Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy Async
The SQLAlchemy async is one of the extension types. It is more connected by using the AsyncEngine with the help of the create_async_engine() method, which helps to create the instance of the ayncengine based on their version of the traditional engine API and also the connect() and begin() transaction methods which deliver both asynchronous context type managers that help for AyncConnection to invoke the statements in the server-side aync results.
What is SQLAlchemy Async?
SQLAlchemy async is one of the features, and it has the default methods for operating the application functions from the front end to the back end. It always creates the instance using the create_aync_engine() method for the AsyncEngine, which offers more for the async version of the traditional engine API. Using the Asyncio platform, which guided and extended the required python version libraries, depends upon the greenlet library on the default machine. With the help of the pip command to install the sqlalchemy asyncio libraries. The greenlet libraries do not support the current default files. It satisfies the architectures on the platform usages for setting up the extra tools with the help of an asynchronous programming thread.
How to Use SQLAlchemy Async?
Asynchronous programming is one of the programming patterns that mainly enables the code to run with a separate application thread. It is supported by ORM and Core and includes the asyncio imported class feature for calling and utilizing the product. The limitation is available for the async feature with the ORM mapping and notified with the lazy loading concept to upload the Core and ORM package feature. And also, there is a new way of creating the queries with significant versions of the SQLAlchemy with boilerplate codes for spoiler alerts on the syntax query essential for each session object directly called for the users and mapped the ids accordingly supported for declarative mapping with data classes and attributes. The ORM layers of the async capabilities joined with the other types of queries with different Routes to add the entries.
The sqlalchemy models will declare the models in a subclass of the declarative style that works well with the verbose the sqlalchemy engine will create with the help of the create_async_engine() method. For this, each user session is calculated using the AsyncSession class with additional parameters like echo=True for passing the engine instance initialization to generate the sql queries based on the user dependencies, and its behaviors are calculated the session expire with parameter expire_on_commit= true or false boolean statements. This is mainly because of the async settings with sqlalchemy sql queries to perform the database operations which are already accessing the committed objects.
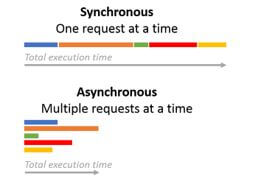
The above diagram shows the difference between the synchronous and asynchronous requests on the sqlalchemy models. In synchronous at a single time request is performed, but asynchronous is the multiple requests passing at a single time.
SQLAlchemy Async Create Models
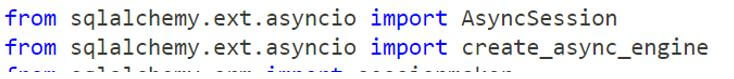
There are different ways to use and declare the sqlalchemy models will use the declarative subclass types works and perform well with the less verbose. It has n number of column fields to store and retrieve the values using the AsyncSession class imported from the sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio. The create_async_engine class is imported from the sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio packages.
We must use the create engine to connect the databases from the front end to back end operations.
1. Init_model()
It is one of the default functions that can be used to declare the async with the specific definition. Then additionally, we can call the engine.begin () method for performing the database engine connectivity operations from the sqlalchemy packages. But, first, we need to install the sqlalchemy async using the pip command below.
Then we can use the devops tools like docker and the databases like Postgres and sqlite to perform the user operations. Here, the init_model() function initially performs the async and sync() methods with the default user session instance for injecting the models.
Mainly we can use the below API called Fastapi. The fastapi_asyncalchemy package is installed and imported first to utilize the model’s classes.
Code:
from fastapi_asyncalchemy.models import *init_model() is the type of the event loop that is only commanded with the CLI command for python execution of the additional arguments.
2. FastAPI Routes
The fast api is the main package that comes under the separate asyncalchemy for the sqlalchemy user and asyncsessions.
Code:
From fastapi import FastAPI
From fastapi import Depends
From sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import AsyncSessionThe above packages are first imported before the async operations start, then the below packages are imported to connect the database models with additional services.
Code:
From fastapi_asyncalchemy.db.base import init_models
From fastapi_asyncalchemy.db.base import get_session
From fastapi_asyncalchemy import serviceBased on the user requirement and its dependencies, the session can be injected with Depends of the routes that will be created a new session. Finally, we can retrieve the datas by using the await() function.
Code:
Employee.py:
from fastapi_users.authentication import JWTAuthentication
from fastapi_users.db import SQLAlchemyUserDatabase
from core.db import database
from .models import Employee
from .schemas import EmployeeDB
emp = Employee.__table__
a = SQLAlchemyUserDatabase(EmployeeDB, database, emp)
SECRET = "dhfh67ewtf8wgf6ewgc8y28g8q893hc7808fwh7w4bynw74y7"
tests= [
JWTAuthentication(secret=SECRET, lifetime_seconds=3600),
]Models.py:
from empls_EmployeeDB import SQLAlchemyBaseUserTable, SQLAlchemyUserDatabase
from sqlalchemy import Column, String, Integer, DateTime, Boolean
from core.db import Base
class Employee(Base, SQLAlchemyBaseUserTable):
name = Column(String, unique=True)
dob = Column(DateTime)
emp = Employee.__table__Schema.py:
import uuid
from typing import Optional
import pydantic
from empls import models
from pydantic import EmailStr, BaseModel
class Employee(models.BaseUser):
class Test1:
orm_mode = True
class Test2(BaseModel):
id: Optional[str]
name: str = "SIva"
@pydantic.validator("id", pre=True, always=True)
def default_id(cls, v):
return v or str(uuid.uuid4())
class Test1:
orm_mode = True
class Test3(Employee, models.BaseUserCreate):
name: str
class Test4(Employee, models.BaseUserUpdate):
pass
class EmployeeDB(Employee, models.BaseUserDB):
passRoutees.py:
from fastapi import APIRouter
from emps import empl
rout = APIRouter()
rout.include_router(empl.router, prefix="/empl")main.py:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from core.db import database
from routes import Routees
from core.empls import empls
app = FastAPI()
@app.on_event("empdet")
async def empdet():
await database.connect()
@app.on_event("empresign")
async def empresign():
await database.disconnect()
app.include_router(Routees)
app.include_router(empls.router, prefix="/employees", tags=["employees"])Outputs:
The above codes are the basic format for creating the sqlalchemy aync model using the fastAPI imported packages in the python libraries. Routing is essential for mapping the database schema model from the front end to the backend.
Examples of SQLAlchemy Async
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
Code:
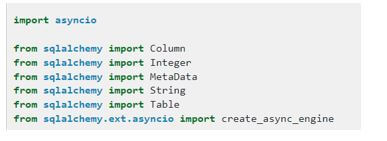
import asyncio
from sqlalchemy import Column
from sqlalchemy import Integer
from sqlalchemy import MetaData
from sqlalchemy import String
from sqlalchemy import Table
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import create_async_engine
md = MetaData()
a = Table(
"emps", md, Column("id", Integer, primary_key=True), Column("name", String)
)
async def async_main():
eng = create_async_engine(
'sqlite:///Mar9.db',
echo=True,
)
async with eng.begin() as con:
await con.run_sync(md.drop_all)
await con.run_sync(md.create_all)
await con.execute(
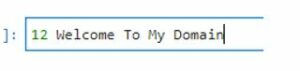
a.insert(), [{"name": "12"}, {"name": "Welcome To My Domain"}]
)
async with eng.connect() as con:
res = await con.execute(a.select())
print(res.fetchall())
res = await con.stream(a.select())
async for outs in res:
print(outs)
asyncio.run(async_main())Output:
In the above example, we first imported all the required libraries like sqlalchemy import all the table columns and asyncio import drivers.
We mainly used the create_async_engine to perform the asynchronous operations in the application task.
Next, we created a basic table-like emps using the Table() method with additional parameters like columns() with value name and datatype.
By using asyncio.the run() method will pass the primary function as the arguments.
Finally the main method is executed on the asyncio.run(async_main()) parameters.
Example #2
Code:
from typing import List
import databases
import sqlalchemy
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
engs = 'sqlite:///Mar9.db'
db = databases.Database(engs)
md = sqlalchemy.MetaData()
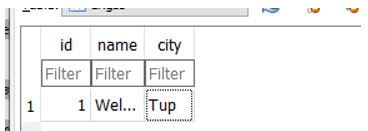
news = sqlalchemy.Table(
"engss",
md,
sqlalchemy.Column("id", sqlalchemy.Integer, primary_key=True),
sqlalchemy.Column("name", sqlalchemy.String),
sqlalchemy.Column("city", sqlalchemy.String),
)
vars = sqlalchemy.create_engine(
engs, connect_args={"Welcome": "Tup"}
)
md.create_all(vars)
class funs(BaseModel):
name: str
city: str1
class funs1(BaseModel):
id: int
name: str
city: str1
app = FastAPI()
@app.on_event("first")
async def first():
await database.connect()
@app.on_event("second")
async def second():
await database.disconnect()
@app.get("/engs/", response_model=List[ab])
async def funsss2():
qury = engs.select()
return await database.fetch_all(qury)
@app.post("/engs/", response_model=funs1)
async def funsss(ab: funs):
qury1 = engs.insert().values(name=ab.name, city=ab.city)
vars2 = await database.execute(qury1)
return {**a.dict(), "id": vars2}Output:
In the second example, we used Fast API in the sqlalchemy packages to perform the async operations.
The packages are first imported with the required libraries, classes, keywords, and methods.
The fast api packages have methods like first() and second() and the async and def keywords.
These keywords are performed to store and retrieve the multiple results using the await keyword.
Conclusion
The sqlalchemy has many features and must be implemented and satisfied with the required libraries. Like that, async is the keyword and feature for performing the database operations like storing and retrieving the datas with multithreaded or multiple requests are called and performed at a single time instance.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQLAlchemy Async. Here we discuss the introduction; SQLAlchemy async creates models and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –