Updated March 8, 2023

Introduction to SQL Update Join
SQL Update Join statement is used to update the column values of records of the particular table in SQL that involves the values resulting from cross join that is being performed between two or more tables that are joined either using inner or left join clauses in the update query statement where the column values that are being updated for the original table can be assigned the values from other table’s column values that are the table that has been joined in the query statement of an Update query.
Syntax:
UPDATE table_to_update
JOIN
another_table1
ON table_to_update.column_name1 = another_table2.column_name2
[JOIN
another_table 2
ON table_to_update.column_name3 = another_table2.column_name4 ....]
SET table_to_update.column_name5 = another_table.column_name6
[WHERE any_restrictions];table_to_update is the name of the original table whose column values we wish to update. another_table is the name of the table with which we have to join the original table depending on certain column values that are matched, which are specified in the ON clause of the JOIN. The join can be either the inner join or the left join. The values that we want to assign to the original table’s column should be specified in the SET statement after the joins with multiple tables are defined in the query statement. We can set as many column values of the table_to_update table as we want and assign them the values that may result from the column values of other joined tables.
Working of Update Join in SQL
- When a simple update statement is written in SQL, we can update the records of one table and assign the values that we want to the columns of that table in which we can update all or some of the columns by specifying the condition in the where clause.
- But in situations where we want to assign the column values of one table to column values of another table, we can make the use of an update join statement.
- Note that at a time, only columns of a single table can be updated in an update join statement. The advantage resides in the assignation of the column values from different tables.
- The update join works with either an inner join that takes into account the common matched records of both the tables or with a left join that considers all the records of the left side table and the matched records while updating.
- We can update all, or some of the records from the query of update join by specifying conditions in the where clause.
Examples of SQL Update Join
Let us create two tables named educba_writers and educba_learning for demonstration purposes. We will use the following create table queries to create the tables. educba_writers table will contain the names of all the writers who will write the study material required to learn the subjects mentioned in the educba_learning table.
Firstly, we will create the educba_writers table using the following query statement:
Code:
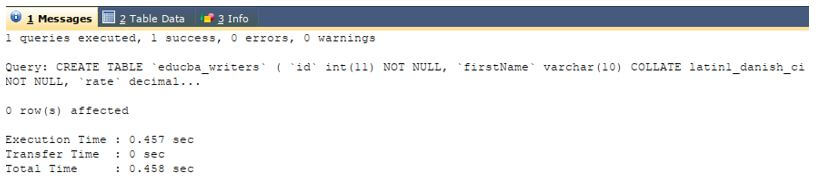
CREATE TABLE `educba_writers` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`firstName` varchar(10) COLLATE latin1_danish_ci NOT NULL,
`rate` decimal(5,2) DEFAULT NULL,
`joining_date_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL
);Output:
Now, we will create the educba_ learning table using the following query statement:
Code:
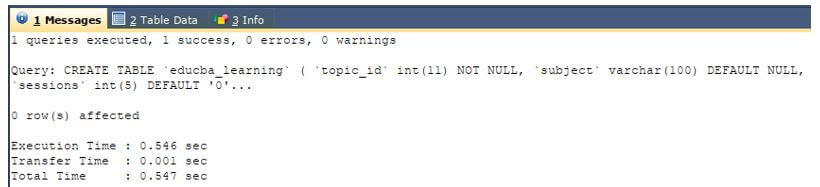
CREATE TABLE `educba_learning` (
`topic_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`subject` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`sessions` int(5) DEFAULT '0',
`expert_name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`charges` decimal(7,2) DEFAULT '0.00'
);Output:
Let us insert some records in both the tables. We will insert the following records in the educba_writers table for demonstration purpose.
Code:
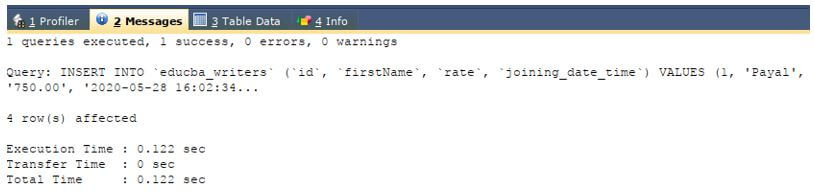
INSERT INTO `educba_writers` (`id`, `firstName`, `rate`, `joining_date_time`) VALUES
(1, 'Payal', '750.00', '2020-05-28 16:02:34'),
(2, 'Vyankatesh', '700.00', NULL),
(3, 'Omprakash', '600.00', '2020-05-28 20:32:50'),
(4, 'Parineeta', '980.00', NULL);Output:
Now, we will insert few records in the educba_learning table with the help of the following query statement:
Code:
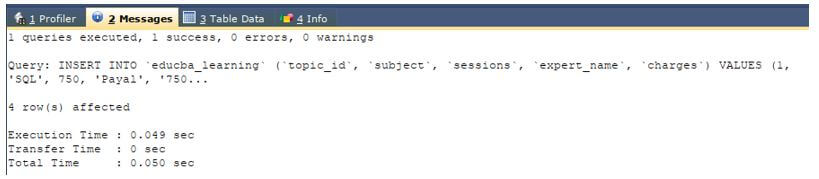
INSERT INTO `educba_learning` (`topic_id`, `subject`, `sessions`, `expert_name`, `charges`) VALUES
(1, 'SQL', 750, 'Payal', '75000.00'),
(2, 'MySQL', 700, 'Vyankatesh', '35000.00'),
(3, 'PostgreSQL', 600, 'Omprakash', '45000.00'),
(4, 'Hadoop', 980, 'Parineeta', '65000.00');Output:
Let us retrieve the records from both the tables and study their contents. We will use the simple select statement mentioned below to do so:
Code:
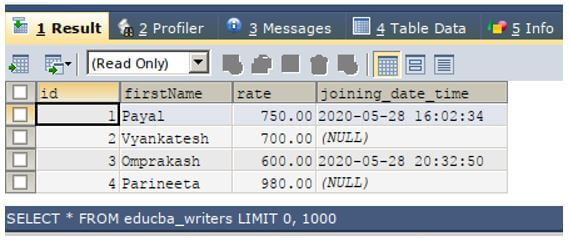
SELECT * FROM educba_writers;Output:
Now, we will retrieve records of the educba_learning table using the following statement:
Code:
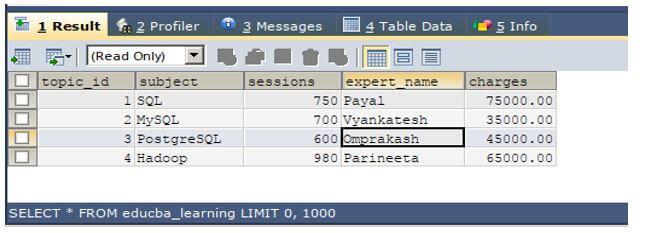
SELECT * FROM educba_learning;Output:
Now, suppose that we want to update the charges column of the educba_learning table with the value that is equivalent to the column value of the rate column of the educba_writers table multiplied by, say, 5. For this, we will first need to join both of the tables based on the writer’s first name from the educba_writers table and the expert name column of the educba_learning table. Then we can see multiple the rate column value of the educba_writers table with 5 and set it to the charges column of the educba_learning table. We will use the inner join and the update join statement here to assign the values of educba_writers table column to column values of educba_learning using the following query statement:
Code:
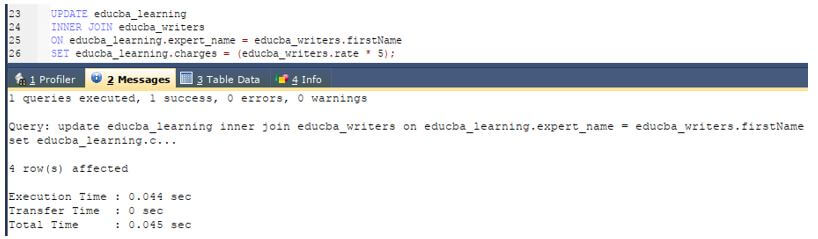
UPDATE educba_learning
INNER JOIN educba_writers
ON educba_learning.expert_name = educba_writers.firstName
SET educba_learning.charges = (educba_writers.rate * 5);Output:
Let us retrieve the records of the educba_learning table and observe the changes that the update query has caused using the following select statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba_learning;Output:
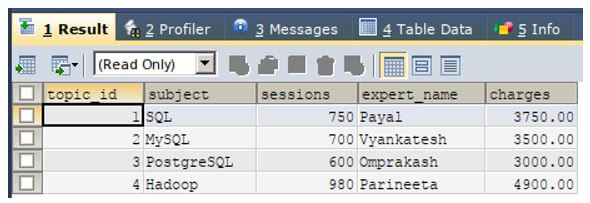
We can observe from the output that the charges for SQL subject are the rate of Payal writer that is 750 * 5 that is equivalent to 3750 which are assigned to the SQL subject. Similarly, you can cross-verify the charges column values of other records.
Conclusion
We can use the update join statement in SQL to update the records of one table’s column(s) and assign them the values that can be column values or expressions derived from the column values of other table’s records by performing join on them. In this article, we have seen how we can use update join in SQL, its implementation, comparison with the simple update statement, and use of update join with left join and inner join, along with some examples to make the implementation concept clear.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Update Join” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

