Updated June 7, 2023
Introduction of SQL Order by Count
ORDER BY COUNT clause in standard query language(SQL) is used to sort the result set produced by a SELECT query in an ascending or descending order based on values obtained from a COUNT function. For the uninitiated, a COUNT() function is used to find the total number of records in the result set. It is usually used with the GROUP BY clause to prepare a summary of each group’s total number of records. It can further be used with the ORDER BY clause to sort the obtained summary table.
By default, the ORDER BY statement arranges the result in ascending order. If we want to sort it in descending order, we might have to mention the DESC keyword.
Nonetheless, we will discuss ORDER BY COUNT() in detail in subsequent sections. Let’s begin with the syntax and parameters used for sorting results by COUNT().
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax used for writing a SELECT query with an ORDER BY COUNT() clause is as follows:
SELECT column_name_1, column_name_2
FROM
table_name
GROUP BY column_name_1
ORDER BY COUNT(column_name_2) ASC | DESC;The parameters used in the syntax mentioned above are as follows :
column_name_1, column_name_2, ..., column_name_n : columns or fields that have to befetched for the final result set
- table_name: Database table from which the above columns have to be fetched.
- GROUP BY column_name_1: We group the result set together for counting based on the specified column.
- COUNT(column_name_2): We count the values of the column and then utilize them as input for the ORDER BY clause to sort the result set.
- ASC | DESC: Order of sorting as in ascending(ASC) or descending(DESC)
Now that we have learned the syntax and parameters for writing ORDER BY clauses, let’s explore a few examples to gain a better understanding of the concept.
Examples of SQL Order by Count
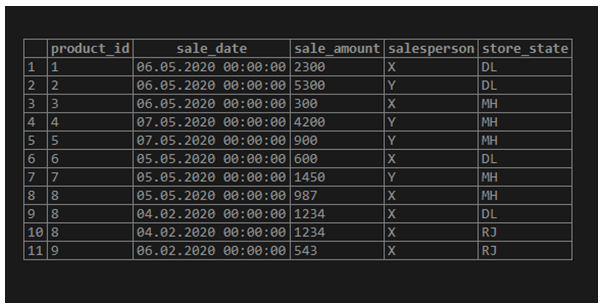
To illustrate the working of the ORDER BY COUNT() statement, let us create a dummy table named “product_details”. This table contains details about sales, such as product_id, sale_date, etc., for a departmental store. We can use the following CREATE TABLE statement to create the table.
CREATE TABLE product_details
(
product_id integer NOT NULL,
sale_date date NOT NULL,
sale_amount numeric NOT NULL,
salesperson character varying(255) NOT NULL,
store_state character varying(255) NOT NULL,
);The table has been successfully created. Let’s insert the following values in it to work with. Use the given insert statement.
INSERT INTO product_ details(
product_id, sale_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES (1,'2020-05-06', 2300,'X','DL'),
(2, '2020-05-06',5300,'Y','DL'),
(3, '2020-05-06',300,'X','MH'),
(4, '2020-05-07',4200,'Y','MH'),
(5, '2020-05-07',900,'Y','MH'),
(6, '2020-05-05',600,'X','DL'),
(7, '2020-05-05',1450,'Y','MH'),
(8, '2020-05-05',987,'X','MH'),
(8, '2020-02-04',1234,'X','DL'),
(8, '2020-02-04',1234,'X','RJ'),
(9, '2020-02-06',543,'X','RJ');
select * from product_details;Now we are all set to discuss a few examples based on ORDER BY COUNT() with the help of the product_details table.
Basic functionality of COUNT() function
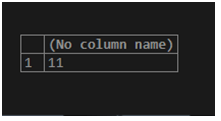
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM product_details;The COUNT() function returns the total number of rows in the result set.
SQL queries to illustrate the basic functionality of ORDER BY COUNT()
Example #1
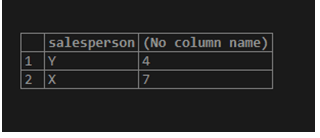
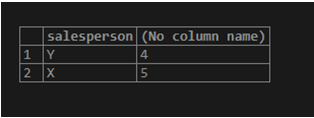
Find the number of sales each salesperson makes and arrange from lowest to highest.
SELECT salesperson, count(product_id)
FROM product_details
GROUP BY salesperson
ORDER BY count(product_id);The query first groups the results by salesperson then counts the number of product_ids corresponding to each group and finally sorts the result set according to the value returned by the count() function.
Example #2
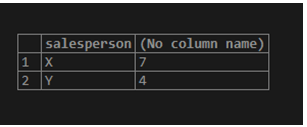
Find the number of sales each salesperson makes and arrange the result from highest to lowest.
SELECT salesperson, count(product_id)
FROM product_details
GROUP BY salesperson
ORDER BY count(product_id) DESC;To sort a given result set in descending order, we use the DESC keyword.
Example #3
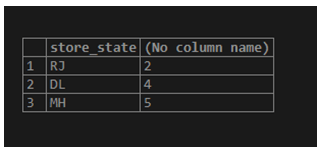
Find the number of sales made in each store location, arranged from lowest to highest.
SELECT store_state, count(product_id)
FROM product_details
GROUP BY store_state
ORDER BY count(product_id);ORDER BY COUNT() statement with COUNT(DISTINCT field_name) function.
Example #4
Find the number of different products each salesperson sells, arranged from lowest to highest.
SELECT salesperson, count( DISTINCT product_id)
FROM product_details
GROUP BY salesperson
ORDER BY count(DISTINCT product_id);When we use the DISTINCT keyword with COUNT, it returns the count of unique records in the specified column. In this specific case, even though there are 11 product_ids, the count only includes 9 unique ones.
ORDER BY COUNT() statement with more than one count() functions
Example #5
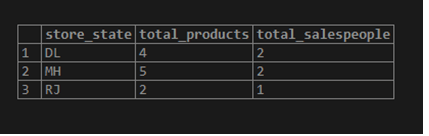
Find the number of sales and unique salespersons for each store location, arranged from highest to lowest count of salespersons and from lowest to highest by number of sales in case of a tie.
SELECT store_state,
count(product_id) as "total_products",
count( DISTINCT salesperson) as "total_salespeople"
FROM product_details
GROUP BY store_state
ORDER BY count(DISTINCT salesperson) DESC, count(product_id) ASC;Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Order by Count” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.