Updated June 6, 2023

Introduction of SQL Server Permission
SQL Server has more than 230 permissions that can be granted to a principal. By principal, we mean different logins, user groups, and server roles. The permissions can range from allowing a user to CREATE, ALTER or MODIFY a database object to restricting it to only SELECT from it. The administrator can play with these permissions and GRANT, REVOKE or DENY them to various user logins, groups, or servers based on the requirement. These permissions in SQL SERVER help maintain the security of the databases.
Here are a few database-level permissions in SQL Server :
- CREATE DATABASE: Database-level permission lets a user create or restore a database. This permission can only be granted in the master database.
- ALTER ANY <>: With this permission, a user can alter any application role, column, key, database trigger, security policy, database name, etc. This permission is usually given to database admins.
- CREATE <>: It is a permission that lets a user create <functions, procedures, tables, aggregate, rule>, etc., in a database.
- DELETE | EXECUTE| INSERT| SELECT| REFERENCES| UPDATE: A database owner or admin can grant these are few other permissions to a user. They apply to schema-level objects in the database.
- BACKUP DATABASE| LOG| CHECKPOINT: Such permissions enable users to take a database backup, create checkpoints, etc. They are usually assigned to backup operators and other trustworthy roles.
- CONTROL DATABASE: This permission is the most crucial, only with db_owner by default. It lets the owner drop or delete a database.
One must note that the db_owner role in SQL Server, by default, has all the permissions on the database. It is pretty intuitive since you are the owner; you should have all the permissions. By now, we have a fair idea of what permissions are in SQL Server. The other thing which must be coming into your head is who manages all these permissions, and how are they granted or revoked? You will find answers to all these questions; hang in there till the end of this article.
If you have created the database, you are the owner, and the entire control is in your hands. It’s up to you to whom you want to grant permission. You can also delegate this task of managing permissions to another user by giving it top-level permissions. In SQL Server, we have three commands, GRANT, REVOKE, and DENY, that let an admin or owner manage permissions. Here is the syntax for all three of these commands.
Syntax and Parameters
The syntax and parameters of sql server permission are given below:
GRANT Permission Syntax
GRANT <permission>
ON database_object
TO role
[WITH GRANT OPTION];The parameters used in the syntax mentioned above are as follows:
- permission: Mention the permissions such as CREATE, EXECUTE, DELETE, ALTER, UPDATE, etc., which you wish to grant to a user_role.
- database_object: Specify the database object, such as database table name, schema name, etc., on which the permissions must be granted.
- role: By role here, we mean a user login, group, or principal to which the said permissions must be given.
- [WITH GRANT OPTION]: This option indicates that the said user role can further grant any of the abovementioned permission to another user. He is delegating or sharing his permissions with someone else.
REVOKE Permission Syntax
REVOKE<Permission>
ON database_object
TO role
CASCADE;The parameters used in the above syntax are very similar to the ones mentioned in the GRANT syntax.
DENY Permission Syntax
DENY <Permissions>
ON database_object
TO role
CASCADE;In the last two syntaxes, using the CASCADE keyword means that permissions granted by this user to others will be revoked.
Examples of SQL Server Permission
To illustrate a few examples of SQL Server permissions, we need to create a dummy user. Let’s call it “user_1”. A user can be created in the following manner.
Step 1: Move to the Security section of the SQL server and right-click on Logins.
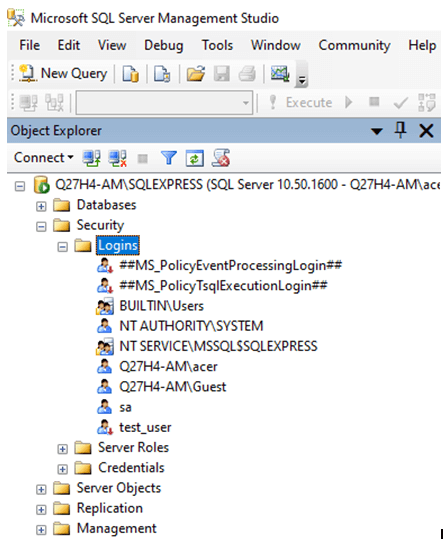
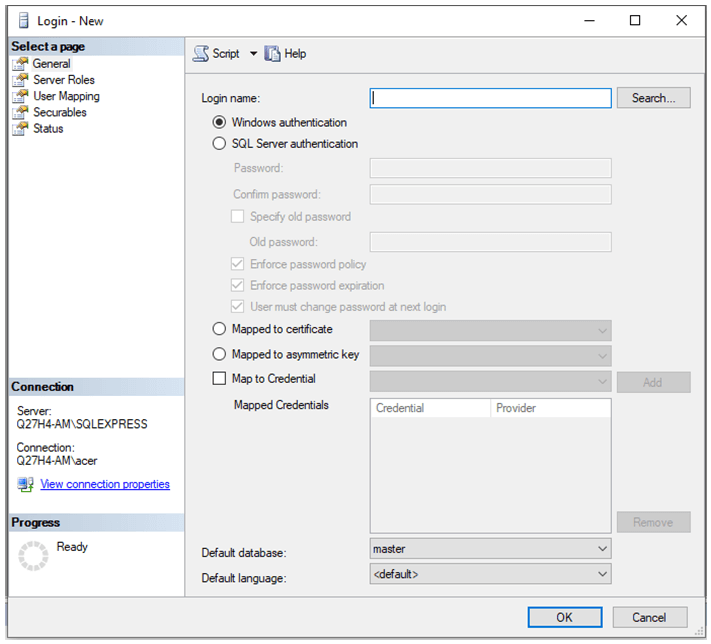
Step 2: Create a new login by filling in all the required details in the dialog box.
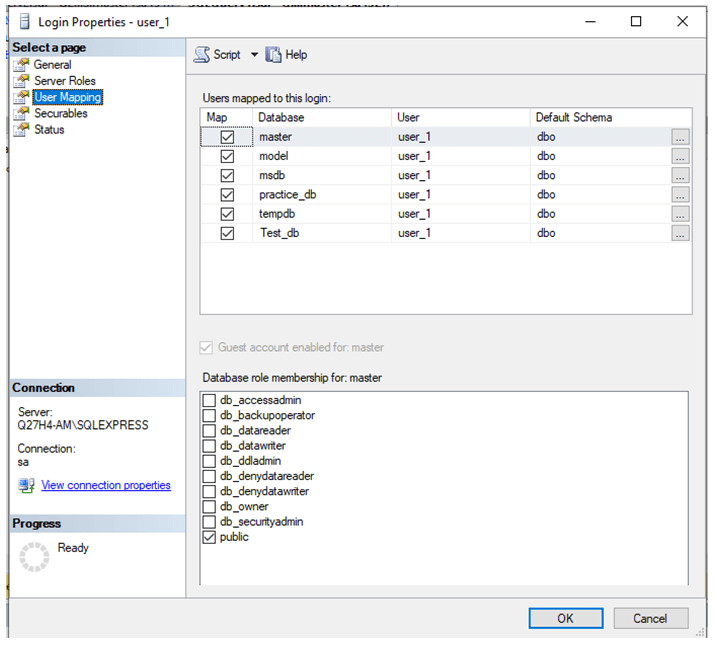
Step 3: After you finish creating a login, remember to use “User Mapping” to map the new user.
And we are all set to grant, revoke and deny permissions to this user.
Example #1
SQL query to grant select permission to a user.
GRANT SELECT ON [master].[dbo].[Account_details]
TO user_1
WITH GRANT OPTION;
Example #2
SQL query to revoke select permission from a user.
REVOKE SELECT ON [master].[dbo].[Account_details]
TO user_1;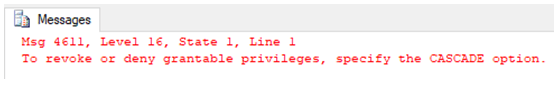
We got an error. Yeah, true because when we granted this user SELECT permission, we granted it with [WITH GRANT OPTION]. So, yeah, we have to revoke that too.
REVOKE SELECT ON [master].[dbo].[Account_details]
TO user_1
CASCADE;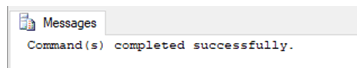
Example #3
SQL query to grant ALTER permission to a user.
GRANT ALTER ON [master].[dbo].[Account_details]
TO user_1;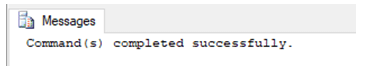
Example #4
SQL query to deny ALTER permission to a user.
DENY ALTER ON [master].[dbo].[Account_details]
TO user_1;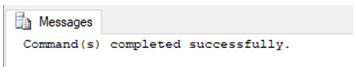
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Server Permission” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

