Updated April 1, 2023
Introduction to SQLite enum
SQLite does not support the enum data type directly, so we can use some encoded statement to implement the SQLite enum data type. Basically, the enum is used to store the group of elements in a single string. It has a different option to select the value from the enum data type, which means we can set a limit to select the value from the group. Normally enum means enumeration that means each column from the table has a specified possible value, either numeric or string, that depends on the user requirement. SQLite does support the enum data type, but it is very compact to store the data.
Syntax
create table specified table name (colm name 1 data type check(specified condition) not null, colm name 2 data type check(specified condition) not null ……….colm name N;Explanation
In the above syntax, we use create table statements with different parameters such as specified table means actual table name that we need to create, after that we use column name that we need to create inside the specified table with check constraint as shown in the above syntax. Similarly, we can apply a check constraint to all column names as per the user requirement.
How does enum work in SQLite?
Now let’s see how enum works in SQLite as follows:
Basically, SQLite does not support the enum data type directly; SQLite uses other data types, and with the help of this data type, we can try to implement the enum in SQLite as per user requirement as follows.
SQLite has the following data types as follows.
Null: This storage is used to store the null value.
Integer: it is used to store the integer value in bytes, and it depends on the magnitude of value.
Real: This class is used to store the floating values, and the size of this class is 8 bytes.
Text: This class is used to store the string value in the database.
Blob: This class is used to store the exact value that we need as input.
Different String data types as follows.
CHAR (size): It is equivalent to the TEXT data types; in the SQLite database, the size parameter is ignored.
VARCHAR (size): It is also equivalent to the TEXT data types; in the SQLite database, the size parameter is ignored.
TINYTEXT (size): it is equivalent to the TEXT data types; in the SQLite database, the size parameter is ignored.
TEXT (size): it is equivalent to the TEXT data types; in the SQLite database, the size parameter is ignored.
So the above-listed data type we can use in SQLite to implement enum.
Sometimes we need to store multiple values in a single column; at that, we can use enum data type in MySQL, but in SQLite, we can use a check constraint instead of an enum data type to get the desired outcome as per the requirement. When we use a check constraint in a statement, then it allows us to define the specified expression to check whether inserted values are correct or not within a specified column. The value does not meet the requirement the then SQLite terminates the statement.
Examples of SQLite enum
Now let’s see the different examples of SQLite enum as follows.
First, create a new table by using the following statement as follows.
CREATE TABLE product (
product_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
product_Name TEXT CHECK( LENGTH(product_Name) <= 50 ) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', product_Type TEXT CHECK( product_Type IN ('A','B','C') ) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'A',
product_Field TEXT CHECK( LENGTH(product_Field) <= 40 ) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
product_Version TEXT CHECK( LENGTH(product_Version) <= 50 ) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
company_id INTEGER NOT NULL DEFAULT '11'
);Explanation
In the above example, we use create table statement to create a new table name as a product with a different attribute such as product_id with integer data type and primary key constraint, product_Name with text data type and here we use check constraint. Also, we set the limit, product_Type with a text data type, and here we use check constraint and here we set a default value is A, product_Field with text data type and here we use check constraint. Also, we set the limit with a default value, product_Version with the text data type, and here we use check constraint, and also we set the limit with a default value and company_id with integer data type with default constraint as shown in the above statement. See here column name product_type has a value A, B, and C same like emu (“A”,” B”, “C”). End result of the above statement as shown in below screenshot as follows.
.table
Now perform insert operation in the product as follows.
insert into product(product_id, product_Name, product_Field, product_Version, company_id) values (1, "HP", "IT", "A.2", 11), (2, "Dell", "IT", "A.3", 22), (3, "LG", "Electrical", "A.3", 22);Explanation
In the above example, we use to insert into the statement to insert records into the product table. We set a default value for the product_Type column, which means there is no need to insert that value; it automatically sets the default value as per user requirement.
Now we need to print inserted records as follows.
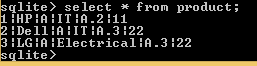
select * from product;Explanation
In the above example, we use a select statement to print all the product table’s inserted values. End result of the above statement is shown below screenshot as follows.
Let’s see another example as follows.
create table item (item_type text primary key, item_id integer);Create one more table as follows.
create table item_price (price integer primary key, item_name text not null, item_type text REFERENCES item (item_type));Now perform the insert operation as follows.
Insert into item (item_type, item_id) values ("A", 1);Explanation
In the above example, we created two different tables and references to each other, as shown in the above example. That means we can use reference value for another table as per requirement.
Now use the select statement to print values as follows.
select * from item;Explanation
End result of the above statement is shown in the below screenshot as follows.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you have understood about the SQLite enum. From the above article, we have learned the enum’s basic syntax, and we also see different examples of an enum. From this article, we learned how and when we use the SQLite enum.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQLite enum” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.