Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQLite functions
SQLite provides different kinds of functions to the user. Basically, SQLite has different types of inbuilt functions, and that function we easily use and handle whenever we require. All SQLite functions work on the string and numeric type data. All functions of SQLite are case sensitive that means we can either use functions in uppercase or lowercase. By using the SQLite function, we sort data as per the user requirements. SQLite functions have a different category, such as aggregate functions, data functions, string functions, and windows functions, and that function we can use as per the requirement.
SQLite functions
Now let’s see the different functions in SQLite as follows.
1. Aggregate Functions
- AVG: It is used to calculate the average value of a non-null column in a group.
- COUNT: It is used to return how many rows from the table.
- MAX: It is used to return the maximum value from a specified
- MIN: It is used to return the minimum value from a specified
- SUM: is used to calculate the sum of non-null columns from the specified table.
- GROUP_CONCAT: It is used to concatenate the null value from the column.
2. String Functions
- SUBSTR: It is used to extract and return the substring from the specified column with predefined length and also its specified position.
- TRIM: It is used to return the copy of the string, and it removes the start the end character.
- LTRIM: It is used to return the copy of the string that removed the starting character of the string.
- RTRIM: It is used to return the copy of the string that removed the ending character of the string.
- LENGTH: It is used to return how many characters in the string.
- REPLACE: It is used to display the copy of the string with each and every instance of the substring that is replaced by the other specified string.
- UPPER: It is used to return the string with uppercase that means it is used to convert the all character into the upper cases.
- LOWER: It is used to return the string with a lowercase, which means converting all character into lower cases.
- INSTR: It is used to return the integer number that indicates the very first occurrence of the substring.
3. Control Flow Functions
- COALESCE: It is used to display the first non-null argument.
- IFNULL: It is used to implement if-else statements with the null values.
- IIF: By using this, we can add if – else into the queries.
- NULLIF: It is used to return the null if first and second the element is equal.
4. Data and Time Function
- DATE: It is used to determine the date based on the multiple data modifiers.
- TIME: It is used to determine the time based on the multiple data modifiers.
- DATETIME: It is used to determine the date and time based on the multiple data modifiers.
- STRFTIME: That returns the date with the specified format.
5. Math Functions
- ABS: It is used to return the absolute value of the number.
- RANDOM: It is used to return the random floating value between the minimum and maximum integer.
- ROUND: It is used to specify the precision.
Examples
Now let’s see the different examples of SQLite functions as follows.
First, we need to create a table by using the following create table statement as follows.
create table comp_worker(worker_id integer primary key, worker_name text not null, worker_age text, worker_address text, worker_salary text);Explanation
In the above example, we use the create table statement to create a new table name as comp_worker with different attributes such as worder_id, worker_name, worker_age, worker_address, and worker_salary with different data types as shown in the above example.
Now insert some record for function implementation by using the following insert into the statement as follows.
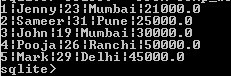
insert into comp_worker(worker_id, worker_name, worker_age, worker_address, worker_salary) values(1, "Jenny", "23", "Mumbai", "21000.0"), (2, "Sameer", "31", "Pune", "25000.0"), (3, "John", "19", "Mumbai", "30000.0"), (4, "Pooja", "26", "Ranchi", "50000.0"), (5, "Mark", "29", "Delhi", "45000.0");Explanation
In the above statement, we use to insert it into the statement. The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now we can perform the SQLite different functions as follows.
a. COUNT Function
Suppose users need to know how many rows are present in the table at that time; we can use the following statement.
select count(*) from comp_worker;Explanation
In the above example, we use the count function. The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot.
b. MAX Function
Suppose we need to know the highest salary of the worker so that we can use the following statement as follows.
select max(worker_salary) from comp_worker;Explanation
In the above example, we use the max function to know the max salary of a worker from the comp_worker table. The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot.
c. MIN Function
Suppose we need to know the lowest salary of the worker so that we can use the following statement as follows.
select min(worker_salary) from comp_worker;Explanation
The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot.
d. AVG Function
Suppose users need to know the total average salary of a worker from comp_worker at that time; we can use the following statement as follows.
select avg(worker_salary) from comp_worker;Explanation
The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot.
e. SUM Function
Suppose users need to know the total sum salary of a worker from comp_worker at that time; we can use the following statement as follows.
select sum(worker_salary) from comp_worker;Explanation
The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot.
f. Random Function
select random() AS Random;Explanation
The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot.
g. Upper Function
Suppose we need to return the worker_name column in the upper case at that time, we can use the following statement as follows.
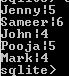
select upper(worker_name) from comp_worker;Explanation
The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot.
h. Length Function
select worker_name, length(worker_name) from comp_worker;Explanation
The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you have understood about the SQLite Function. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of Function statements, and we also see different examples of Function. From this article, we learned how and when we use SQLite Functions.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQLite functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.