Updated April 11, 2023
Introduction to SQL TO_DATE()
TO_DATE() function in most SQL database management servers such as PostgreSQL and ORACLE is used to convert data values of character data types such as VARCHAR, NVARCHAR, CHAR, etc., to standard DATE data type. The function takes two arguments, first, the value of the character data type that has to be converted, and second the datetime format in which the first argument has been written.
Some SQL databases, such as SQL Server and MYSQL, use a different function to convert character values into DATE data type. In SQL server and MYSQL, we can use CONVERT(datetime, ‘date in character type’) and STR_TO_DATE() functions, respectively.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for using the above-mentioned date conversion function is as follows :
to_date(text, datetime format);The syntax for the CONVERT() function in the SQL server is as follows :
CONVERT(datetime, text);The syntax for STR_TO_DATE() function in MYSQL is as follows :
STR_TO_DATE(text, datetime format);Parameters:
- Text: Data value in character data types like char, text, varchar, nchar, varchar, etc., that has to be converted into date time format.
- Datetime format: The specific format based on date specifiers in which the mentioned text is written.
Examples of SQL TO_DATE()
Following are the examples are given below:
Example #1
Basic SQL queries to illustrate the working of to_date() function in PostgreSQL and Oracle SQL databases.
Suppose you want to convert ‘20200526’ into YYYY-MM-DD format (stands for 4 characters of the year, followed by two characters of month and day each.) We can use the to_date() function in the following manner.
SELECT to_date('20200526','YYYYMMDD');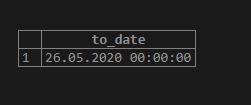
Next, suppose we have some date information written in text format like the one in this example. We can use the following piece of code to perform the task.
SELECT to_date('2020-JAN-15', 'YYYY-MON-DD');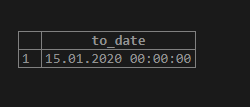
Suppose we have some entries which are in shorthand format like ‘070920,’ and we want to convert it into YYYY-MM-DD format. The following query can help us.
SELECT TO_DATE('070920', 'MMDDYY');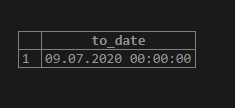
We can sometimes have date information mixed with a timestamp string. This can be solved by using the to_date function with the following set of arguments.
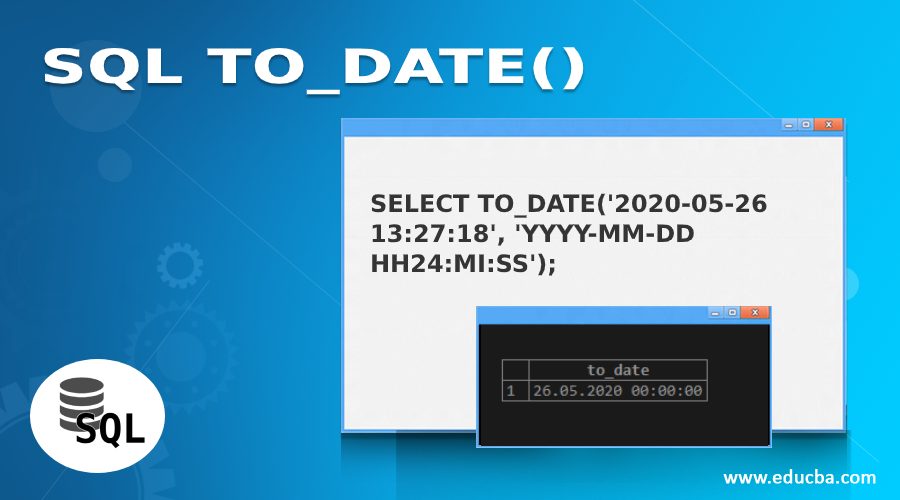
SELECT TO_DATE('2020-05-26 13:27:18', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS');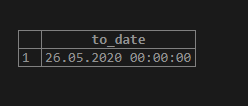
In PostgreSQL, we can simply convert a character string written in date format to date data type without using the to_date() function in the following way.
SELECT '2020/02/03'::date;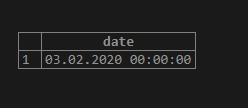
Great, we just learned to convert character strings into date data type using the to_date() function. Since the SQL server and MYSQL do not have to_date() as a built-in function, we cannot use it there. So, let us try some examples which will work there as well.
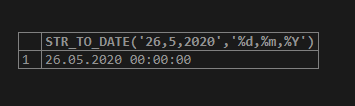
SELECT STR_TO_DATE('26,5,2020','%d,%m,%Y');The above-mentioned query returns the input string in YYYY-MM-DD date format in the MYSQL database.
SELECT CONVERT(DATETIME, '2020-05-26');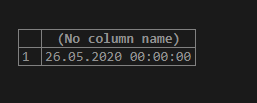
Example #2
SQL query to illustrate the use of the to_date() function in INSERT statements.
In order to illustrate the uses of the to_date() function, let us create a dummy “students” table. We can use the following code snippet to perform the given task.
CREATE TABLE students (
student_id INT GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY,
first_name VARCHAR ( 255 ) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR ( 255 ) NOT NULL,
birth_date DATE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ( student_id )
);Now let us try to insert data records in the “students” table using the following queries.
INSERT INTO students(first_name, last_name, birth_date)
VALUES('Kritika','Sharma', TO_DATE('May 01 2000','Mon DD YYYY'));
INSERT INTO students(first_name, last_name, birth_date)
VALUES('Rohit','Verma', TO_DATE('070798','MMDDYY'));
INSERT INTO students(first_name, last_name, birth_date)
VALUES('Ariel','Winter', TO_DATE('2001-02-20 13:27:18', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'));
INSERT INTO students(first_name, last_name, birth_date)
VALUES('Mathew','Jones', TO_DATE('2020-52-5', 'IYYY-IW-ID'));In these queries, the given birth_date is not in the standard PostgreSQL date format. The first three birth_dates are in familiar formats, as we have already discussed examples based on them. The fourth query has birth_date written in Year, week number, and weekday format. We have to use to_date() to convert it into standard YYYY-MM-DD format, as shown in the code snippet given above.
Now, let us check if the birth_dates for the given students have been inserted in the required format. We can use the following SELECT statement to fetch records from the students’ table.
SELECT student_id,
first_name,
last_name,
birth_date
FROM students;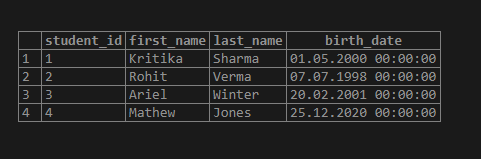
We can clearly observe that the birth_dates have been successfully converted to standard date format (YYYY-MM-DD) using the to_date() function.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL TO_DATE()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

