Updated April 3, 2023
Definition of SQL to Number Format
Have you ever come across a situation where you need to convert a string of numbers in SQL to a specific number format? If so, then you are familiar with SQL to number format. In simple terms, SQL to number format is the process of converting a string of numbers in SQL to a specific numerical format. The numerical formats can vary depending on the requirements of your project or application. For instance, you may need to convert a string of numbers into currency format, percentage format, or scientific notation. Three variables number, the number of decimal places, and an optional locale—are accepted by this function. It gives back a structured nvarchar string.
The purpose of this conversion is to ensure that the data is presented in a readable and understandable manner for end-users. Understanding SQL to number format is essential for database administrators and developers who work with large amounts of data. By knowing how to convert strings of numbers into specific numerical formats, they can improve the accuracy and efficiency of their applications. The following section will provide an overview of SQL to number format and its various use cases.
Key Takeaways
- This new function obtains output in a certain culture and format. The output is of the data type NVARCHAR.
- While it might have performance difficulties, we should only utilize it when locale-aware changes are necessary.
Overview of SQL to Number Format
In Microsoft SQL Server, numbers may need to be formatted differently based on cultural disparities. For example, the use of decimal points versus commas varies between countries. As a result, it is essential to know how to modify the structure of numbers in SQL Server to display them correctly.
There are various SQL procedures available for formatting numbers in SQL Server. These include:
- CAST: Converts data types into other data types, including converting numbers to specific data types.
- CONVERT: Converts data types to specific data types, including numbers.
- FORMAT: Formats values based on the specified format.
- ROUND: Rounds a numeric value to the specified length or precision.
- TRUNCATE: Removes decimal places from a numeric value.
- PARSE: You can convert a string representation of a number to a numeric value.
By utilizing these SQL procedures, you can modify the structure of numbers in SQL Server to display them correctly and consistently. This can be important in situations where data is being shared or analyzed across different cultures and countries.
Syntax:
FORMAT(value, format, culture)SQL Server to Number Format (String of type)
The format has the respective parameters:
- Value: Formatting is good enough to justify doing it. It should be compatible with the data type format.
- Format: We must obtain the output in this specific format. An appropriate.NET format string of the NVARCHAR data type should be included in the argument.
- Culture: It is a choice-based parameter. The default culture for SQL Server is the language being used for the current session.
Example
Let us see the examples using Xampp Server for Number types cases and For String Using SQL Server. Let’s Get started
A string of type returns an NVARCHAR value formatted according to the culture and format you choose (if specified). Typically, date-time types are converted to strings using this.
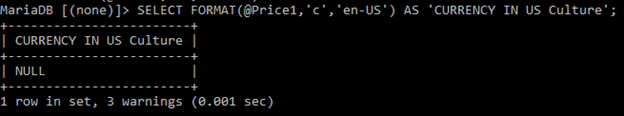
1. The Below Query shows how to use a string in Currency format:
Code:
SELECT FORMAT(@price1,'c','en-US') AS 'CURRENCY IN US Culture';Output:
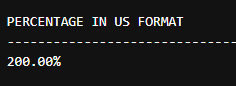
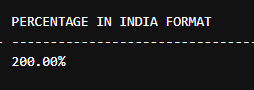
2. Using Percentage format in the Currency Declaration.
Code:
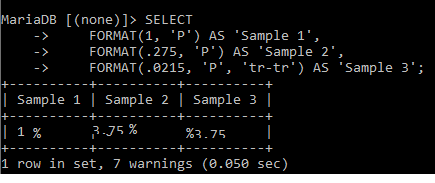
SELECT FORMAT(2, 'P', 'en-US')AS [PERCENTAGE IN US FORMAT],
FORMAT(2, 'P', 'en-IN') AS [PERCENTAGE IN INDIA FORMAT];Output:
1. String Types
The first Query here Shows How the String is formatted using numbers.
Code:
SELECT 'Hi'+ STR(13.12) + 'Hello'Output:
2. Using String in different country currencies
Here we are taking Float Data value for the currency.
Code:
Declare @tt as float=1234.766
Declare @strfor as varchar(10) ='0.00%'
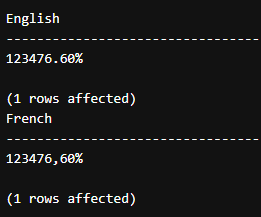
select format(@tt,@strfor ,'en-US') as English
select format(@tt,@strfor ,'fr-FR') as FrenchOutput:
3. With int, float value, and adding Exponent in the result
Code:
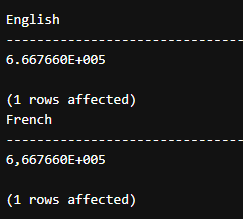
Declare @tt as int=666766
Declare @strfor as varchar(10) ='E'
select format(@tt,@strfor ,'en-US') as English
select format(@tt,@strfor ,'fr-FR') as FrenchOutput:
4. Using Cast
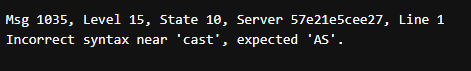
When we specify int in the below query, it shows an error.
Code:
select cast(5.2)as intOutput:
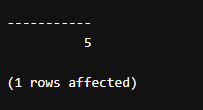
To rectify this below query is formatted to produce an integer/ decimal value in the output.
Code:
select cast(cast('5.2'AS decimal(10,5)) AS int)Output:
5. Date-Time Format
The DATE FORMAT() function returns a value that has been converted using the requested format. It is used to format date/time and number values into strings in a locale-aware manner. Certain SQL Date Functions are used rather frequently. The time between two dates is returned by GETDATE().
Code:
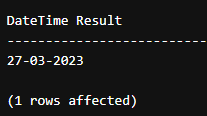
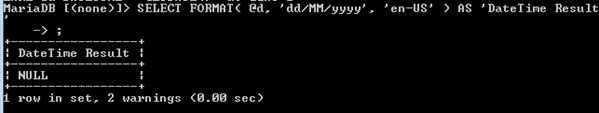
DECLARE @d DATETIME = GETDATE();
SELECT FORMAT( @d, 'dd/MM/yyyy', 'en-IN' ) AS 'DateTime Result'Output:
6. Taking only month from the date format
Code:
SELECT FORMAT( GETDATE(), 'M' ) AS TodayOutput:
SQL to Number Format Function
We can format numbers using commas in MySQL by using the FORMAT() function:
No specific direction for the commas is required. Where to put them is known by the function. An additional argument, which specifies the locale, is also accepted by its function. Note that all locales were using a comma to distinguish groups; few also use commas to separate decimals.
A value in the requested format and optional culture is returned by FORMAT. Date, time, datetime, currency, and numeric data types can all be converted using FORMAT. This function provides both generic and personalized format specifies that are versatile.
In the below Query, the result has no decimal places since the expression utilizes the FORMAT function with the second argument set to zero.
Code:
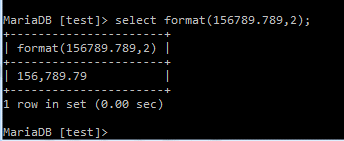
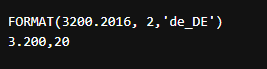
SELECT FORMAT(3200.2016, 2,'de_DE');Output:
Now let’s see another case where it gives back a value that has been formatted using the chosen format and optional culture. For now, let’s format a number. so we utilize the following method:
In the below query, we are changing the currency format.
1. Using Decimal Places
Decimal places refer to the number of digits after the decimal point in a numeric value. In SQL, decimal places can be specified when defining a column’s data type or when converting a value from one data type to another.
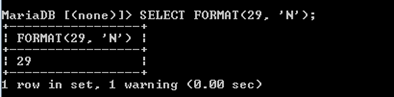
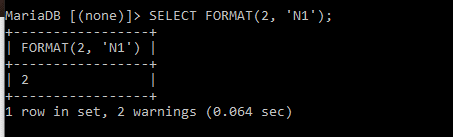
N1 and N2 sequences, we can indicate the decimal places. In the below example, we have specified N1 with the decimal 2; it takes two decimal places.
N1, and N2 sequences, we can indicate the decimal places. In the below example, we have specified N1 with the decimal 2; it takes two decimal places.
Also, we can increase the number of decimal places, like N3 and N7. Here 3,2, and 7 are called Precision Specifiers.
2. Using Percent
In SQL, percent (%) is a special character used as a wildcard to match any string of characters. However, the percent symbol can also represent a percentage in numeric values. It is essential to ensure that the appropriate decimal places and rounding rules are used when working with percentages in SQL to maintain the accuracy of the calculations.
Here, the number is formatted as a percentage value using the P parameter. The number is multiplied by 100 before a localized percent indicator is added.
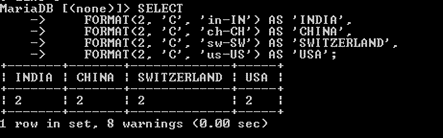
3. Using Currency
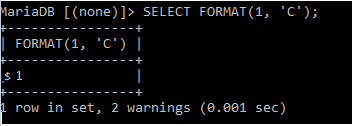
In SQL, the currency is a common data type used to represent monetary values. Currency values typically include a currency symbol, such as “$” or “€”, and a decimal value representing the amount. Here the Symbol ‘C’ is used for a currency.
4. Using SQL Server
Code:
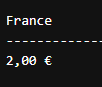
SELECT
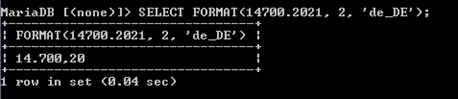
FORMAT(2, 'C', 'fr-FR') AS France,
FORMAT(2, 'C', 'ja-JP') AS Japan;Output:
5. Exponential
Exponential notation (or scientific notation) is a way of expressing very large or minimal numeric values using a compact format. The exponential notation uses the letter “E” to indicate the power of 10 that the number is being multiplied by. In the Below Example, along with the number, the format to be converted is ‘E.’ And the Output is shown as:
Code:
SELECT FORMAT(5682.8719, 'E');Output:
6. HexaDecimal
Hexadecimal notation (or hex notation) is a way of representing numeric values using a base-16 numbering system. Hexadecimal notation is commonly used for representing colors, memory addresses, and other types of data that are represented in binary format. The hexadecimal notation uses the digits 0-9 and the letters A-F to represent values from 0 to 15. Each digit in a hexadecimal number represents a power of 16, with the rightmost digit representing the unit’s place, the next digit representing 16’s place, and so on. Even hexadecimal formatting is an option for numbers. Use the X parameter to achieve this:
Code:
SELECT FORMAT(12, 'X');The base of hexadecimal equals 16. Thus the number is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F, and then it starts over. Because A follows 9 in hexadecimal, the example given produces a C.
Output:
Conclusion
Understanding SQL to number format is essential for anyone working with databases. It allows for the conversion of data from a string type to a numeric type, making it easier to perform calculations and analysis on the data. The syntax for SQL to number format is straightforward and can be easily implemented in SQL servers. The SQL to number format function also provides a convenient way to convert data in bulk. By utilizing these tools, database professionals can streamline their workflow and better use their data.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL to Number Format” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.