Updated March 28, 2023
Introduction to SQL with Clause
SQL WITH clause, also known as subquery refactoring or common table expressions(CTEs) is used for creating a temporary result set using a simple sql query, such that this temporary set can further be used multiple times within the main SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE statements, i.e, WITH clause creates a temporary virtual table with can be further used in main SQL queries.
Syntax and parameters
-- Define the CTE(temporary table) name and column list
WITH temp_table_name ( column_name1, column_name2, ...)
AS
-- Define the CTE query
(
SELECT column_name1, column_name2
FROM table_name1
WHERE condition
)
-- Define the main query
SELECT column_name1, column_name2
FROM temp_table_name;The different parameters used in the syntax are :
- WITH: With clause is used for creating a common table expression or temporary tables
- temp_table_name ( column_name1, column_name2, …): Here, temp_table_name is the name of CTE and ( column_name1, column_name2, …) is the definition of column names of the CTE which we will be using further in the main query.
- AS (SELECT column_name1, column_name2 FROM table_name1 WHERE condition): This section specifies a SELECT statement whose result set will populate the CTE.
- SELECT column_name1, column_name2 FROM temp_table_name: This section specifies the main outer query. The SELECT statement which will use the columns from the resultant CTE and produces the final result.
Of the above-mentioned parameters, all the parameters are mandatory. You may use WHERE, GROUP BY, ORDER BY and HAVING clauses based on your requirement.
How SQL WITH Clause works?
WITH clause allows us to give a subquery block a name that can be used in multiple places within the main SELECT, INSERT, DELETE or UPDATE SQL query. The name assigned to the subquery is treated as though it was an inline view or a table.
It is very helpful when you need the same set of results data multiple times. In such a case you can simply define a CTE for this data and reuse the same again and again by referencing it. It’s a kind of code reuse.
Going ahead we will be discussing the above-mentioned WITH clause in great detail.
In order to demonstrate and explain the WITH clause in SQL effectively, we will be using the following “Orders” table. This table is made for an e-commerce website. The table contains order id, customer names, city and the details of the items purchased by them.
The schema for the above mentioned “orders” table is :
Number of records: 15
| Customers |
| Order_id(primary key) |
| Customer_name |
| City |
| Items_purchased |
| Amount_paid |
| Order_date |
Let’s have a look at the records in the orders table. So that later, we can understand how
WITH clause is helpful:
| Order_id | Customer_name | City | Items_purchased | Amount_paid | Order_date |
| 1 | Peter King | Manchester | Books | 120 | 2020-01-13 00:00:00.000 |
| 2 | Priya Krishna | New Delhi | pen | 50 | 2020-01-12 00:00:00.000 |
| 3 | Jim Halpert | Manchester | pencil | 43 | 2020-02-13 00:00:00.000 |
| 4 | Michael Scott | New York | Books | 250 | 2020-02-10 00:00:00.000 |
| 5 | Harvey Spector | Birmingham | pencil | 100 | 2020-01-10 00:00:00.000 |
| 6 | Deepa Kamat | Mumbai | Books | 370 | 2019-12-13 00:00:00.000 |
| 7 | Anita Desai | London | pencil | 50 | 2019-12-01 00:00:00.000 |
| 8 | Rachel Zane | Michigan | pen | 70 | 2019-12-13 00:00:00.000 |
| 9 | Petoria John | Canberra | pen | 190 | 2020-01-13 00:00:00.000 |
| 10 | John L | Budapest | Books | 540 | 2020-01-13 00:00:00.000 |
| 11 | Justin Green | Ottawa City | pen | 65 | 2020-02-13 00:00:00.000 |
| 12 | Babita Ghosh | Kolkata | pencil | 75 | 2020-02-13 00:00:00.000 |
| 13 | Krish Pratt | London | eraser | 30 | 2019-12-01 00:00:00.000 |
| 14 | Elizabeth Blunt | London | pencil | 340 | 2019-12-01 00:00:00.000 |
| 15 | Nina Debrov | Amsterdam | Books | 452 | 2019-12-01 00:00:00.000 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
Examples of SQL with Clause
Here are a few examples to illustrate WITH clause in SQL.
Example #1
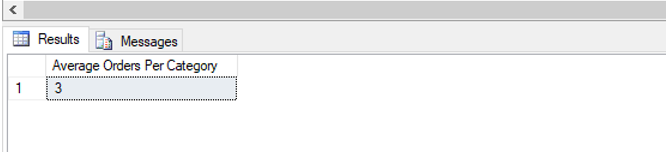
Find the average number of orders placed per month for each category of an item sold at the e-commerce site.
Code:
WITH Orders_CTE (Order_id, Number_of_Orders)
AS
(
SELECT Items_purchased, COUNT(Order_id) as Number_of_Orders
FROM orders
GROUP BY Items_purchased
)
SELECT AVG(Number_of_Orders) AS "Average Orders Per Category"
FROM Orders_CTE;Output:
Example #2
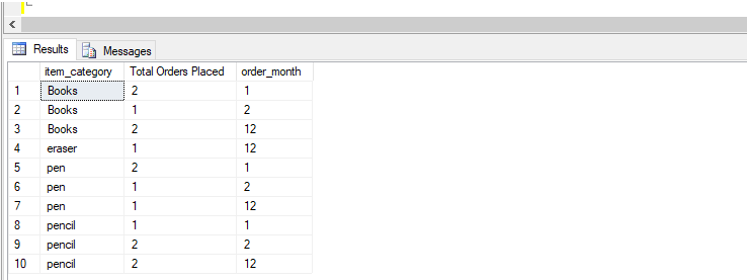
Find the total number of orders placed per month for each category item sold at the e-commerce site.
Code:
WITH Orders_CTE (item_category,Order_id, order_month)
AS
(
SELECT items_purchased as item_category, Order_id, MONTH(Order_date) AS order_month
FROM Orders
WHERE Order_id IS NOT NULL
)
SELECT item_category, COUNT(Order_id) AS "Total Orders Placed",order_month
FROM Orders_CTE
GROUP BY order_month, item_category
ORDER BY item_category, order_month;Output:
You can see in the above example that we have first created a CTE of Orders. It has a list of all orders, their item category, and the month of order.
Next, we have defined the main query referencing the Orders_CTE. It makes use of the orders_cte to group orders by item_category and order_month
Example #3
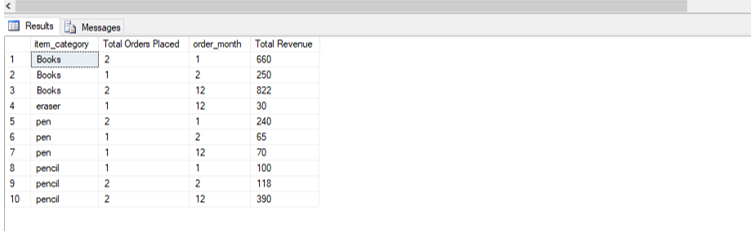
Find the total number of orders placed and the total revenue generated per month by different categories of items sold at the e-commerce site.
Code:
WITH Orders_CTE (item_category,Order_id, order_month,Amount_paid)
AS
(
SELECT items_purchased as item_category, Order_id, MONTH(Order_date) AS order_month, Amount_paid
FROM Orders
WHERE Order_id IS NOT NULL
)
SELECT item_category, COUNT(Order_id) AS "Total Orders Placed",order_month, SUM(Amount_paid)as "Total Revenue"
FROM Orders_CTE
GROUP BY order_month, item_category
ORDER BY item_category, order_month;Output:
Example #4
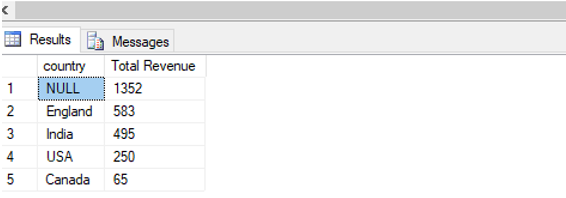
Find the total revenue generated country wise by the e-commerce country.
In this example, we will be learning to use multiple WITH clauses in a single query.
Code:
WITH Orders_CTE (City,Amount_paid)
AS
(
SELECT City,Amount_paid
FROM Orders
WHERE Order_id IS NOT NULL
),
Cities_CTE (city, country)
AS
(
SELECT city_name, country
FROM cities
)
SELECT c.country, SUM(o.Amount_paid)as "Total Revenue"
FROM Orders_CTE as o LEFT JOIN Cities_CTE as c
ON o.City =c.city
GROUP BY c.country
ORDER BY 2 DESC;Output:
Conclusion
SQL WITH clause is used for creating temporary tables that can be used further in the main SQL query. They reduce the cost of join operations and help in reusing the same piece of code again and again by referencing.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL with Clause” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
- SQL Set Operators
- SQL Right Join
- Custom SQL in Tableau
- SQL Clauses