Updated July 28, 2023

Introduction to SQL Views
In SQL, views are equivalent to virtual tables that don’t contain data. The rows and columns of a view are identical to those in a database’s actual table. By choosing fields from one or more database tables, we can build a view. A view may include all table rows or only certain rows according to a set of criteria.
Let’s say we want to create a new structure with data from several different records, but we do not wish to remove the information from the original tables. We can always just make a new table, but that could result in redundant data being kept in several locations. If part of the data changes, having to update it in various places may be very inconvenient. Viewpoints are useful in situations like this. Since a SQL view does not save the rows and columns on the disc like a solid table, it is referred to as a virtual table. It merely includes the SQL query instead. In relational databases, SQL views are frequently utilised. Relational databases come with several capabilities, such as SQL constraints like main and foreign keys or indexing. These features may result in challenging queries. The virtual tables rows can easily be updated.
Key Takeaways
- Views were created to simplify the delivery of data and lessen the complexities of numerous tables. Views serve as a security mechanism by assisting with data integrity maintenance and data security.
- Clients do not need to have the authorization to access each table or column to receive data from the VIEW because we can allow users to do so.
- The structure of the view as well as the view’s data will be stored by a DBMS. Since that is basically what views are: queries that have been saved under a unique name for easy access, views are frequently referred to as saved queries.
Syntax to Create View
A View can be created using CREATE VIEW statement as below:
CREATE VIEW VIEW_NAME AS
SELECT column1, column2, column3.......
FROM table_name WHERE [condition];How to Create SQL Views?
Let’s look at how to create a SQL view the syntax is given below:
Command:
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column field
FROM tables ;A view concept is done using CREATE statement. The above syntax shows that we need to give a view name in place of the table name and select the respective column fields from the table to add to the view table.
SQL Views Virtual Tables
Since views are virtual tables, they require extremely minimal storage because the database just keeps a view’s definition and not copies of all the tables it creates. For instance, compared to a single real table in the database, even if we generate several views, it still won’t take up much space.
SQL Views – Insert, Delete, and Drop
Let’s start by creating a view with the view name and the syntax shown below. Once the view creation is over we need to insert the needed values from both tables.
The insert, delete and drop options are described below:
1. Inserting into View
By inserting new rows into the view using the INSERT INTO command, they may update the view with only a new row.
Command:
Insert into analysis values ('prabha','madurai');2. Delete in View
A row can be excluded from a view using DELETE FROM table and using where clause.
Command:
DELETE FROM Tablename where col= "col field";3. DROP in View
It is used to scrap a virtual table. And SQL uses DROP to delete the entire records.
Command:
DROP VIEW drop name;Let’s now examine the various operations in views using examples and code snippets.
Examples
Before going into an example we need to connect to a database. In this article, I’m using MySQL prompt and setting up my new database before creating a table. Here my database name is ‘text’. Once the database is created successfully we shall receive output as Query ok, created database.
Command:
Initial setting:
C:\xampp\pp\mysql\bin>mysql -h localhost -u root;Creating a table:
create table patient(pno int, pname varchar(15), pdiagnose varchar(15), address varchar(10));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.561 sec)Second table:
create table amazonproduct (prodid int, pname varchar(15), rate int, location varchar(15));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.301 sec)Inserting a value in amazonproduct table:
insert into amazonproduct values(122, 'alexa', 1000, 'chennai');
insert into amazonproduct values(123, 'walkman', 2000, 'mumbai');
insert into amazonproduct values(124, 'headphone', 3000, 'kolkata');
insert into amazonproduct values(125, 'kurta', 4000, 'hydrabad');And we can view by select statement:
select * from amazonproduct;Output:
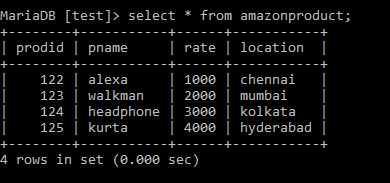
Next inserting the value in patient table:
insert into patient values(150, 'Akash', 'Kidney', 'SRM');
insert into patient values(151, 'Fizaa', 'Lungs', 'Billro');
insert into patient values(152, 'Thoams', 'Brain', 'GKM');
select * from patient;Output:
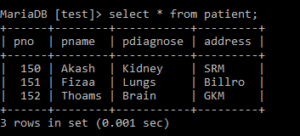
When we add null using the Check option.
Output:
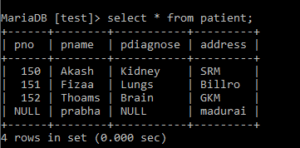
Creating a view:
create view analysis AS select pname, address from patient where pno=150;Output:
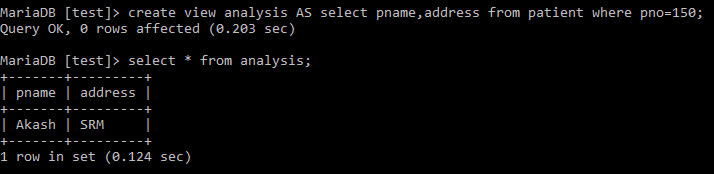
View with check option:
create view analysis1 AS select pname, address from patient where pno IS NOT NULL WITH CHECK OPTION;Output:

When we try to insert a value in Analysis1 with the check option its output is shown below:
Command:
insert into analysis1 values ('prabha','madurai');
ERROR 1369 (44000): CHECK OPTION failed `test`.`analysis1`select * from analysis1;Output:
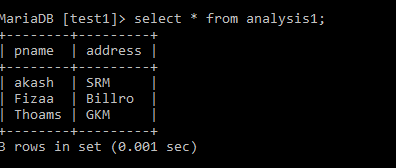
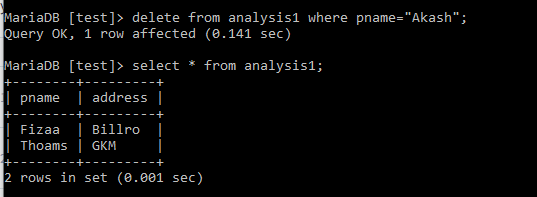
Delete:
When we try to delete a field from the view table. A particular field is deleted.
Delete from analysis1 where pname="Akash";
Select * from analysis1;Here pname =’Akash’ is deleted.
Therefore, the table looks like this:
Output:
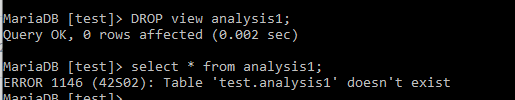
Dropping a view:
DROP view analysis1;
select * from analysis1;Output:
Advantages and Disadvantages of SQL Views
Given below are the advantages and disadvantages mentioned:
Advantages:
- If we need to maintain any sensitive information by providing limited access to the users, views are used for that purpose. Views are used to only display the required data to the users by keeping sensitive data safe.
- As a database view is associated with many tables upon which the view is created, it simplifies the complexity of the query.
- The view is used to hide the complexity of the underlying tables used in a database from the end-users.
- Views are useful in case of re-designing the database so as not to affect any other applications using the same database.
- The data of the computed columns can be calculated very easily when we query the data from the view, as views enable computed columns.
Disadvantages:
- One of the major disadvantages of using view comes into the picture when we change the table structures frequently upon which the view is created. So when the table structures are changed, the view also needs to be changed.
- Also, the usage of view slows down the performance of the queries.
FAQs
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. What is the difference between a table and a view?
Answer: In a database, a table (or “concrete table”) contains its data in columns and rows. Whereas a view (virtual table) is constructed over the actual table or tables from which it retrieves data; it doesn’t keep any of its data in the database. Only the SQL query that was used to retrieve the data is contained in a view.
Q2. How do views help in Security-Based?
Answer: To guarantee accuracy during displaying data, the views could dynamically verify that the data a user or any other third party is attempting to access satisfies the requirements listed in the views.
Q3. How SQL is making use of views?
Answer: One of SQL’s key advantages is that it has a wide range of options and clauses that enable users to filter the data with great detail and granularity. Writing out sophisticated queries regularly might rapidly become tedious if you need to run them frequently. Using views is one method to get around these problems.
Conclusion
The overview of SQL views in this article explains what they are and their practical benefits. It also demonstrates how to use conventional SQL syntax to create, query, change, and destroy views.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Views” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

