Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQL INTERSECT
INTERSECT operator in SQL is used to obtaining only the resultset that is common and that is also retrieved from all the queries. There are some operators in SQL that help us to combine the resultsets of the two or more queries to obtain the desired resultset from the resultsets of two or more queries. These are UNION, INTERSECT, and EXCEPT operators. Each one of them behaves differently and can be used according to our purpose and necessity. Note that MySQL does not supports intersect but SQL does.
Syntax of SQL INTERSECT
Given below is the syntax :
SELECT colOrExpr1, colOrExpr2, ... colOrExpr_n
FROM name_of_table1
[WHERE conditionsOrRestrictions]
INTERSECT
SELECT colOrExpr1, colOrExpr2, ... colOrExpr_n
FROM name_of_table2
[WHERE conditionsOrRestrictions];- colOrExpr: These are the names of the columns or any other expressions retrieved from the values of columns of the table. Note that the number of columns or expressions retrieved from each of the select queries should be the same and also the order in which they are being retrieved needs to be the same. The data type of the columns retrieved from each of the tables should be similar and compatible.
- name_of_table1 and name_of_table2: This is the name of the table from which you want to retrieve the resultset containing values of columns and expressions. There can be one or more select statements while using the INTERSECT operator.
- conditionsOrRestrictions: These are the conditions that we wish to apply on the column values of the table to filter out the resultset and apply only the desired result from the tables.
Result of INTERSECT Operator
- When two query result sets are intersected then the final resultset consists of the common and unique records that are retrieved from the resultsets of both the queries.
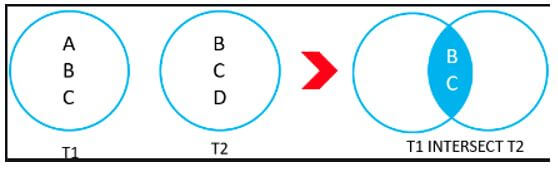
- To know using the Venn diagram, consider there is certain resultset retrieved from query 1 say T1 and other resultset retrieved from query 2 is T2.
- The contents of the resultset are shown in the below Venn diagram. When both the queries are intersected then only the common data present in both T1 and T2 results are obtained in data T1 INTERSECT T2.
- As B and C are common in both T1 and T2 both records are fetched in the intersected result.
- As A is not present in T2 and D is not present in T1, both A and D are skipped in the resultset of T1 INTERSECT T2.
Necessities for Using the INTERSECT Operator
There are certain things that you need to make sure before using the INTERSECT operator that are listed below:
- Both select statements should contain the same number of columns or expressions. Also, the order in which they are mentioned should be the same.
- The data type of the columns or values of expressions of the corresponding columns of both the tables should be similar and compatible with each other.
Example of SQL INTERSECT
Given below is the example mentioned :
Let us consider one example, suppose there are two tables named hospitals and patients that have the following structures as mentioned in the create table queries:
Hospital Table:
Code:
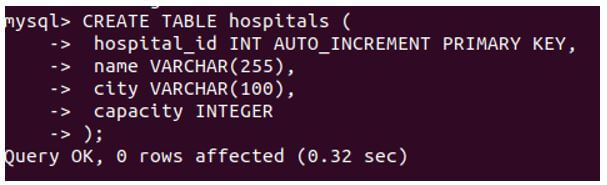
CREATE TABLE hospitals (
hospital_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255),
city VARCHAR(100),
capacity INTEGER
);Output:
Patient Table:
Code:
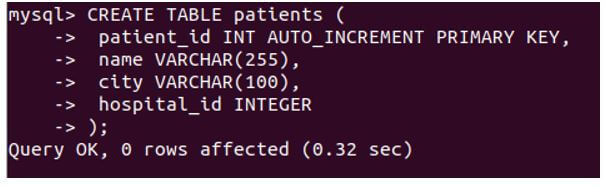
CREATE TABLE patients (
patient_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255),
city VARCHAR(100),
hospital_id INTEGER
);Output:
Let us insert some of the records in both the tables using the following queries:
Code:
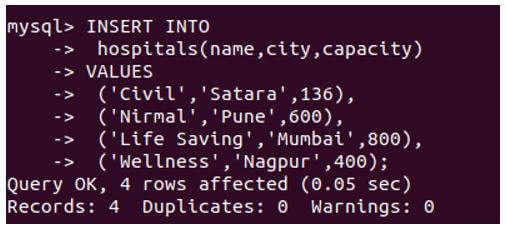
INSERT INTO
hospitals(name,city,capacity)
VALUES
('Civil','Satara',136),
('Nirmal','Pune',600),
('Life Saving','Mumbai',800),
('Wellness','Nagpur',400);Output:
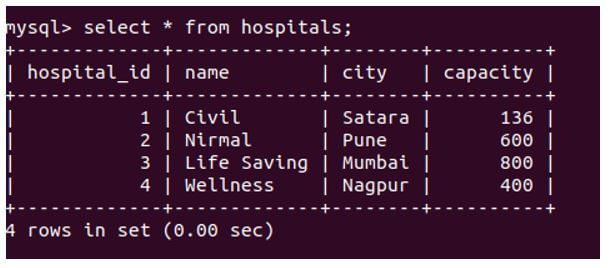
Let us select the inserted records of hospitals table:
Code:
SELECT * FROM hospitals ;Output:
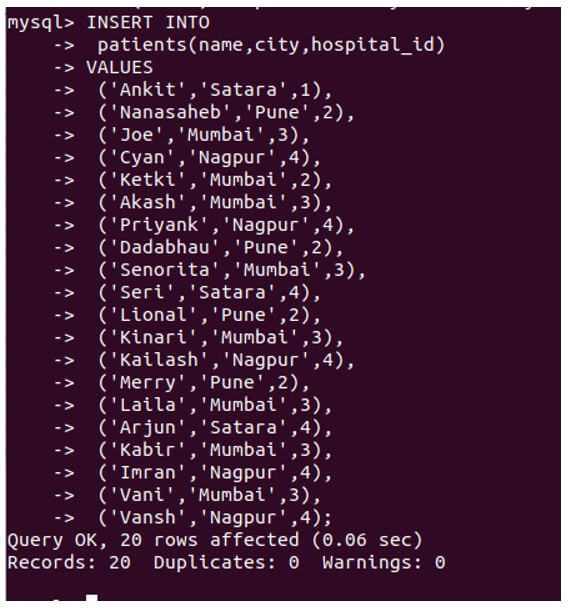
Let us insert some records in patients table:
Code:
INSERT INTO
patients(name,city,hospital_id)
VALUES
('Ankit','Satara',1),
('Nanasaheb','Pune',2),
('Joe','Mumbai',3),
('Cyan','Nagpur',4),
('Ketki','Mumbai',2),
('Akash','Mumbai',3),
('Priyank','Nagpur',4),
('Dadabhau','Pune',2),
('Senorita','Mumbai',3),
('Seri','Satara',4),
('Lional','Pune',2),
('Kinari','Mumbai',3),
('Kailash','Nagpur',4),
('Merry','Pune',2),
('Laila','Mumbai',3),
('Arjun','Satara',4),
('Kabir','Mumbai',3),
('Imran','Nagpur',4),
('Vani','Mumbai',3),
('Vansh','Nagpur',4);Output:
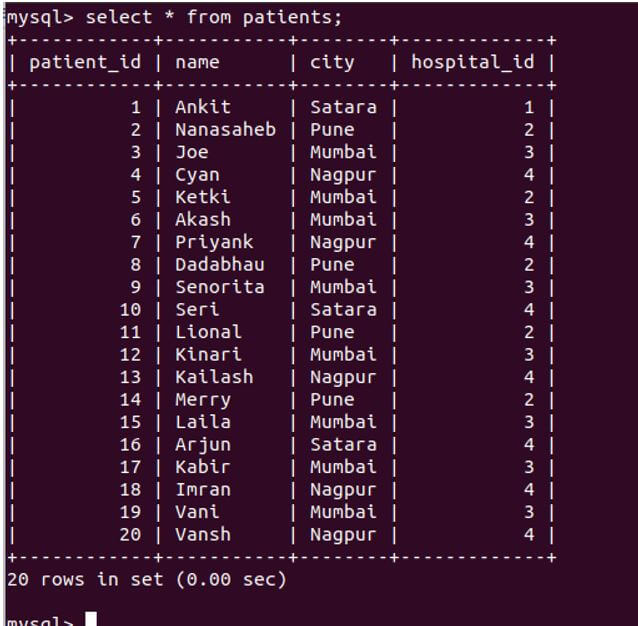
Let us retrieve all the records from patients table:
Code:
select * from patients;Output:
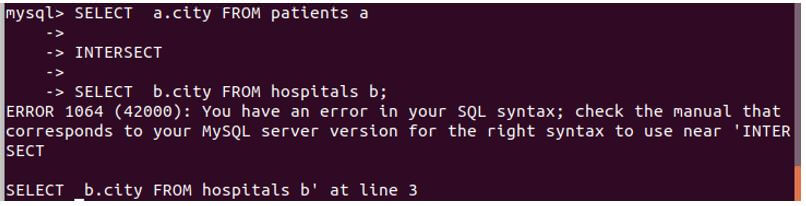
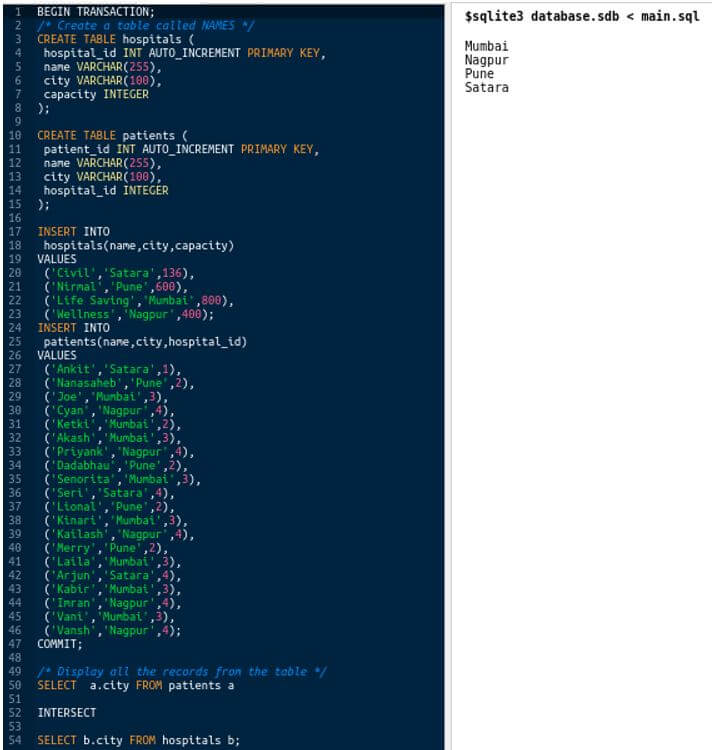
Let us intersect the resultsets from the queries involving patients and hospitals:
Code:
SELECT a.city FROM patients a
INTERSECT
SELECT b.city FROM hospitals b;Output:
It gives error in MySQL because MySQL does not supports intersect. Let us try it on the SQL lite database. Here, we will use an online SQL editor. You can install it and check running all these commands over thereby creating and inserting the table and records in SQL lite.
Here is the output that we get on running our main.sql.
Output:
We can see that we only get the cities for which there is an entry in the hospitals’ table as well as the patients’ table.
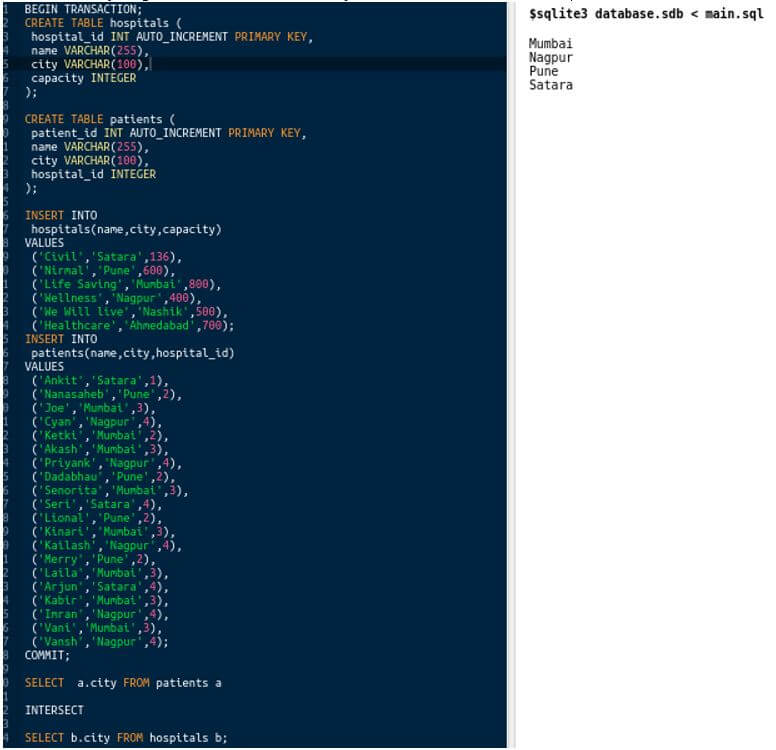
Let us insert some extra cities in the hospital table by keeping the patients’ table records the same and observe the result.
We have added 2 records:
(‘We Will live’,’Nashik’,500),
(‘Healthcare’,’Ahmedabad’,700)
In the hospital table in my SQLite script. The output of intersection still seems to be same because there is no entry in patients table with the city as Ahmedabad or Nashik:
Output:
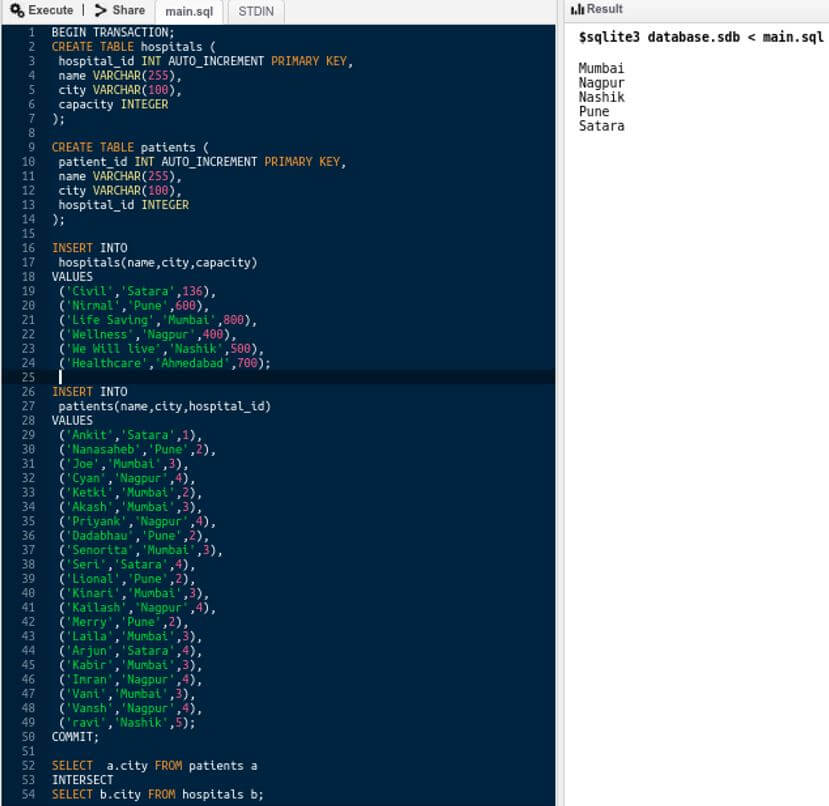
Now, let us add a patient with Nashik city and observe the output.
We have added the following record in the patients table in my main.sql file.
(‘ravi’,’Nashik’,5)
Let us now execute and observe the results of the intersect operation:
Output:
We can see that Nashik city is also added in output because it had an entry in both tables patients as well as hospitals while Ahmedabad city has entry only in hospitals table.
Conclusion
We can make the use of the INTERSECT operator to fetch all the unique records that are common in two or more queries in the SQL language. MySQL does not support the intersect operator. We should be careful while using it as using the INTERSECT operator requires that both queries should retrieve the same columns or expressions and of the compatible datatypes that are similar.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL INTERSECT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.