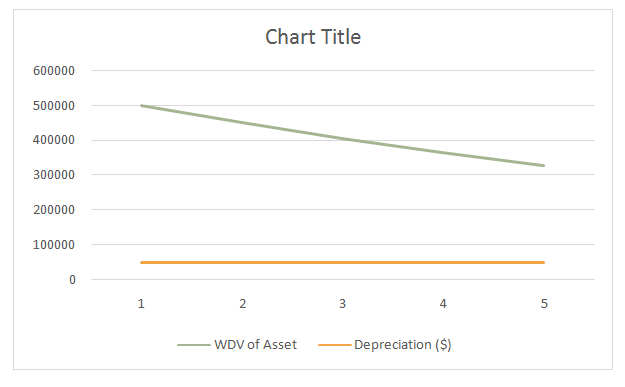
Straight Line Depreciation Method Graph
Explanation of graph with the help of an example:
ABM Ltd purchased the asset costing $ 500,000. The Depreciation rate is 10% of the initial cost per Straight line method. Calculate the Value of Assets at the end of year 5 and draw the graph for the same.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Value of Asset | 500,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation @ 10% | -50,000.00 |
| WDV at year 2 | 450,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation @ 10% | -50,000.00 |
| WDV at year 3 | 400,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation @ 10% | -50,000.00 |
| WDV at year 4 | 350,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation @ 10% | -50,000.00 |
| WDV at year 5 | 300,000.00 |
| Less: Depreciation @ 10% | -50,000.00 |
| WDV at year 6 | 250,000.00 |
| Year | WDV of Asset | Depreciation ($) |
| 1 | 500,000.00 | 50,000.00 |
| 2 | 450,000.00 | 50,000.00 |
| 3 | 405,000.00 | 50,000.00 |
| 4 | 364,000.00 | 50,000.00 |
| 5 | 328,050.00 | 50,000.00 |
It can be observed in the above graph that the depreciation amount remains constant over a period of time (which is shown by a straight orange line), and only the written-down value of the asset decreases due to depreciation charged (as shown by the green line).
When to Use Straight Line Depreciation Method
Straight line depreciation method is to be used in the following cases:
- When the organization wants to make the individual record of the assets maintained.
- When the organization has fewer assets.
- When the organization runs its business on a small scale.
- When the organization sells the assets before the life of assets comes to an end, to calculate the accurate profit or loss.
Advantages
The advantages of the straight-line depreciation method are determined as under:
- It maintains a separate record of assets maintained.
- The profit or loss on the sale of assets can be easily determined.
- The rate or the amount of depreciation is constant throughout the asset’s life.
- The easiest way of calculating depreciation.
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages are given below:
- As the rate or amount of depreciation is constant, it does not account for the loss of efficiency.
- If the capital expenditure is incurred, the depreciation will be recalculated prospectively.
- It is not useful when the life of an asset is unpredictable.
- It is not suitable for an organization that keeps a large number of assets.
Conclusion
This method of depreciation is one of the methods of depreciation in which the amount of depreciation is constant over the life of the asset. It is the easiest way of calculating depreciation. The formula for calculating depreciation is the value of the asset less salvage value divided by the asset’s life. The profit or loss on sale can be recorded separately in the case of the straight-line depreciation method. But at the same time, this method is not efficient for organizations that have a large number of assets.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Straight Line Depreciation Method. Here we also discuss the definition and how to calculate the straight line depreciation method. Along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –