Updated March 13, 2023

Introduction to SQL UNION ALL
UNION ALL operator in standard query language (SQL) is used to combine results from two or more SELECT queries into a single result set. When combining results, UNION ALL does not remove duplicate records from the final result set. A very popular comrade of this operator is UNION which is used to combine the results obtained from two or more SELECT statements but while combining the results it removes duplicate records from the final result set.
While working with UNION or UNION ALL operators we should keep the following points in mind:
- The number of columns in the SELECT statement on which we want to use the UNION ALL operator must be the same.
- The selected columns should have the same data type. If not, they should at least have data types which are convertible to the same data type.
- The order of the columns must be in the same order as mentioned in the SELECT statement.
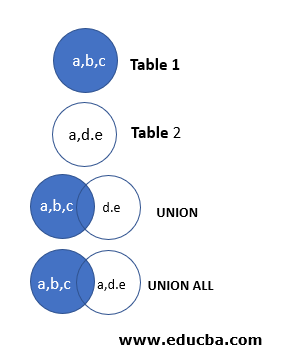
For the uninitiated, a pictorial depiction of UNION ALL command.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for writing SELECT queries with UNION ALL operators is as follows:
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name_1
UNION ALL
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name_2
UNION ALL
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name_3
.
.
.The parameters used in the above mentioned syntax are as follows:
- column_name: Specify the column name on which you want to perform UNION ALL operation and want it to feature in the result set.
- FROM table_name_1: Specify the first table name from which the column has to be fetched.
- FROM table_name_2: Specify the second table name from which the column has to be fetched.
Of the above mentioned parameters, all the parameters are mandatory. You may feel free to use WHERE, GROUP BY and HAVING clauses based on your requirement.
Examples of SQL UNION ALL
Given below are the examples mentioned:
In order to illustrate usage and functionality of UNION ALL operator in SQL, let us create two dummy tables “sales_april” and “sales_may”. These tables have similar structure and they contain details pertaining to salesperson, sales made, sales target, store location etc.
Code:
CREATE TABLE public.sales_april
(
salesperson_id integer NOT NULL,
salesperson character varying(255) NOT NULL,
store_state character varying(255) NOT NULL,
sales_target numeric NOT NULL,
sales_current numeric NOT NULL
);Output:
Code:
CREATE TABLE public.sales_may
(
salesperson_id integer NOT NULL,
salesperson character varying(255) NOT NULL,
store_state character varying(255) NOT NULL,
sales_target numeric NOT NULL,
sales_current numeric NOT NULL
);Output:
Let us insert some data records in sales_april and sales_may tables.
Code:
INSERT INTO sales_april
(salesperson_id
,salesperson
,store_state
,sales_target
,sales_current)
VALUES
(101,'Danish K','KA',10000,10000),
(102,'Rashmi Sharma','DL',23000,18000),
(103,'Mohak Patel','MH',21000,21000),
(104,'Devika Ramaswamy','TN',10000,8000),
(105,'Reema Ray','WB',0,10000);
INSERT INTO sales_may
(salesperson_id
,salesperson
,store_state
,sales_target
,sales_current)
VALUES
(106,'Rohit Khanna','PB',10000,10000),
(102,'Rashmi Sharma','DL',13000,12000),
(107,'Hardik Mahajan','RJ',20000,19000),
(104,'Devika Ramaswamy','TN',10000,18000),
(105,'Reema Ray','WB',10000,10000);Example #1
Find all the salespersons who have worked for the departmental store during the month of April and May.
Code:
SELECT salesperson
FROM sales_april
UNION ALL
SELECT salesperson
FROM sales_may;Output:
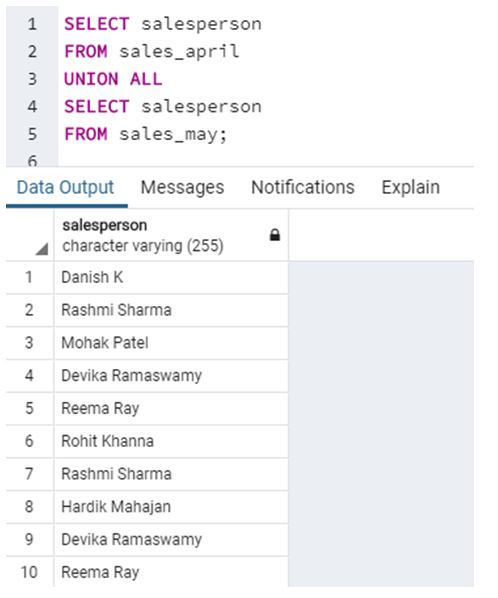
In this example, we have used the UNION ALL operator to combine results from sales_april and sales_may tables. We observe that we have received duplicate values such as Reema Ray, Rashmi Sharma etc.
Consider this query now.
Code:
SELECT salesperson
FROM sales_april
UNION
SELECT salesperson
FROM sales_may;Output:
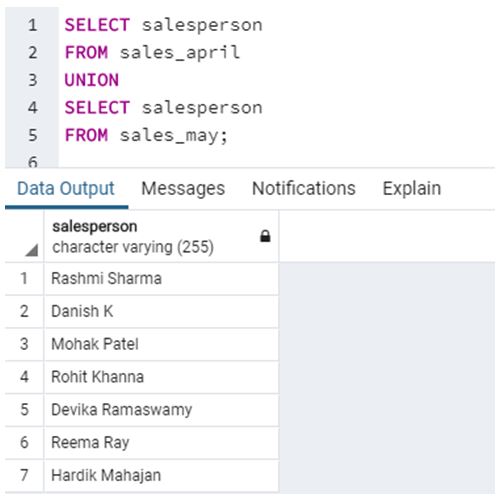
Here, we have used the UNION operator to combine results from sales_april and sales_may tables similar to previous query. But unlike UNION ALL operator, we did not get duplicate values in case of UNION operator.
Example #2
Find all the salespersons and the store locations, who worked for the departmental store during April and May and have made sales for more than $15000.
Code:
SELECT salesperson, store_state, sales_current
FROM sales_april
WHERE sales_current > 15000
UNION ALL
SELECT salesperson, store_state, sales_current
FROM sales_may
WHERE sales_current < 15000;Output:

Here, we have used the UNION ALL function to combine results from sales_april and sales_may tables.
Example #3
Find all the store locations along with the total sales target and total current sales.
Code:
WITH CTE AS (SELECT *
FROM sales_april
UNION ALL
SELECT *
FROM sales_may)
SELECT store_state, sum(sales_target) as sales_target, sum(sales_current) as sales_current
FROM CTE
GROUP BY store_state
ORDER BY sales_current DESC;Output:
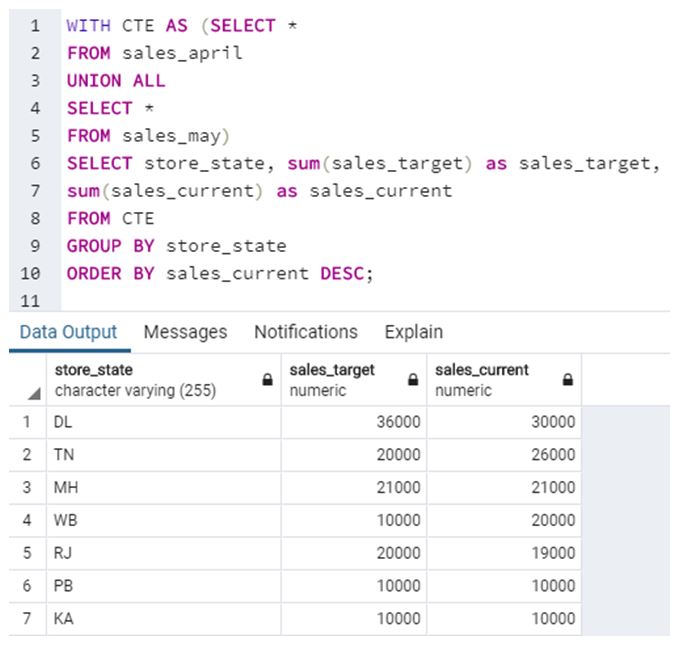
In this example, we have first combined the results from sales_april and sales_may tables and then found aggregate sales_target and sales_current for each store by grouping the records by store_state field.
Conclusion
UNION ALL operator is used as a combinator to combine results from two or more SELECT statements. However, it returns duplicate records in the final result set.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL UNION ALL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

