Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy Raw SQL
The SQLAlchemy Raw SQL is one toolkit that can be built using the python programming language with advanced features like designing and managing quality and high-performance databases. It will also explore and deep dive into the primary type of sql statements and the queries; it will require more comfortable language like python scripts to execute the user operations from UI to backend.
What is SQLAlchemy Raw SQL?
The SQLAlchemy Raw toolkit is an inbuilt feature that will handle user data transactions using the databases. It will be accepted and satisfied with all the database drivers and the required import packages like methods, classes, and other default keywords. All other required packages are to be imported along with the specified modules so that they will be accessed easily to perform the user data operations, and mainly will be encrypted the datas like keywords, passwords, etc. While we encrypt, the datas are to be safe and secure. If we want to remove the encryption, we can remove the security using decryption techniques to retrieve the original datas.
Using SQLAlchemy Raw SQL
As per the python-based programming language, the APIs are called and executed using the pre-defined libraries, and other inbuilt functions are required to start installing the sqlalchemy libraries. Once installed, the operations are created and performed using the python-based scripting codes, and other pre-defined modules are easily accessed through the sqlalchemy database engines. In addition, the create_engine package will be mainly imported and utilized with the whole data set; operations for importing many modules will be created and executed in the new tables. Not only for creating the tables but the additional modules are also required to access and perform the other user operations with more needs.
Creating Table
The creating table is mainly essential for building the sqlalchemy raw tools, and it is more sophisticated with the basic functionality. Any table columns in the database would be mapped to the specific attributes already configured on the sqlalchemy. The Expressions are the other important part of performing and automatically triggering the attributes or column values based on the user inputs. It will be validated by using both client and server-side scripting languages.
In the above screenshot, we can first create the Metadata to initialize the table events that include the table rows and columns. Then we can declare the new variable to create the table with the help of metadata and add additional columns that will calculate the n number of table columns along with the datatypes. Using the database engine, we can connect the database for the required columns and use the create_engine() and create_all() methods to call the necessary number of database drivers and other util packages. In the table() method, we can give the table name as the required input, and with that complete, the table will be fitted among each other while we inspect the modules that will handle the table columns as the view and expand the datas among each other.
Then next, we can execute the sql statements with the below scenario.
Execute the SQL Statements
It is one of the other methods mainly utilized with the execution part of the databases. The other raw sql uses the sqlalchemy with text modules that will be imported and connected by using the database engine, which is already created as the database instance, which defines the text sql statements before executing the sql queries on the database.
We can see the above screenshot; after importing the sqlalchemy packages, the database engine should connect with the backend database, which is on the required drivers already associated with the engine creation. After that, we can call the connect() method with the help of an engine instance like eng.connect(). It will be called the separate variable called ‘a’, and then we can execute() the method by using the instance, and it will be stored on the separate variable like outs. Finally, we can retrieve and iterate the values using conditional loop statements like iterating them and printing them on the console screen.
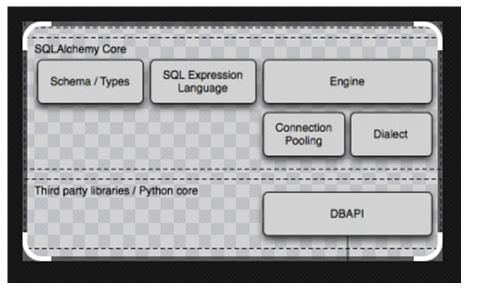
The sqlalchemy core is the central part and will calculate among the database schema and types. Next, it will be moved to the sql expression language, and then it will go forward to the engine. Once the connection is executed, it validates that connection pooling and Dialect are the two essential features of the engine. If we want to validate and include the third-party libraries, maybe the Python-based packages in the DBAPI.
Examples of SQLAlchemy Raw SQL
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
Code:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
eng = create_engine('sqlite:///Mar9.db', echo = True)
with eng.connect() as a:
outs = a.execute('SELECT * FROM employees')
ress = outs.fetchone()[0]
print "Welcome To My Domain: %s" % res
for b in outs:
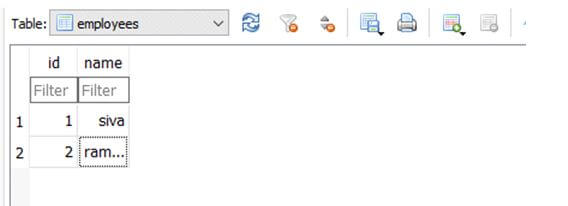
print bOutput:
In the above example, we can create the raw data sql queries.
But, first, we can import the required sqlalchemy package along with the database drivers and required files.
Create the database engine using the create_engine() method to create the database engine here; I used sqlite to connect the UI data to the backend.
The database engine will be created successfully; then, we can make the local variable, call the default connection methods and store it on a separate variable. Finally, the same will be printed on the console screen.
Using for loop to iterate the values with the help of required loop conditions.
Example #2
Code:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.sql import text
eng = create_engine('sqlite:///Mar9.db', echo = True)
with eng.connect() as connec:
connec.execute(text('DROP TABLE IF EXISTS employees'))
connec.execute(text('''CREATE TABLE employees(Id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
Name TEXT)'''))
x= ( { "Id": 1, "Name": "Sivaraman" },
{ "Id": 2, "Name": "raman"},
{ "Id": 3, "Name": "arun" },
{ "Id": 4, "Name": "sanjay" },
{ "Id": 5, "Name": "brandon" },
{ "Id": 6, "Name": "Chidramabam"},
{ "Id": 7, "Name": "Hogen" },
{ "Id": 8, "Name": "Vietnamvidusundaram"}
)
for y in x:
connec.execute(text("""INSERT INTO employees(Id, Name)
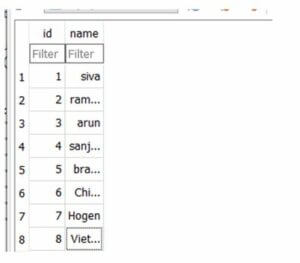
VALUES(:Id, :Name)"""), **y)Output:
In the second example, similar to the previous example, we must import all the required packages and connect the databases.
Here additionally, we have added the text package in the sqlalchemy imports.
The rest of the codes and functions are the same as previously; we created variables and calls the same in the default functions.
The DROP keyword is used to check and validate the table conditions; if already created, it will drop the existing table and create a new table.
Finally, we can insert the table values per the requirement using the insert query statement and the for loop iterations.
Conclusion
The SQLAlchemy has many features and functions for performing data operations; among them, it has the required number of tools to handle a vast number of datas. That will be calculated the database performance, and other tuning advisors like sqlalchemy raw is the toolkit that will optimize the database queries and implement the basic set of sql statements.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQLAlchemy Raw SQL. Here we discuss the introduction, using SQLAlchemy raw SQL and examples, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –