Updated April 3, 2023
Definition of SQLite Boolean Types
SQLite provides the different data types, the Boolean is also one of the data types in SQLite database. Basically, SQLite uses different storage classes for different data types but does not have any separate storage class for Boolean data types. In SQLite Boolean data types instead of Boolean values we use integer values that are 0 and 1, where 0 for false and 1 for true. In Boolean data types that have a true or false value at that time, they return the true or false value to combine more than one true or false value as per the requirement.
Syntax:
create table specified table name (colm name1 data type , colm name2 data type, ……….colm name N integer not null check (colm name in (0, 1)));Explanation
In the above syntax, we create table statements with different parameters such as specified table name is used for actual table name that we need to create, colm name1 , 2 N is specified column name that we need to create under the table name. In this syntax, we use not null and check constraint with integer data type for the particular column as shown in the above syntax.
How SQLite Boolean types work?
Now let’s see how a Boolean type works in SQLite as follows.
Basically, SQLite does not support the Boolean data type, so instead of Boolean type SQLite uses the integer data type to execute the Boolean expression in the form of true or false here 0 is used for false and 1 for true that we already discussed. The integer store the numeric value as a signed number it either positive or negative but Boolean type only works on the positive values in form of 0 or 1. Actually, integer is one of the storage classes in SQLite and specifically it works on integer values. In Boolean, it stores only two values so it requires a single bit to store the value. SQLite does not have any separate storage class for the Boolean type, so inserted all Boolean values stored as integer values that 0 and 1.
Examples
Now let’s see the different examples of Boolean type as follows.
CREATE TABLE sample (name BOOLEAN NOT NULL CHECK (name IN (0, 1)));
.tableExplanation
In the above example, we use a create table statement to create a new table name as a sample with a name attribute and see its data type we defined as Boolean with not null and check constraint as shown in the above statement. After that, we use the in a keyword to specify the Boolean values for the specified column here column name is a name. The end out of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot.
So we successfully created a new table with Boolean data type and now perform insert operation on the table as follows.
insert into sample values(0);Explanation
In the above example, we use to insert into a statement and we inserted 0 successfully. The end out of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot.
Now insert 1 by using insert into the statement as follows.
insert into sample values(1);Explanation
In the above example, we use to insert into a statement and we inserted 1 successfully. The end out of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot.
Now insert 0 and 1 in different forms as follows.
insert into sample values(0.0);
insert into sample values(1.1);Explanation
In the above statement, we use to insert into the statement to insert new records, here we inserted 0.0 and 1.1 in decimal format successfully. The end out of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot.
Now insert records by using double quotes as follows.
insert into sample values("0.0");
insert into sample values("1.1");Explanation
In the above statement, we insert into the statement to insert new records, here we inserted “0.0” and “1.1” in decimal format successfully. The end out of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot.
Now let’s see the inserted records by using the following statement as follows.
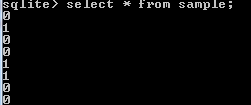
select * from sample;Explanation
In the above statement select a statement to see the inserted records into the table. The end out of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot.
Now let see the type of column by using the following statement as follows.
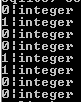
select name, typeof(name) from sample;Explanation
In the above example, we use a select clause with typeof function to see what type of name column from the sample table is. The end out of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot.
Boolean does not allow inserting in negative values or less than 0 values.
Now let’s try to insert -1 into the sample table as follows.
insert into sample values("-1");Explanation
In the above example, we try to insert -1 into the table, but the Boolean type does not allow inserting -1, so at that time it shows an error message. The end out of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot.
Now let’s see how check constraint works as follows.
First, create a new table by using the following statement as follows.
create table demo (demo_id integer primary key, b_name text not null check(typeof ("b_name") = "text" and b_name in ("true", "false")));Explanation
In the above example, we use a create table statement to create a new table name as a demo with different attributes such as demo_id and b_name with different attributes as shown in the above statement. Here we use check constraint in true and false form as shown. But Boolean does not allow text data type, so it shows error messages when we insert new records as follows.
Insert into demo (b_name) values ("true");Explanation
In the above example, we insert text Boolean value into the demo table but it shows an error message. The end out of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you have understood about the SQLite Boolean types. From the above article, we see different examples of SQLite Boolean types. We also learned the rules of SQLite Boolean types. From this article, we learned how and when we use SQLite Boolean types.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQLite Boolean” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.