Updated May 15, 2023
Introduction to SQL Plus Command
- The following article provides an outline for SQL Plus Command. The SQL plus term is defined as a command-line tool that delivers the Oracle RDBMS access. This SQL plus supports any user entering the SQL plus command to form the SQL plus environment.
- Further, we can use this SQL plus command to either startup or blackout an Oracle database. It establishes a connection to an Oracle Database and inserts and runs the SQL commands and PL/SQL blocks.
- After that, this SQL plus, serving as a command tool, allows to design and print the query outcomes to the user. The SQL plus command is present on various platforms.
SQL plus Command Explain
- SQL plus command is known to be a collaborative and batch query tool that is connected with each Oracle Database installation. The command consists of a command-line user interface, the iSQL plus web-centered user interface, and a Windows GUI (Graphical User Interface).
- Further, the SQL plus Instant Client is also available, an individual type command-line interface, on platforms that upkeep the OCI Instant Client. This SQL plus Instant Client relates to any present Oracle database, but its installation of the Oracle database is not compulsory. You can view the Oracle Call Interface Programmer’s Guide based on the OCI Instant client for more facts and info.
- Possessing its own commands and environment, SQL plus command offers access to the Oracle database. It allows the user to type and run the SQL, PL/SQL, operating system, and SQL plus commands to accomplish the below activities:
- Format, execute calculations on, store and print from the query results.
- Finally, observe the table along with object definitions.
- Create and implement the batch scripts
- Execute database administration
- In addition, SQL plus can also be implemented to produce reports correlatively, to produce reports as the batch processes, and to result in the outcomes to a text file, to HTML file for surfing on the Internet and to screen. Also, the reports can be generated vigorously by means of the HTML output capacity of SQL plus or even by means of the lively reporting proficiency of SQL plus for executing a script provided from a web page.
- While form SQL plus 10.2, the connections to an Oracle7 database are not supported.
Standard SQL Commands
The SQL plus commands have been improved with scripting and formatting abilities and can be implemented for many diverse purposes having simple basic functionality. So the following operations can be performed with SFirst, concern:
- Concern a SELECT query and display the results.
- Next, inserting, deleting, and updating data records from database tables.
- Finally, the PL/SQL blocks are submitted to the Oracle server for execution.
- Produce DDL statements like create, alter, or remove the database objects (such as tables, indexes, and users) and other kinds of SQL statements that Oracle supports.
- Implementing SQL*Plus script files
- Programming output to an external file.
- Run procedures and functions which are warehoused in the database.
A list of SQL plus commands with their functions is listed as follows:
- /: It executes the present SQL command in the buffer, similar to RUN.
- ACCEPT: It accepts a value from the operator and inserts it into a variable.
- APPEND: It adds text to the termination of the present line of the SQL declaration in the buffer.
- AUTOTRACE: It traces the execution scheme of the SQL declaration and collects statistics.
- BREAK: Configures the structuring behavior for the result of SQL commands.
- BTITLE: Positions a title on the foot of every page in the printout from a SQL declaration.
- CHANGE: Substitutes text on the present line of the SQL statement, including a new text.
- CLEAR: It clears the buffer.
- COLUMN: Swaps the appearance of an output column from a query.
- COMPUTE: Performs calculations on table rows resumed from a SQL statement.
- CONNECT: It connects to another Oracle database server or to the similar Oracle database involved under a separate username.
- COPY: It copies data from one database table to other in the same or separate databases.
- DEL: Deletes the present line available in the buffer.
- DESCRIBE: Lists the table columns having data types of the table.
- EDIT: Edits the present SQL command in the buffer by means of an external editor like emacs or vi.
- EXIT: To exit the program of SQL plus.
- GET: Loads a SQL declaration into the buffer; however, does not implement it.
- HELP: Get help found in some installations for a SQL plus command.
- HOST: Drops to the OS shell.
- INPUT: To add single or multiple lines to the SQL declaration in the buffer.
- LIST: Lists the prevailing SQL statement in the buffer.
- QUIT: Terminates the program of SQL plus.
- REMARK: Positions a comment succeeding the REMARK keyword.
- [pRUN: Runs the present SQL declaration in the buffer.
- SAVE: Saves the prevailing SQL declaration to a script file.
- SET: Sets the specific variable to a new value.
- SHOW: Displays the present value of a provided variable.
- SPOOL: It sends the result from the SQL declaration to a file.
- START: It loads a SQL command situated in a script file and, after that, executes that SQL command.
- TIMING: Applied to time the implementation of SQL commands for performance study.
- TITLE: Positions a title on the top of every page from a SQL command in the printout.
- UNDEFINE: It deletes a user-defined variable.
SQL plus Command Examples
The user can find this SQL plus command as a simple language to code with. Suppose, for renaming a table column which is labeled as LastName consisting of the heading named FamilyName, the command to be entered is:
COLUMN LastName HEADING 'FamilyName';Likewise, we will insert the command below to view column definitions for the specific table:
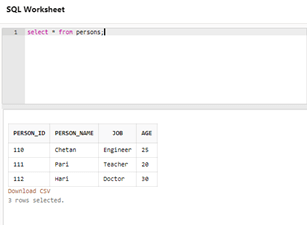
DESCRIBE TableName;Suppose we have a sample database table named Persons with fields as id, name, job, and age. The table is as follows:
SELECT * FROM Persons;Output:
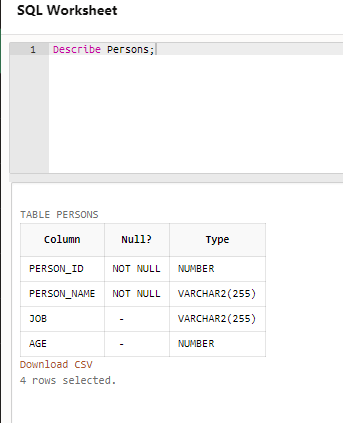
Now, let us use the SQL plus command as below:
Describe Persons;Output:
Conclusion
The SQL plus command is an easy-to-use language. The SQL Plus, PL/SQL, and SQL command languages are authoritative enough to attend to the needs of operators with little database experience but direct enough for the new ones who may be fairly learning to work with the Oracle Database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Sql Plus Command” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.